一:线程标识:pthread_equal 若相等,返回值为0,若不等,返回值非0
#include<pthread.h>
pthread_t pthread_self();
int pthread_equal(pthread_t id1,pthread_t id2);
二:线程创建:
#include <pthread.h>
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,
void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
//线程创建成功后,thread保存线程ID
//attr设置线程的属性,默认为NULL,属性后面介绍
//void *(*start_routine) (void *)为线程函数,它的参数为第4个参数void *arg,返回值为void *指针
//pthread_create创建成功的返回值为0,若失败,返回错误编号,注意它并不设置errno的值
三:线程终止
线程终止方式:
1.从线程函数start_route返回;2.线程被同一进程的其它线程取消(调用pthread_cancel); 3.线程自己调用pthread_exit退出。
void pthread_exit(void *ret_val);
同进程waitpid函数,线程可以使用pthread_join函数等待线程结束
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **ret_val); //调用线程将阻塞,直到指定的线程终止。如果线程是被取消的,ret_val的值会被设为THREAD_CANCEL
特别强调一下,线程函数的返回值,线程函数的返回值是一个void指针,这预示着,返回值可能不止一个值,也有可能是一个复杂结构,另外当线程从线程函数返回后,线程栈内容就已经不存在了,所以试图访问返回线程局部变量指针,总是会出错的,eg:
#include "apue.h"
#include <pthread.h>
struct foo {
int a, b, c, d;
};
void printfoo(const char *s, const struct foo *fp)
{
printf("%s", s);
printf(" structure at 0x%lx\n", (unsigned long)fp);
printf(" foo.a = %d\n", fp->a);
printf(" foo.b = %d\n", fp->b);
printf(" foo.c = %d\n", fp->c);
printf(" foo.d = %d\n", fp->d);
}
void * thr_fn1(void *arg)
{
struct foo foo = {1, 2, 3, 4};
printfoo("thread 1:\n", &foo);
pthread_exit((void *)&foo);
}
void * thr_fn2(void *arg)
{
printf("thread 2: ID is %lu\n", (unsigned long)pthread_self());
pthread_exit((void *)0);
}
int main(void)
{
int err;
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
struct foo *fp;
err = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thr_fn1, NULL);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't create thread 1");
err = pthread_join(tid1, (void *)&fp);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't join with thread 1");
sleep(1);
printf("parent starting second thread\n");
err = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thr_fn2, NULL);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't create thread 2");
sleep(1);
printfoo("parent:\n", fp);
exit(0);
}
/*程序执行后输出:
[root@localhost threads]# ./a.out
thread 1:
structure at 0x7f656d781f00
foo.a = 1
foo.b = 2
foo.c = 3
foo.d = 4
parent starting second thread
thread 2: ID is 140073605015296
parent:
structure at 0x7f656d781f00
foo.a = 1836590848
foo.b = 32613
foo.c = 1
foo.d = 0
*/
int pthread_cancel(pthread_t thread); //取消同一进程的其它线程,该函数不会阻塞,它发送取消请求后,立即返回。
注册线程退出时的清理处理程序(类似atexit):
#include <pthread.h>
void pthread_cleanup_push(void (*routine)(void *),void *arg);
void pthread_cleanup_pop(int execute);
其中arg为routine函数的参数,跟atexit不同的是routine只在下列情形下才被调用:
1.线程函数调用,pthread_exit退出后,会调用routine
2.其它线程函数调用pthread_cancel,使得该线程函数退出后,会调用routine
3.在线程函数中自己调用pthread_cleanup_pop,且execute参数非0,会调用routine,若execute参数为0,routine不会调用且被删除。
注意从线程函数return返回,不会调用routine。eg:
#include "apue.h"
#include <pthread.h>
void
cleanup(void *arg)
{
printf("cleanup: %s\n", (char *)arg);
}
void *
thr_fn1(void *arg)
{
printf("thread 1 start\n");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup, "thread 1 first handler");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup, "thread 1 second handler");
printf("thread 1 push complete\n");
if (arg)
return((void *)1);
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
return((void *)1);
}
void *
thr_fn2(void *arg)
{
printf("thread 2 start\n");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup, "thread 2 first handler");
pthread_cleanup_push(cleanup, "thread 2 second handler");
printf("thread 2 push complete\n");
if (arg)
pthread_exit((void *)2);
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
pthread_cleanup_pop(0);
pthread_exit((void *)2);
}
int
main(void)
{
int err;
pthread_t tid1, tid2;
void *tret;
err = pthread_create(&tid1, NULL, thr_fn1, (void *)1);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't create thread 1");
err = pthread_create(&tid2, NULL, thr_fn2, (void *)1);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't create thread 2");
err = pthread_join(tid1, &tret);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't join with thread 1");
printf("thread 1 exit code %ld\n", (long)tret);
err = pthread_join(tid2, &tret);
if (err != 0)
err_exit(err, "can't join with thread 2");
printf("thread 2 exit code %ld\n", (long)tret);
exit(0);
}
/*输出结果
[root@localhost threads]# ./exitstatus
thread 1 returning
thread 1 exit code 1
thread 2 exiting
thread 2 exit code 2
[root@localhost threads]# ./cleanup
thread 1 start
thread 1 push complete
thread 1 exit code 1
thread 2 start
thread 2 push complete
cleanup: thread 2 second handler
cleanup: thread 2 first handler
thread 2 exit code 2
*/
最后一个线程函数:
int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
线程结束后,一般会存储线程退出状态信息,其他线程可以调用pthread_join获取该信息(类似waitpid),如若调用pthread_detach,则使得thread标识的线程在结束后,内核自动回收该线程资源,且该线程不能被pthread_join。
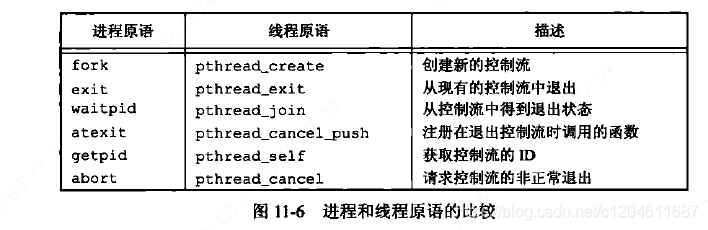
在全文最后,我们类比一下,进程跟线程的相关API:



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








