
本博客是 One Day One GAN [DAY 3] 的 learning notes!用 CGAN 来做 MNIST 图片的生成!
文章目录
1 CGAN(Conditional Generative Adversarial Nets)
condition的意思是就是条件
原始 GAN
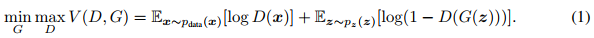
如果我们已知输入的 ground truth 的 label 信息,那么我们便可以在这个基础上结合条件概率的公式得到 CGAN 的目标函数:
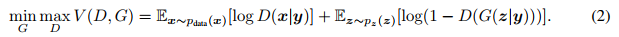
如下图所示

2 CGAN for MNIST
2.1 导入必要的库
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout, multiply
from keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, Embedding, ZeroPadding2D
from keras.layers.advanced_activations import LeakyReLU
from keras.layers.convolutional import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from keras.models import Sequential, Model
from keras.optimizers import Adam
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
2.2 搭建 generator
通过,embedding,把 label 嵌入到 100 维,然后和噪声 z multiply,做为模型的输入,原来的 GAN 只是把 z 作为输入
# build_generator
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=100))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(1024))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(np.prod((28,28,1)), activation='tanh'))
model.add(Reshape((28,28,1)))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(100,)) # input 100,这里写成100不加逗号不行哟
label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32')
label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(10, 100)(label))#class, z dimension
model_input = multiply([noise, label_embedding]) # 把 label 和 noise embedding 在一起,作为 model 的输入
print(model_input.shape)
img = model(model_input) # output (28,28,1)
generator = Model([noise,label], img)
和原始 GAN 不同的地方是,多了 label_embedding,也即把 noise 和 label 信息 embedding,关于 embedding,可以参考 深度学习中Keras中的Embedding层的理解与使用。
- input_dim 为 classes,也即 10
- output_dim 为要嵌入的向量空间的大小,这里是 100
- input_length 这里为 1 (也即 0-9)中的一种
output
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 256) 25856
_________________________________________________________________
leaky_re_lu_1 (LeakyReLU) (None, 256) 0
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_1 (Batch (None, 256) 1024
_________________________________________________________________
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 512) 131584
_________________________________________________________________
leaky_re_lu_2 (LeakyReLU) (None, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_2 (Batch (None, 512) 2048
_________________________________________________________________
dense_3 (Dense) (None, 1024) 525312
_________________________________________________________________
leaky_re_lu_3 (LeakyReLU) (None, 1024) 0
_________________________________________________________________
batch_normalization_3 (Batch (None, 1024) 4096
_________________________________________________________________
dense_4 (Dense) (None, 784) 803600
_________________________________________________________________
reshape_1 (Reshape) (None, 28, 28, 1) 0
=================================================================
Total params: 1,493,520
Trainable params: 1,489,936
Non-trainable params: 3,584
_________________________________________________________________
(?, 100)
2.3 搭建 discriminator
通过 embedding,把 label 嵌入到 28281 维,然后和图片 multiply,做为模型的输入,原来的 GAN 只是把图片作为输入
# build_discriminator
model = Sequential()
model.add(Flatten(input_shape=(28,28,1)))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.4))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dropout(0.4))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=(28,28,1)) # 输入 (28,28,1)
label = Input(shape=(1,), dtype='int32')
label_embedding = Flatten()(Embedding(10, np.prod((28,28,1)))(label))
flat_img = Flatten()(img)
model_input = multiply([flat_img, label_embedding])
validity = model(model_input) # 把 label 和 G(z) embedding 在一起,作为 model 的输入
discriminator = Model([img, label], validity)
output
_________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param #
=================================================================
flatten_2 (Flatten) (None, 784) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_5 (Dense) (None, 512) 401920
_________________________________________________________________
leaky_re_lu_4 (LeakyReLU) (None, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_6 (Dense) (None, 512) 262656
_________________________________________________________________
leaky_re_lu_5 (LeakyReLU) (None, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_1 (Dropout) (None, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_7 (Dense) (None, 512) 262656
_________________________________________________________________
leaky_re_lu_6 (LeakyReLU) (None, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dropout_2 (Dropout) (None, 512) 0
_________________________________________________________________
dense_8 (Dense) (None, 1) 513
=================================================================
Total params: 927,745
Trainable params: 927,745
Non-trainable params: 0
_________________________________________________________________
2.4 compile 模型,对学习过程进行配置
这里训练 GAN 分为两个过程
- 训练 discriminator,图片由固定 generator 产生
- 训练 generator,联合 discriminator 和 generator,但是 discriminator 的梯度不更新,所以 discriminator 固定住了
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# discriminator
discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
noise = Input(shape=(100,))
label = Input(shape=(1,))
img = generator([noise,label])
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
validity = discriminator([img,label])
discriminator.trainable = False
# Trains the generator to fool the discriminator
combined = Model([noise,label], validity)
combined.summary()
combined.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer)
2.5 保存生成的图片
def sample_images(epoch):
r, c = 2, 5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, 100))
sampled_labels = np.arange(0, 10).reshape(-1, 1)
gen_imgs = generator.predict([noise, sampled_labels])
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].set_title("Digit: %d" % sampled_labels[cnt])
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("images/%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
2.6 训练
这里的 epoch 理解为 iteration
batch_size = 32
sample_interval = 200
# Load the dataset
(X_train, y_train), (_, _) = mnist.load_data() # (60000,28,28)
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = X_train / 127.5 - 1. # tanh 的结果是 -1~1,所以这里 0-1 归一化后减1
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3) # (60000,28,28,1)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(20001):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size) # 0-60000 中随机抽
#imgs = X_train[idx]
imgs, labels = X_train[idx], y_train[idx]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 100))# 生成标准的高斯分布噪声
# Generate a batch of new images
gen_imgs = generator.predict([noise,labels])
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = discriminator.train_on_batch([imgs, labels], valid) #真实数据对应标签1
d_loss_fake = discriminator.train_on_batch([gen_imgs,labels], fake) #生成的数据对应标签0
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
#noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, 100))
sampled_labels = np.random.randint(0, 10, batch_size).reshape(-1, 1)
# Train the generator (to have the discriminator label samples as valid)
g_loss = combined.train_on_batch([noise, sampled_labels], valid)
# Plot the progress
if epoch % 500==0:
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
sample_images(epoch)
output
0 [D loss: 0.692575, acc.: 32.81%] [G loss: 0.680311]
200 [D loss: 0.442047, acc.: 76.56%] [G loss: 5.113770]
400 [D loss: 0.332470, acc.: 85.94%] [G loss: 2.495651]
……
19600 [D loss: 0.644090, acc.: 57.81%] [G loss: 0.867414]
19800 [D loss: 0.682952, acc.: 54.69%] [G loss: 0.818742]
20000 [D loss: 0.662673, acc.: 60.94%] [G loss: 0.831777]
2.7 结果展示
0 iteration
200 iteration

400 iteration

19600 iteration

19800 iteration

20000 iteration









 本文介绍如何使用条件生成对抗网络(CGAN)生成MNIST手写数字图片,详细讲解了CGAN原理,包括如何利用条件概率改进GAN目标函数,以及在Keras框架下搭建CGAN模型的具体步骤。
本文介绍如何使用条件生成对抗网络(CGAN)生成MNIST手写数字图片,详细讲解了CGAN原理,包括如何利用条件概率改进GAN目标函数,以及在Keras框架下搭建CGAN模型的具体步骤。
















 784
784

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








