从文件中读取数据
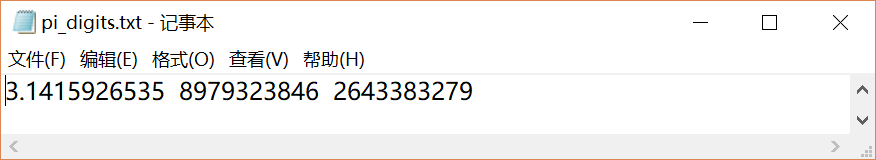
读取圆周率文件pi_digits.txt
with open('pi_digits.txt') as file_object:
contents = file_object.read()#读取整个文件
print(contents.rstrip())
with open('pi_digits.txt') as file_object:
for line in file_object:#逐行读取
print(line.rstrip())
with open('pi_digits.txt') as file_object:
lines = file_object.readlines()
#创建一个包含文件各行内容的列表
for line in lines:
print(line.rstrip())
结果相同:
3.1415926535
8979323846
2643383279
使用文件内容
with open('pi_digits.txt') as file_object:
lines = file_object.readlines()
pi_string = ''
for line in lines:
pi_string += line.strip()
print(pi_string)
print(len(pi_string))
line.strip()删除左右两边的空格
3.141592653589793238462643383279
32
写入文件
with open('programming.txt','w') as file_object1:
file_object1.write('I love you\n')
file_object1.write('mylove\n')

打开文件时open(),三个模式:读取模式’r’ 写入模式’w’ 附加模式’a’
附加模式处理文件不会删除覆盖i原有内容,而是再文件末尾添加你写入文件的行。
异常
try-except-else代码块工作原理如下:
Python尝试执行try代码块中的代码(只有可能引发异常的代码才需要放try语句中)
except代码块告诉python,如果它尝试运行try代码块中的代码时引发指定异常如何操作。
else代码块中存放仅在try代码块成功执行时才需要运行的代码。
print("Give me two numbers, and I'll divide them.")
print("Enter 'q' to quit.")
while True:
first_number = input("\nFirst number: ")
if first_number == 'q':
break
second_number = input("Second number: ")
try:
answer = int(first_number) / int(second_number)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("You can't divide by 0!")
else:
print(answer)
Give me two numbers, and I'll divide them.
Enter 'q' to quit.
First number: 5
Second number: 0
You can't divide by 0!
First number: q
如果不加else:
print("Give me two numbers, and I'll divide them.")
print("Enter 'q' to quit.")
while True:
first_number = input("\nFirst number: ")
if first_number == 'q':
break
second_number = input("Second number: ")
try:
answer = int(first_number) / int(second_number)
except ZeroDivisionError:
print("You can't divide by 0!")
print(answer)
同样输入5 和0
会报错:
During handling of the above exception, another exception occurred:
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:/code/python code/PythonCrashCourse/资源/chapter_10/division.py", line 14, in <module>
print(answer)
NameError: name 'answer' is not defined
因为不合法,所以answer变量不存在,所以无法打出来。
pass
Python中pass的用法:
1、空语句 do nothing
2、保证格式完整
3、保证语义完整
4、在失败时一声不吭(由你决定什么时候向用户报什么错误)
存储数据
json.dump() 2个参数 :要存储的数据 及 可用于存储数据的文件对象
json.load() 1个参数: 文件对象
例:第一次使用。询问用户名,存入文件。再次登陆,直接呈现欢迎语句。
import json
def get_stored_username():
"""Get stored username if available."""
filename = 'username.json'
try:
with open(filename) as f_obj:
username = json.load(f_obj)
except FileNotFoundError:
return None
else:
return username
def get_new_username():
"""Prompt for a new username."""
username = input("What is your name? ")
filename = 'username.json'
with open(filename, 'w') as f_obj:
json.dump(username, f_obj)
return username
def greet_user():
"""Greet the user by name."""
username = get_stored_username()
if username:
print("Welcome back, " + username + "!")
else:
username = get_new_username()
print("We'll remember you when you come back, " + username + "!")
greet_user()
利用了重构的思路:将代码划分为一系列完成具体工作的函数。
扩展例子:在打印并欢迎用户回来的消息前,先询问她用户名是否是对的,如果不对,输入正确用户名。
import json
def get_stored_username():
"""Get stored username if available."""
filename = 'username.json'
try:
with open(filename) as f_obj:
username = json.load(f_obj)
except FileNotFoundError:
return None
else:
return username
def get_new_username(username):
"""Prompt for a new username."""
print("There're nobody in json,you're the one.")
filename = 'username.json'
with open(filename, 'w') as f_obj:
json.dump(username, f_obj)
return username
def greet_user():
"""Greet the user by name."""
username = input("What is your name? ")
storedname = get_stored_username()
if storedname:
while(username != storedname):
username = input("no,What is your name? ")
print("Welcome back, " + username+ "!")
else:
storedname = get_new_username(username)
print("We'll remember you when you come back," + storedname+"!")
greet_user()
第一次输入:
What is your name? l
There're nobody in json,you're the one.
We'll remember you when you come back,l!
后面输入:
What is your name? pp
no,What is your name? oo
no,What is your name? kk
no,What is your name? l
Welcome back, l!





 本文深入探讨Python中文件操作的多种方式,包括读取、写入和异常处理技巧,通过实例展示了如何有效管理和存储数据。
本文深入探讨Python中文件操作的多种方式,包括读取、写入和异常处理技巧,通过实例展示了如何有效管理和存储数据。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








