背景
目前HuggingFace发布了关于微调LLMs的方法包——Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning(PEFT),其中包含下面6种方法:
- LoRA: LORA: LOW-RANK ADAPTATION OF LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS
- Prefix Tuning: Prefix-Tuning: Optimizing Continuous Prompts for Generation, P-Tuning v2: Prompt Tuning Can Be Comparable to Fine-tuning Universally Across Scales and Tasks
- P-Tuning: GPT Understands, Too
- Prompt Tuning: The Power of Scale for Parameter-Efficient Prompt Tuning
- AdaLoRA: Adaptive Budget Allocation for Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
- LLaMA-Adapter: Efficient Fine-tuning of Language Models with Zero-init Attention
此外也列出了该包对不同的任务中,不同方法和模型的支持情况(我只列出了关于NLP的,还有部分图像的):
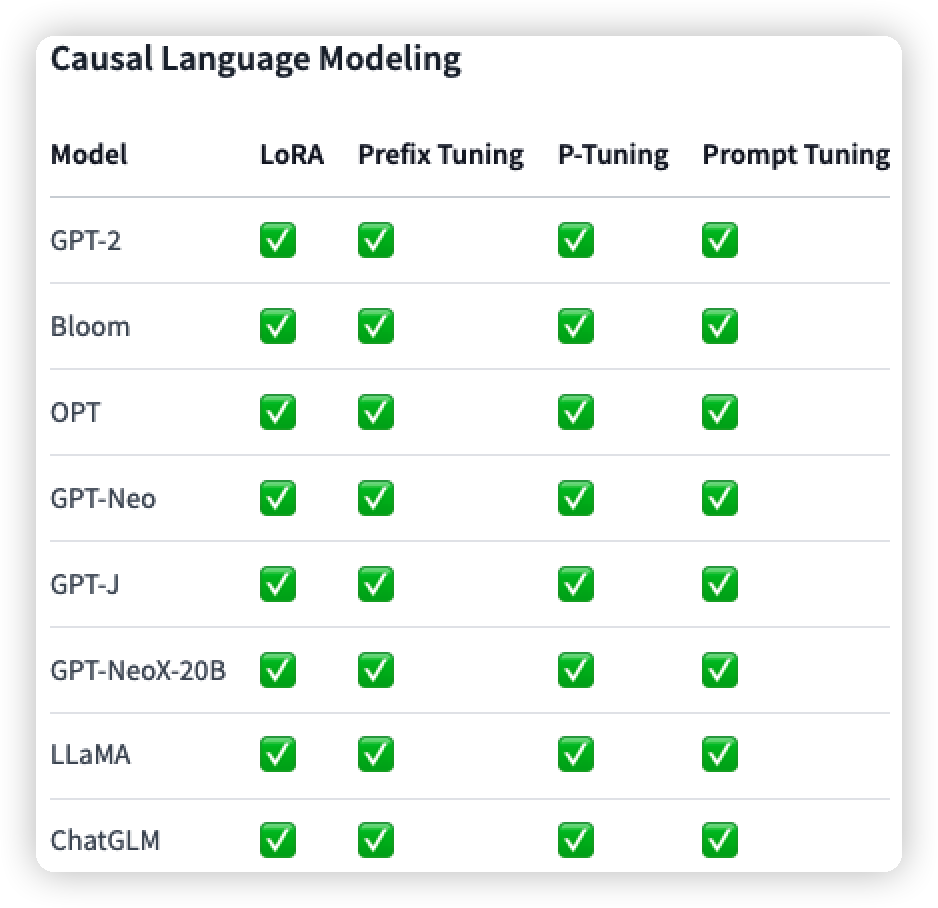

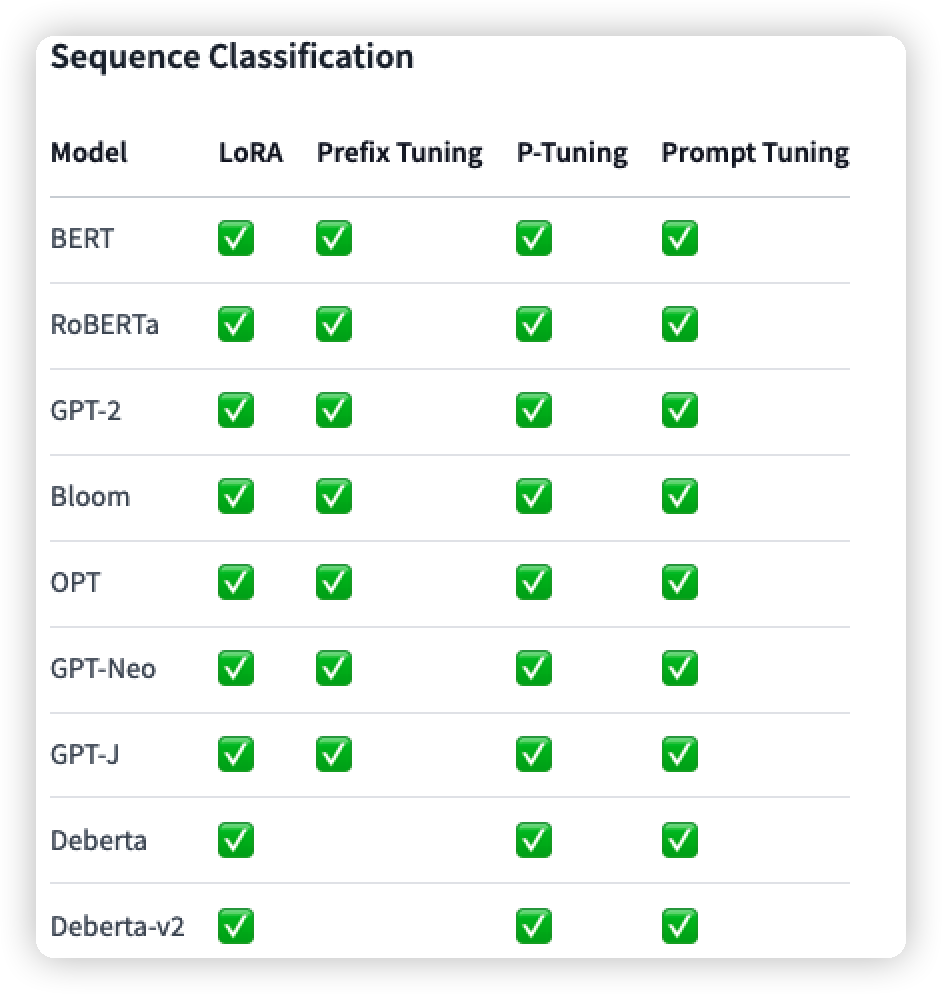

但是还没有P-Tuning v2: Prompt Tuning Can Be Comparable to Fine-tuning Universally Across Scales and Tasks的方法,因此我就看源码是怎么处理的。
在研究和阅读其他人blog期间,发现有些人对P-Tuning描述不准确。下面是一些存在的不准确描述情况❎:
- 把Prompt Tuning称作是P-Tuning ❎;
- 使用P-Tuning V2的时候,直接称作是P-Tuning❎;
- 使用了P-Tuning,但是却说是使用了P-TuningV2❎
- ……
因此需要注意甄别(主要是P-Tuning和Prompt-Tuning的方法提出时间就差了一个月,并且在方法上有一定的相似性,都是在Embedding中使用了continuous prompt)
Prompt-Tuning一文中对两者的不同做了说明:
P-tuning” where learnable continuous prompts are interleaved throughout the embedded input, using patterns based on human design. Prompt tuning approach removes this complication by simply prepending the prompt to the input. To achieve strong SuperGLUE results, P-tuning has to be used in conjunction with model tuning, that is, models jointly update both the prompt and the main model parameters【也就是全量微调,但是文章的论点是GPT在NLU任务上的表现,并且还突出few-shot场景下效果】, whereas our approach keeps the original language model frozen” “As another difference, P-tuning requires the addition of “anchor” tokens in the input (e.g. a question mark following the hypothesis in the RTE task) to achieve strong performance, while prompt tuning leaves inputs untouched.”
P-Tuning V2源码定位
这里以run_script/run_rte_roberta.sh为例,下面是代码:
export TASK_NAME=superglue
export DATASET_NAME=rte
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0
bs=32
lr=5e-3
dropout=0.1
psl=128
epoch=100
python3 run.py \
--model_name_or_path roberta-large \
--task_name $TASK_NAME \
--dataset_name $DATASET_NAME \
--do_train \
--do_eval \
--max_seq_length 128 \
--per_device_train_batch_size $bs \
--learning_rate $lr \
--num_train_epochs $epoch \
--pre_seq_len $psl \
--output_dir checkpoints/$DATASET_NAME-roberta/ \
--overwrite_output_dir \
--hidden_dropout_prob $dropout \
--seed 11 \
--save_strategy no \
--evaluation_strategy epoch \
--prefix
通过查看arguments.py文件可以查看到prefix参数是如下定义的:
prefix: bool = field(
default=False,
metadata={
"help": "Will use P-tuning v2 during training"
}
)
【为什么非要用prefix呢?我一开始以为这个参数是使用prefix Tuning呢QAQ】
因为shell脚本中的task=superglue,可以看到第96行中引用了get_trainer:
if data_args.task_name.lower() == "superglue":
assert data_args.dataset_name.lower() in SUPERGLUE_DATASETS
from tasks.superglue.get_trainer import get_trainer
最终定位到了BertPrefixForQuestionAnswering类,可以看到P-Tuning V2的关键入口代码:
class BertPrefixForQuestionAnswering(BertPreTrainedModel):
def __init__(self, config):
super().__init__(config)
self.num_labels = config.num_labels
self.pre_seq_len = config.pre_seq_len
self.n_layer = config.num_hidden_layers
self.n_head = config.num_attention_heads
self.n_embd = config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
self.bert = BertModel(config, add_pooling_layer=False)
self.qa_outputs = torch.nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_labels)
self.dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
self.prefix_enc




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 4396
4396










