
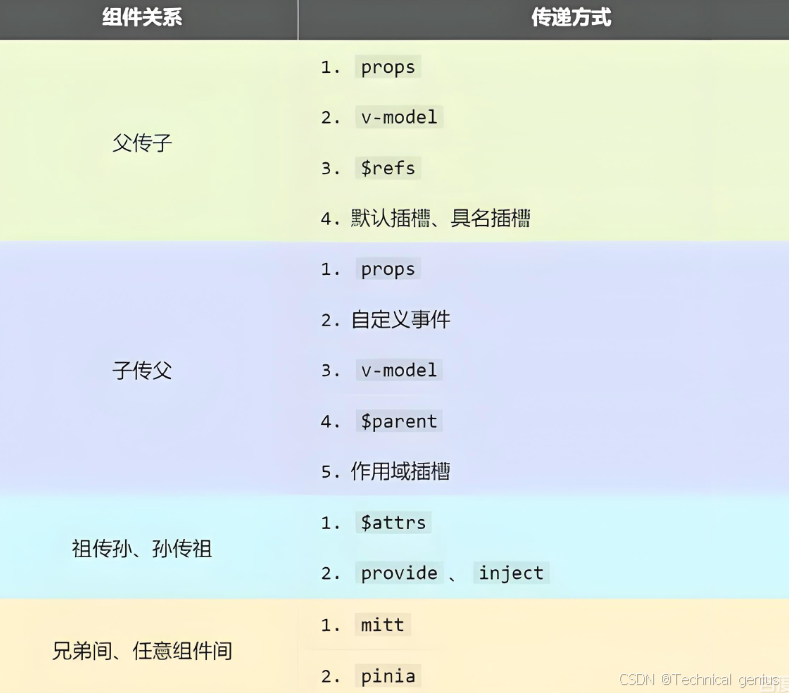
一、组件通信概述与重要性
1.1 为什么需要组件通信?
在现代前端开发中,组件化架构已成为主流。Vue3的组件通信机制如同应用的神经系统,负责数据流动和状态管理。良好的通信机制能够:
- ✅ 降低耦合度:组件间依赖关系清晰
- ✅ 提升可维护性:代码结构更易于理解和修改
- ✅ 增强复用性:组件可在不同场景下重复使用
- ✅ 支持复杂业务:应对大型应用的复杂数据流
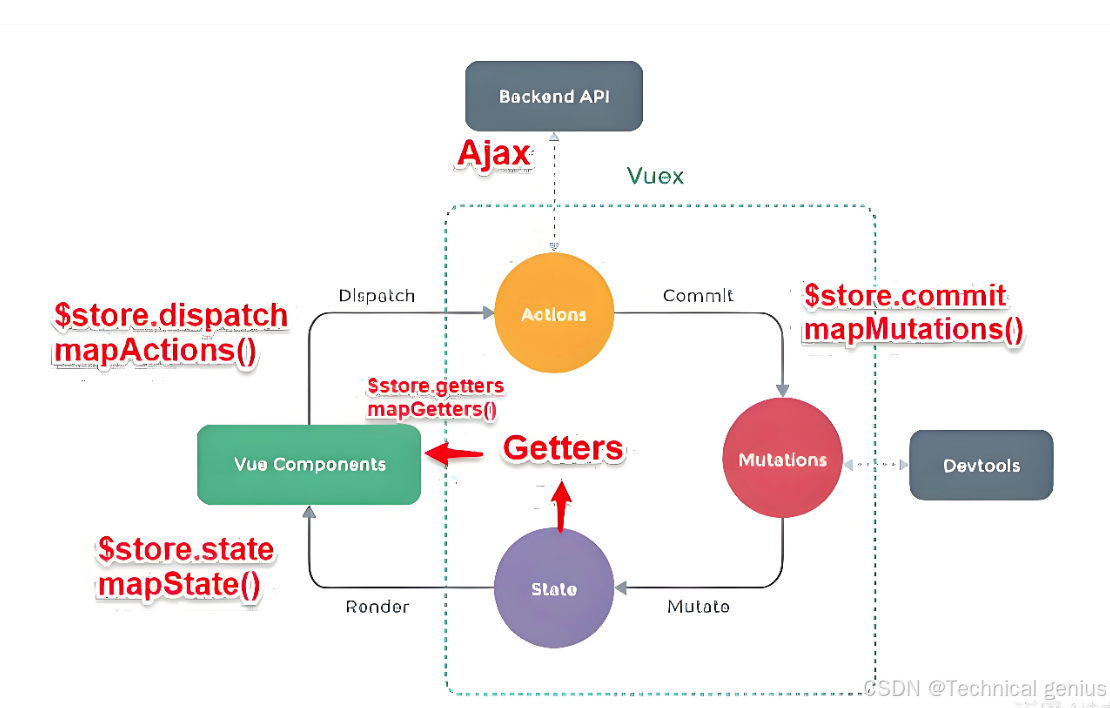
1.2 Vue3通信方式全景图
Vue3提供了从简单到复杂的多层次通信方案:
基础通信:
├── Props/Emits(父子)
├── v-model(双向绑定)
├—— ref/expose(方法调用)
高级通信:
├── Provide/Inject(跨层级)
├── 事件总线(任意组件)
├—— Pinia/Vuex(状态管理)
└── 全局状态(小型应用)
二、Props:单向数据流的基础
2.1 基本用法
Props是父组件向子组件传递数据的主要方式,遵循单向数据流原则。
<!-- 父组件 Parent.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<h2>父组件</h2>
<ChildComponent
:user-info="userData"
:is-visible="showChild"
:count="counter"
@update-data="handleUpdate"
/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, reactive } from 'vue'
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent.vue'
const userData = reactive({
name: '张三',
age: 25,
email: 'zhangsan@example.com'
})
const showChild = ref(true)
const counter = ref(0)
const handleUpdate = (newData) => {
Object.assign(userData, newData)
}
</script>
<!-- 子组件 ChildComponent.vue -->
<template>
<div v-if="isVisible" class="child-container">
<h3>子组件接收的数据:</h3>
<p>姓名:{{ userInfo.name }}</p>
<p>年龄:{{ userInfo.age }}</p>
<p>计数:{{ count }}</p>
<button @click="updateUserInfo">更新用户信息</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
// 定义Props - 对象写法(推荐)
const props = defineProps({
userInfo: {
type: Object,
required: true,
default: () => ({})
},
isVisible: {
type: Boolean,
default: false
},
count: {
type: Number,
default: 0
}
})
// 定义Emits
const emit = defineEmits(['update-data'])
const updateUserInfo = () => {
// 向父组件发送更新请求
emit('update-data', {
name: '李四',
age: 30
})
}
</script>
<style scoped>
.child-container {
border: 1px solid #e1e1e1;
padding: 20px;
margin: 10px 0;
border-radius: 8px;
background: #f9f9f9;
}
</style>
2.2 Props验证与默认值
完整的Props验证确保数据类型的正确性:
<!-- 子组件 WithValidation.vue -->
<template>
<div class="validation-demo">
<h4>Props验证示例</h4>
<p>标题:{{ title }}</p>
<p>标签:{{ tags.join(', ') }}</p>
<p>配置:{{ config }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
// 字符串类型,必需
title: {
type: String,
required: true,
validator: (value) => value.length > 0
},
// 数组类型,带默认值
tags: {
type: Array,
default: () => ['默认标签']
},
// 对象类型,复杂验证
config: {
type: Object,
default: () => ({
theme: 'light',
size: 'medium'
}),
validator: (value) => {
return ['light', 'dark'].includes(value.theme) &&
['small', 'medium', 'large'].includes(value.size)
}
},
// 自定义验证函数
score: {
type: Number,
default: 0,
validator: (value) => value >= 0 && value <= 100
}
})
</script>
三、自定义事件:子向父通信
3.1 基础事件通信
<!-- 子组件 EventEmitter.vue -->
<template>
<div class="event-emitter">
<button @click="sendSimpleEvent">发送简单事件</button>
<button @click="sendComplexEvent">发送复杂事件</button>
<input
v-model="inputValue"
@input="sendInputEvent"
placeholder="输入内容实时传递"
/>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const inputValue = ref('')
// 定义事件类型(TypeScript风格)
const emit = defineEmits<{
// 简单事件,无参数
(e: 'simple-event'): void
// 复杂事件,带参数
(e: 'complex-event', data: { id: number; message: string }): void
// 输入事件,实时传递
(e: 'input-change', value: string): void
}>()
const sendSimpleEvent = () => {
emit('simple-event')
}
const sendComplexEvent = () => {
emit('complex-event', {
id: Date.now(),
message: '来自子组件的复杂数据'
})
}
const sendInputEvent = () => {
emit('input-change', inputValue.value)
}
</script>
3.2 事件验证与参数处理
<!-- 父组件 EventHandler.vue -->
<template>
<div class="event-handler">
<h2>事件处理示例</h2>
<EventEmitter
@simple-event="handleSimple"
@complex-event="handleComplex"
@input-change="handleInput"
/>
<div class="event-log">
<h4>事件日志:</h4>
<ul>
<li v-for="(log, index) in eventLogs" :key="index">
{{ log }}
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import EventEmitter from './EventEmitter.vue'
const eventLogs = ref<string[]>([])
const handleSimple = () => {
eventLogs.value.push(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 收到简单事件`)
const handleComplex = (data) => {
eventLogs.value.push(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 收到复杂事件:${JSON.stringify(data)}`)
const handleInput = (value) => {
eventLogs.value.push(`[${new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}] 输入变化:${value}`)
}
</script>
四、v-model:双向绑定进阶
4.1 基础v-model实现
<!-- 自定义输入组件 CustomInput.vue -->
<template>
<div class="custom-input">
<label v-if="label">{{ label }}</label>
<input
:value="modelValue"
@input="$emit('update:modelValue', $event.target.value)"
:placeholder="placeholder"
class="input-field"
/>
<div v-if="error" class="error-message">
{{ error }}
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
modelValue: {
type: [String, Number],
default: ''
},
label: String,
placeholder: String
})
const emit = defineEmits(['update:modelValue'])
</script>
<style scoped>
.custom-input {
margin: 10px 0;
}
.input-field {
width: 100%;
padding: 8px 12px;
border: 1px solid #ddd;
border-radius: 4px;
font-size: 14px;
}
.error-message {
color: #e74c3c;
font-size: 12px;
margin-top: 4px;
}
</style>
4.2 多v-model绑定
Vue3支持多个v-model绑定,极大提升了组件灵活性:
<!-- 用户表单组件 UserForm.vue -->
<template>
<div class="user-form">
<div class="form-group">
<label>用户名:</label>
<input
:value="userName"
@input="$emit('update:userName', $event.target.value)"
/>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label>邮箱:</label>
<input
:value="email"
@input="$emit('update:email', $event.target.value)"
/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
userName: String,
email: String
})
const emit = defineEmits(['update:userName', 'update:email'])
</script>
<!-- 父组件使用多v-model -->
<template>
<UserForm
v-model:userName="formData.name"
v-model:email="formData.email"
/>
</template>
<script setup>
import { reactive } from 'vue'
import UserForm from './UserForm.vue'
const formData = reactive({
name: '',
email: ''
})
</script>
五、Provide/Inject:跨层级通信
5.1 基础provide/inject
<!-- 祖先组件 Ancestor.vue -->
<template>
<div class="ancestor">
<h2>祖先组件</h2>
<div class="control-panel">
<button @click="changeTheme">切换主题</button>
<button @click="incrementCounter">增加计数</button>
</div>
<MiddleComponent />
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, provide } from 'vue'
import MiddleComponent from './MiddleComponent.vue'
// 提供响应式数据
const theme = ref('light')
const globalCounter = ref(0)
const changeTheme = () => {
theme.value = theme.value === 'light' ? 'dark' : 'light'
}
const incrementCounter = () => {
globalCounter.value++
}
// 提供数据给后代组件
provide('theme', {
theme,
changeTheme
})
provide('globalCounter', globalCounter)
5.2 注入和使用
<!-- 后代组件 Descendant.vue -->
<template>
<div class="descendant" :class="themeClass">
<h3>后代组件</h3>
<p>当前主题:{{ themeData.theme }}</p>
<p>全局计数:{{ counterValue }}</p>
<button @click="themeData.changeTheme()">
切换主题(来自祖先)
</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { inject, computed } from 'vue'
// 注入数据
const themeData = inject('theme', {
theme: 'light',
changeTheme: () => {}
})
const counterValue = inject('globalCounter', ref(0))
const themeClass = computed(() => ({
'theme-light': themeData.theme === 'light',
'theme-dark': themeData.theme === 'dark'
}))
</script>
<style scoped>
.theme-light {
background: #ffffff;
color: #333333;
}
.theme-dark {
background: #2c3e50;
color: #ffffff;
}
</style>
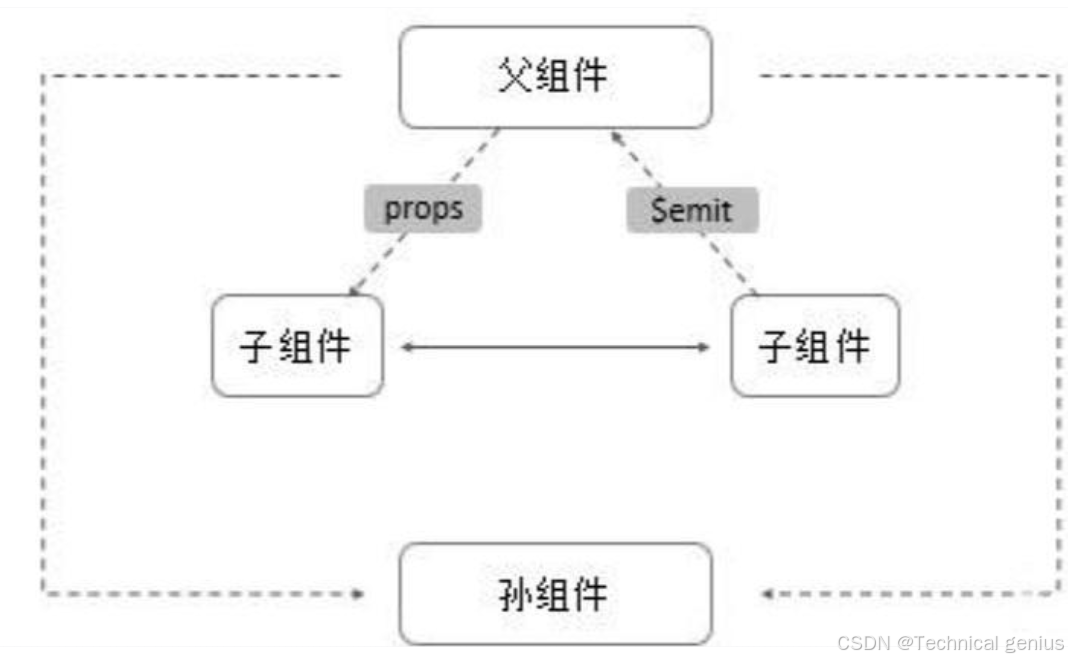
六、模板引用与expose
6.1 使用ref获取组件实例
<!-- 父组件 ParentWithRef.vue -->
<template>
<div>
<h2>模板引用示例</h2>
<ChildWithMethods ref="childRef" />
<div class="control-buttons">
<button @click="callChildMethod">调用子组件方法</button>
<button @click="getChildState">获取子组件状态</button>
</div>
<div class="child-state">
{{ childState }}
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import ChildWithMethods from './ChildWithMethods.vue'
const childRef = ref(null)
const childState = ref('')
const callChildMethod = async () => {
if (childRef.value) {
try {
const result = await childRef.value.fetchData()
childState.value = `子组件返回:${result}`
} catch (error) {
childState.value = `调用失败:${error.message}`
}
}
}
const getChildState = () => {
if (childRef.value) {
childState.value = `子组件内部计数:${childRef.value.internalCount}`
}
}
</script>
<!-- 子组件 ChildWithMethods.vue -->
<template>
<div class="child-with-methods">
<p>内部状态:{{ internalCount }}</p>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
const internalCount = ref(0)
const fetchData = () => {
internalCount.value++
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(`异步数据 ${internalCount.value}`)
}, 1000)
})
}
const reset = () => {
internalCount.value = 0
}
// 暴露方法给父组件
defineExpose({
fetchData,
reset,
internalCount
})
</script>
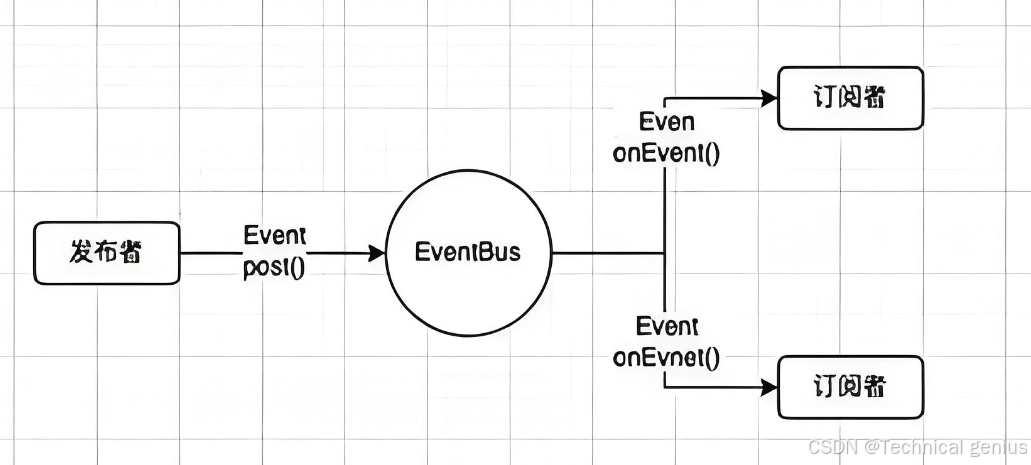
七、事件总线:任意组件通信
7.1 使用mitt实现事件总线
// eventBus.js
import mitt from 'mitt'
// 创建事件总线实例
const emitter = mitt()
// 定义事件类型
export const EventTypes = {
USER_LOGIN: 'user-login',
USER_LOGOUT: 'user-logout',
DATA_UPDATED: 'data-updated',
GLOBAL_NOTIFICATION: 'global-notification'
}
// 导出常用方法
export const useEventBus = () => {
const emitEvent = (type, payload) => {
emitter.emit(type, {
timestamp: new Date(),
payload
})
}
const onEvent = (type, handler) => {
emitter.on(type, handler)
// 返回取消监听函数
return () => {
emitter.off(type, handler)
}
}
return {
emit: emitEvent,
on: onEvent,
off: emitter.off
}
}
export default emitter
7.2 组件中使用事件总线
<!-- 组件A:事件发送者 -->
<template>
<div class="event-sender">
<h3>事件发送者</h3>
<button @click="sendLoginEvent">发送登录事件</button>
<button @click="sendDataUpdate">发送数据更新</button>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { useEventBus, EventTypes } from './eventBus.js'
const { emit } = useEventBus()
const sendLoginEvent = () => {
emit(EventTypes.USER_LOGIN, {
userId: 123,
username: '张三'
})
}
const sendDataUpdate = () => {
emit(EventTypes.DATA_UPDATED, {
type: 'user',
action: 'update'
})
}
<!-- 组件B:事件接收者 -->
<template>
<div class="event-receiver">
<h3>事件接收者</h3>
<div class="event-log">
<h4>收到的事件:</h4>
<ul>
<li v-for="(event, index) in receivedEvents" :key="index">
{{ event }}
</li>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref, onMounted, onUnmounted } from 'vue'
import { useEventBus, EventTypes } from './eventBus.js'
const receivedEvents = ref([])
const { on } = useEventBus()
const handleUserLogin = (event) => {
receivedEvents.value.push(`用户登录:${JSON.stringify(event.payload)}`)
}
const handleDataUpdate = (event) => {
receivedEvents.value.push(`数据更新:${JSON.stringify(event.payload)}`)
}
// 组件挂载时注册事件监听
onMounted(() => {
// 监听用户登录事件
on(EventTypes.USER_LOGIN, handleUserLogin)
// 监听数据更新事件
on(EventTypes.DATA_UPDATED, handleDataUpdate)
})
// 组件卸载时取消监听
onUnmounted(() => {
// 自动清理
})
八、Pinia状态管理
8.1 创建Store
// stores/userStore.js
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
import { ref, computed } from 'vue'
export const useUserStore = defineStore('user', () => {
// 状态
const user = ref(null)
const isLoggedIn = ref(false)
// Getter
const userName = computed(() => user.value?.name || '未登录')
// Action
const login = async (credentials) => {
try {
// 模拟登录API调用
const response = await fakeLoginApi(credentials)
user.value = response.user
isLoggedIn.value = true
return true
} catch (error) {
isLoggedIn.value = false
throw error
}
}
const logout = () => {
user.value = null
isLoggedIn.value = false
}
return {
user,
isLoggedIn,
userName,
login,
logout
}
})
// 模拟API
const fakeLoginApi = (credentials) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve({
user: {
id: 1,
name: credentials.username,
email: 'user@example.com'
})
}, 1000)
})
8.2 在组件中使用Store
<!-- UserProfile.vue -->
<template>
<div class="user-profile">
<div v-if="userStore.isLoggedIn" class="logged-in">
<h3>用户信息</h3>
<p>用户名:{{ userStore.userName }}</p>
<p>邮箱:{{ userStore.user?.email }}</p>
<button @click="handleLogout" class="logout-btn">
退出登录
</button>
</div>
<div v-else class="logged-out">
<LoginForm @login-success="handleLoginSuccess" />
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
import { useUserStore } from './stores/userStore'
import LoginForm from './LoginForm.vue'
const userStore = useUserStore()
const handleLoginSuccess = () => {
console.log('登录成功,用户信息:', userStore.user)
}
const handleLogout = () => {
userStore.logout()
}
</script>
九、实战场景:完整通信示例
9.1 电商购物车系统
<!-- 商品组件 ProductItem.vue -->
<template>
<div class="product-item">
<h3>{{ product.name }}</h3>
<p>价格:¥{{ product.price }}</p>
<p>库存:{{ product.stock }}</p>
<div class="product-actions">
<button
@click="addToCart"
:disabled="product.stock === 0"
class="add-btn"
>
{{ product.stock === 0 ? '缺货' : '加入购物车' }}
</button>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
const props = defineProps({
product: {
type: Object,
required: true
}
})
const emit = defineEmits(['add-to-cart'])
const addToCart = () => {
if (props.product.stock > 0) {
emit('add-to-cart', {
productId: props.product.id,
quantity: 1,
price: props.product.price
})
}
}
</script>
<!-- 购物车组件 ShoppingCart.vue -->
<template>
<div class="shopping-cart">
<h3>购物车</h3>
<div v-if="cartItems.length === 0" class="empty-cart">
购物车为空
</div>
<div v-else class="cart-items">
<CartItem
v-for="item in cartItems"
:key="item.id"
:item="item"
@update-quantity="updateQuantity"
@remove-item="removeItem"
/>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { computed } from 'vue'
import { useCartStore } from './stores/cartStore'
import CartItem from './CartItem.vue'
const cartStore = useCartStore()
const cartItems = computed(() => cartStore.items)
</script>
9.2 实时聊天系统
<!-- 聊天室组件 ChatRoom.vue -->
<template>
<div class="chat-room">
<div class="messages">
<Message
v-for="message in messages"
:key="message.id"
:message="message"
/>
</div>
<MessageInput @send-message="handleSendMessage" />
</div>
</template>
<script setup>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import { useEventBus, EventTypes } from './eventBus.js'
import Message from './Message.vue'
import MessageInput from './MessageInput.vue'
const messages = ref([])
const { on, emit } = useEventBus()
const handleSendMessage = (content) => {
const message = {
id: Date.now(),
content,
timestamp: new Date(),
sender: 'current-user'
})
messages.value.push(message)
// 通知其他组件有新消息
emit(EventTypes.NEW_MESSAGE, message)
}
// 监听其他用户的消息
on(EventTypes.NEW_MESSAGE, (event) => {
if (event.payload.sender !== 'current-user') {
messages.value.push(event.payload)
}
})
</script>
十、最佳实践与性能优化
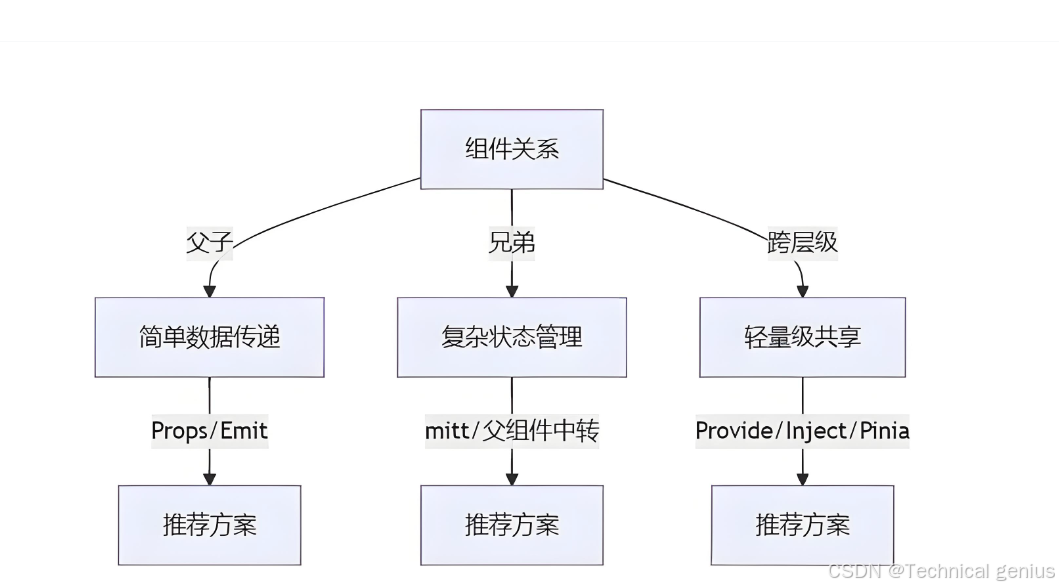
10.1 通信方式选择指南
根据不同的场景选择合适的通信方式:
| 场景 | 推荐方式 | 理由 |
|---|---|---|
| 父子组件简单数据传递 | Props/Emits | 简单直接,符合单向数据流 |
| 表单组件双向绑定 | v-model | 语法简洁,符合用户习惯 |
| 跨多层组件状态共享 | Provide/Inject | 避免prop逐层传递 |
| 任意组件事件通知 | 事件总线 | 灵活,解耦 |
| 复杂全局状态管理 | Pinia | 类型安全,开发体验好 |
10.2 性能优化技巧
// 避免不必要的响应式
import { shallowRef, markRaw } from 'vue'
// 大型静态数据使用shallowRef
const largeData = shallowRef({/* 大量数据 */})
// 大型配置对象使用markRaw
const config = markRaw({
// 配置项...
})
10.3 内存泄漏防护
<script setup>
import { onUnmounted } from 'vue'
import { useEventBus } from './eventBus.js'
const { on, off } = useEventBus()
// 注册事件监听器
const unsubscribes = []
onMounted(() => {
// 添加事件监听,保存取消函数
unsubscribes.push(
on('some-event', handler)
)
})
// 组件卸载时清理所有事件监听
onUnmounted(() => {
unsubscribes.forEach(unsubscribe => unsubscribe())
})
</script>
十一、总结
Vue3提供了丰富而灵活的组件通信方案,从简单的父子通信到复杂的全局状态管理,覆盖了各种开发场景。选择合适的通信方式需要考虑:
- 组件关系紧密程度
- 数据流动的复杂度
- 项目的规模和维护需求
- 团队的技术偏好和规范
掌握这些通信技术,能够帮助开发者构建出结构清晰、维护性高、性能优秀的Vue3应用。






















 73
73

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










