一、论文主要内容总结
论文围绕扩散型大语言模型(dLLMs)的推理效率问题展开,核心是提出“自推测解码(SSD)”框架,在不损失生成质量的前提下提升推理速度,具体内容可分为三部分:
-
背景与问题
- dLLMs作为自回归模型(ARMs)的替代方案,虽有双向注意力、并行生成等优势,但现有并行解码方法会偏离逐步解码过程,导致性能下降,且传统推测解码需额外辅助模型,存在冗余和内存开销。
- dLLMs因双向注意力机制,难以直接应用ARMs的KV缓存策略,虽有自适应缓存框架将其从计算密集型转为内存密集型,但仍需更高效的解码方法。
-
SSD框架设计
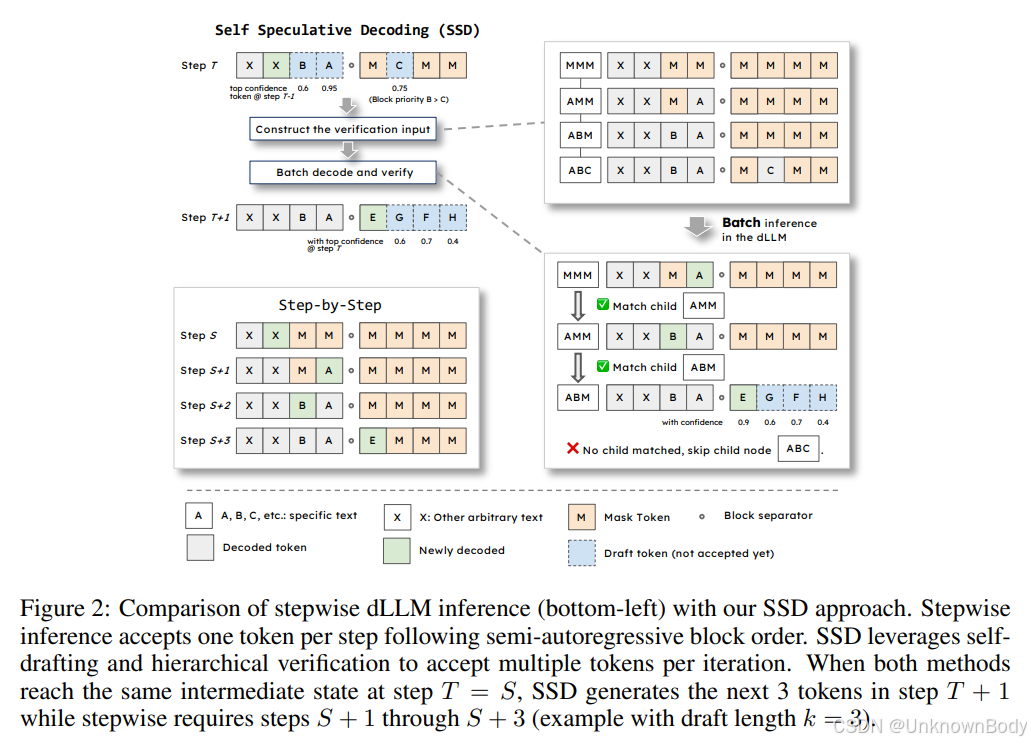
- 自生成机制:让dLLM自身同时为多个位置生成候选 tokens,并输出置信度分数,无需额外草稿模型。
- 分层验证树:基于生成的候选 tokens 构建分层验证树,父节点验证通过后才验证子节点,确保符合逐步解码逻辑。
- 批量验证:在单次前向传播中批量验证验证树的所有节点,最多可在一次迭代中接受N+1个tokens(N为草稿长度),减少解码步骤。











 订阅专栏 解锁全文
订阅专栏 解锁全文


















 181
181

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










