C++中实现多态的方法:
1.在派生类中重新定义基类的方法
2.使用虚方法
先看一个带虚方法的基类和派生类的声明:
// brass.h
#ifndef BRASS_H_
#define BRASS_H_
#include <string>
// 基类
class Brass
{
private:
std::string fullName;
long acctNum;
double balance;
public:
Brass(const std::string & s = "Default", long an = -1, double bal = 0.0);
void Deposit(double amt);
// 虚方法
virtual void WithDraw(double amt);
double Balance() const;
// 虚方法
virtual void ViewAcct() const;
// 虚析构函数
virtual ~Brass();
};
// 派生类
class BrassPlus: public Brass
{
private:
// 最高欠款数
double maxLoan;
// 利率
double rate;
double owesBank;
public:
BrassPlus(const std::string & s = "Default", long an = -1, double bal = 0.0,
double ml = 500, double r = 0.11125);
BrassPlus(const Brass & ba, double ml = 500, double r = 0.11125);
// 子类重写父类方法
virtual void ViewAcct() const;
virtual void WithDraw(double amt);
void ResetMax(double m)
{
maxLoan = m;
}
void ResetRate(double r) {rate = r;}
void ResetOwes() {owesBank = 0;}
};
#endif
这里着重看一下虚方法
使用虚方法时, 如果方法使通过引用或指针而不是对象调用的, 它将确定使用哪一种方法. 如果没有使用关键字virtual, 程序将根据引用类型选择方法; 如果使用了virtual, 程序将根据引用或指针指向的对象的类型来选择方法.
接上面的类, 假如ViewAcct()不是虚函数, 则程序的结果如下:
Brass dom("Dor", 11224, 4183.45);
BrassPlus dot("Dom", 12117, 2592.00);
Brass & b1_ref = dom;
Brass & b2_ref = dot;
// 调用的是Brass::ViewAcct()
b1_ref.ViewAcct();
// 调用的是Brass::ViewAcct()
b2_ref.ViewAcct();
由于引用变量的类型为Brass, 所以选择了Brass::ViewAcct().
如果ViewAcct()是虚的, 则结果如下:
Brass dom("Dor", 11224, 4183.45);
BrassPlus dot("Dom", 12117, 2592.00);
Brass & b1_ref = dom;
Brass & b2_ref = dot;
// 调用的是Brass::ViewAcct()
b1_ref.ViewAcct();
// 调用的是BrassPlus::ViewAcct()
b2_ref.ViewAcct();
虽然两个引用的类型都是Brass, 但是b2_ref引用的是一个BrassPlus对象, 所以使用的是BrassPlus::ViewAcct().
还有一点, 基类声明了一个虚析构函数, 这样做的目的是为了确保释放派生对象时, 按正确的顺序调用析构函数.
注意:如果要在派生类中重新定义基类的方法, 通常应将基类方法声明为虚的, 这样, 程序将根据对象类型而不是引用或指针的类型来选择方法版本. 为基类声明一个虚沟函数也是一种惯例.
类实现:
// brass.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "brass.h"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
// 格式化输出
typedef std::ios_base::fmtflags format;
typedef std::streamsize precis;
format setFormat();
void restore(format f, precis p);
// Brass方法
// 构造方法
Brass::Brass(const string & s, long an, double bal)
{
fullName = s;
acctNum = an;
balance = bal;
}
// 存款方法
void Brass::Deposit(double amt)
{
if(amt < 0)
cout << "Negative deposit not allowed; deposit is cancelled" << endl;
else
balance += amt;
}
// 提款
void Brass::WithDraw(double amt)
{
// 设置输出格式
format initialState = setFormat();
precis prec = cout.precision(2);
if(amt < 0)
cout << "Withdrawl amount must be positive; withdrawal canceled" << endl;
else if(amt <= balance)
balance -= amt;
else
cout << "Withdrawl amount of $" << amt << " exceeds your balance." << endl << "Withdrawal canceled" << endl;
// 设置回原来格式
restore(initialState, prec);
}
double Brass::Balance() const
{
return balance;
}
void Brass::ViewAcct() const
{
// 设置输出格式
format initialState = setFormat();
precis prec = cout.precision(2);
cout << "Client: " << fullName << endl;
cout << "Account Number : " << acctNum << endl;
cout << "Balance : $" << balance << endl;
// 设置回原来格式
restore(initialState, prec);
}
Brass::~Brass()
{
cout << fullName << " delete " << endl;
}
// 派生类方法
// 使用成员初始化列表调用父类的构造函数
BrassPlus::BrassPlus(const string & s, long an, double bal, double ml, double r):Brass(s, an, bal)
{
maxLoan = ml;
owesBank = 0.0;
rate = r;
}
// 调用的是父类的隐式复制构造函数
BrassPlus::BrassPlus(const Brass & ba, double ml, double r): Brass(ba)
{
maxLoan = ml;
owesBank = 0.0;
rate = r;
}
// 重新定义子类的ViewAcct方法
void BrassPlus::ViewAcct() const
{
// 设置输出格式###.##
format initialState = setFormat();
precis prec = cout.precision(2);
// 调用父类的方法, 派生类可以调用基类的公共方法
// 由于派生类定义了ViewAcct, 所以调用基类的方法必须使用作用域解析符
// 否则会造成递归调用派生类的方法
Brass::ViewAcct();
cout << "Maximum loan: $" << maxLoan << endl;
cout << "Owed to bank : $" << owesBank << endl;
// ###.###
cout.precision(3);
cout << "Loan Rate : " << 100 * rate << "%" << endl;
// 设置回原来格式
restore(initialState, prec);
}
void BrassPlus::WithDraw(double amt)
{
// 设置输出格式
format initialState = setFormat();
precis prec = cout.precision(2);
// 由于派生类没有重新定义Balance()方法, 所以不必使用作用域解析运算符
double bal = Balance();
if(amt < bal)
Brass::WithDraw(amt);
else if(amt <= bal + maxLoan - owesBank){
double advance = amt - bal;
owesBank += advance * (1.0 + rate);
cout << "Bank advance: $" << advance << endl;
cout << "Finance charge: $" << advance * rate << endl;
Deposit(advance);
Brass::WithDraw(amt);
}
else
cout << "Credit limit exceeded. Transaction cancelled" << endl;
// 设置回原来格式
restore(initialState, prec);
}
format setFormat()
{
return cout.setf(std::ios_base::fixed, std::ios_base::floatfield);
}
void restore(format f, precis p)
{
cout.setf(f, std::ios_base::floatfield);
cout.precision(p);
}
第三个文件:
// usebrass1.cpp
// compile with brass.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "brass.h"
int main()
{
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Brass Piggy("Por", 381299, 4000.00);
BrassPlus Hoggy("Hog", 382288, 3000.00);
Piggy.ViewAcct();
cout << endl;
Hoggy.ViewAcct();
cout << endl;
cout << "Depositing $1000 into the Hog Account: " << endl;
// 调用的是基类的相应方法, 由于子类没有对应的方法
Hoggy.Deposit(1000.00);
cout << "New Balance : $" << Hoggy.Balance() << endl;
cout << "WithDrawing $4200 from the Pig Account: " << endl;
Piggy.WithDraw(4200.00);
cout << "Piggy account balance: $" << Piggy.Balance() << endl;
cout << "WithDrawing $4200 from the Hogg Account: " << endl;
Hoggy.WithDraw(4200.00);
Hoggy.ViewAcct();
return 0;
}
程序运行结果为:
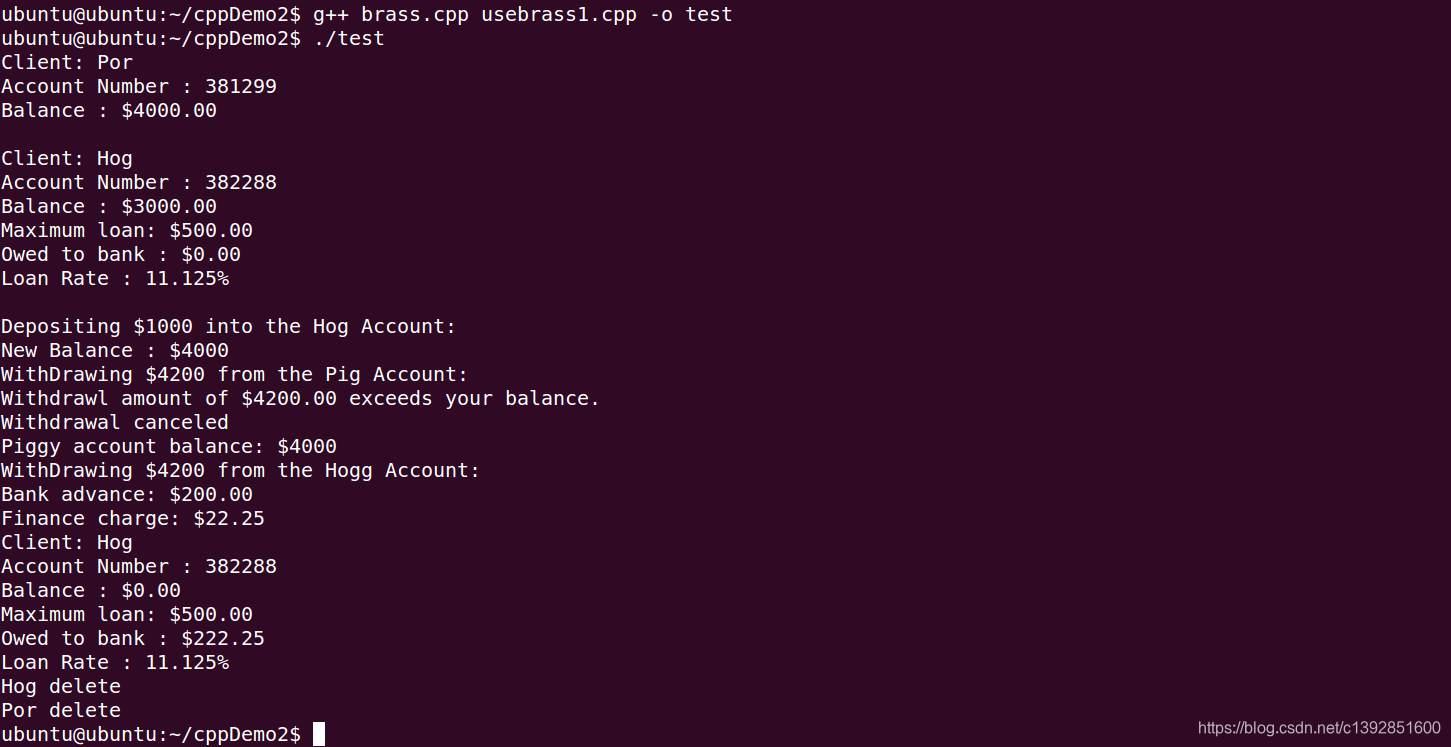
演示多态的例子, 利用指针既可以指向Brass对象, 也可以指向BrassPlus对象, 使用虚方法来调用具体对象的相应方法:
// usebrass2.cpp
// compile with brass.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "brass.h"
const int CLIENTS = 4;
int main()
{
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
// 指针数组
Brass * p_clients[CLIENTS];
std::string temp;
long tempnum;
double tempbal;
char kind;
for(int i = 0; i < CLIENTS; i++)
{
cout << "Enter client's name: ";
getline(cin, temp);
cout << "Enter client's account number: ";
cin >> tempnum;
cout << "Enter opening ballance: $";
cin >> tempbal;
cout << "Enter 1 for Brass Account or 2 for BrassPlus Account: ";
while(cin >> kind && (kind != '1' && kind != '2'))
cout << "Enter either 1 or 2 : ";
if(kind == '1')
// 指针指向一个新创建的Brass对象
p_clients[i] = new Brass(temp, tempnum, tempbal);
else {
double tmax, trate;
cout << "Enter the overdraft limit: $";
cin >> tmax;
cout << "Enter the interest rate as a decimal fraction: ";
cin >> trate;
p_clients[i] = new BrassPlus(temp, tempnum, tempbal, tmax, trate);
}
while(cin.get() != '\n')
continue;
}
cout << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < CLIENTS; i++)
{
// 指针调用对象的方法
p_clients[i]->ViewAcct();
cout << endl;
}
for(int i = 0; i < CLIENTS; i++)
{
// 由于基类有虚的析构函数, 所以在delete的时候
// 先调用BrassPlus的析构函数, 然后自动调用基类的析构函数.
// 使用虚析构函数可以确保正确的析构函数序列被调用
delete p_clients[i];
}
cout << "Done " << endl;
return 0;
}
程序运行结果为:
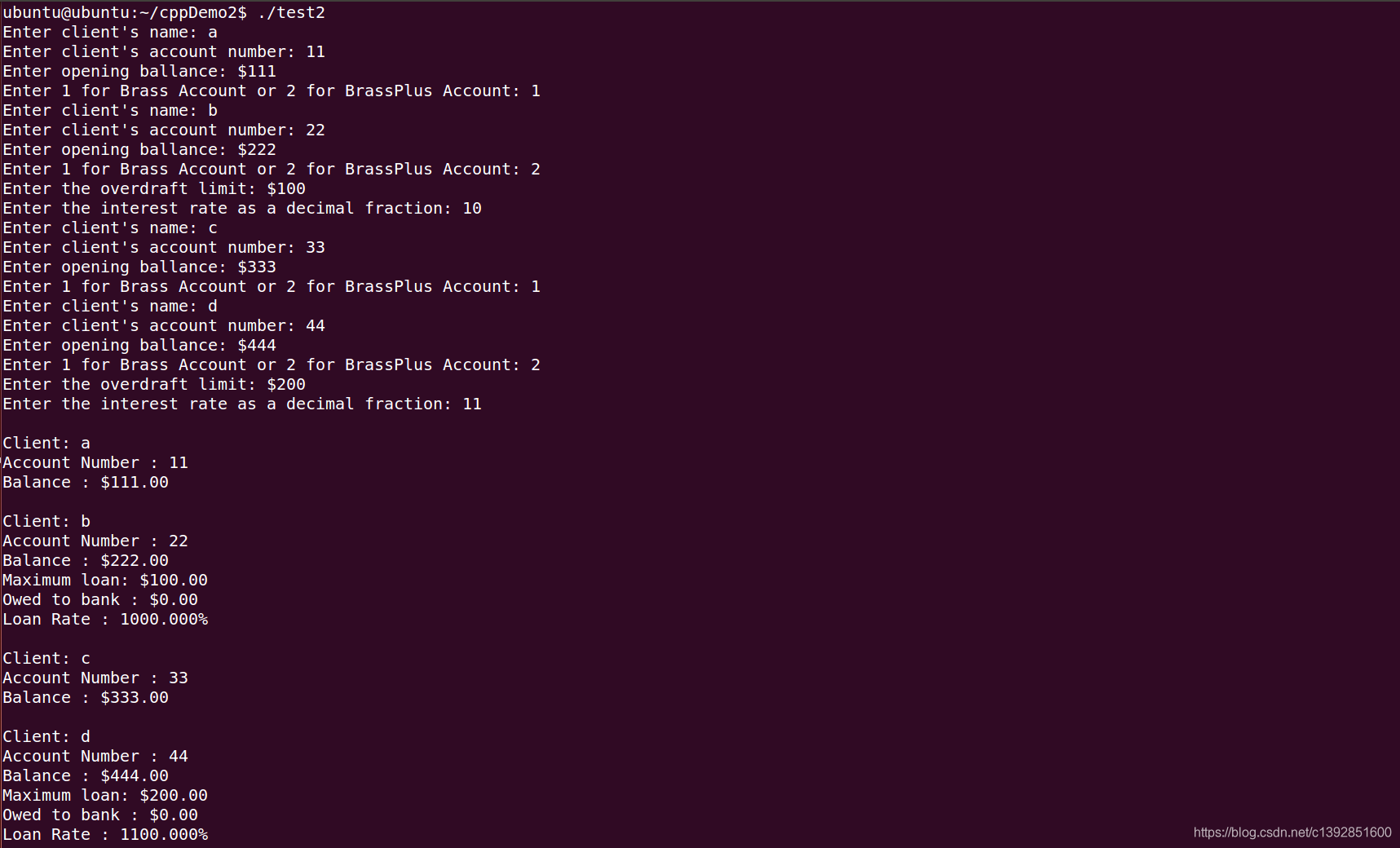
需要注意的地方在注释里都有








 本文介绍了C++中实现多态的方法,包括在派生类中重新定义基类方法和使用虚函数。重点讲解了虚函数的概念,当通过引用或指针调用方法时,程序会根据对象的实际类型选择执行哪个版本的方法。同时强调了基类声明虚析构函数的重要性,以确保正确调用派生对象的析构函数。文章还给出了相关代码示例,展示了多态的运用。
本文介绍了C++中实现多态的方法,包括在派生类中重新定义基类方法和使用虚函数。重点讲解了虚函数的概念,当通过引用或指针调用方法时,程序会根据对象的实际类型选择执行哪个版本的方法。同时强调了基类声明虚析构函数的重要性,以确保正确调用派生对象的析构函数。文章还给出了相关代码示例,展示了多态的运用。
















 2679
2679

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








