SpringCloud包含了微服务框架的各个方面。没有配置文件。需要配合Docker等容器技术进行集群部署。
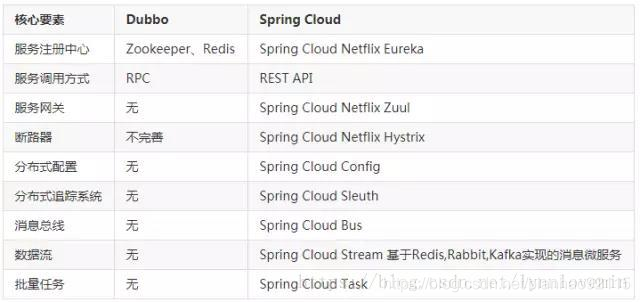
SpringCloud和阿里系Dubbo对比
SpringBoot
SpringBoot是在Spring的基础上做了一层封装。直接运行启动类main方法就会启动自带的Tomcat容器。
启动类上有@SpringBootApplication注解。
SpringBoot只有一个配置文件,那就是.properties或.yml文件。
server.port=8081server.servlet.context-path=/api
这时启动main方法,请求的地址就变成了http://localhost:8081/api/hello
yml文件这需要注意格式,文件名必须是application。
通过marven可以将SpringBoot打包成war或者jar包。SpringBoot持久化封装了MyBatis。
SpringBoot中配置文件区分测试环境与正式环境的方法:
先在application.yml文件添加如下内容:
spring: profiles: active: dev
然后创建多环境配置文件信息,application-dev.yml 等等
编译打包时运行命令:java -jar api.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev
常用注解
@SpringBootApplication
SpringBoot支持main方法启动,我们需要在主类中加入此注解,告诉SpringBoot,这个类是程序的主入口。
可以用@SpringBootConfiguration@EnableAutoConfiguration@ComponentScan这个三个注解来替代它。
SpringBootConfiguration 表示是Spring Boot的配置注解,EnableAutoConfiguration表示自动配置,ComponentScan表示Spring Boot扫描bean的规则,比如扫描那些包。
@Configuration
这个注解表示是SpringBoot的配置类,可以通过配置文件application.yml设置一些配置,也可以通过代码。
@Bean
方法级别的注解,定义一个bean。
@Value
可以将定义在配置文件里的变量取出来交给spring来管理。
异常处理可以使用Spring的AOP特性来完成。
在传统的SpringMVC框架中,我们一般将JSP,HTML页面放到webapps目录下,但是SpringBoot没有webapps,更没有web.xml,如果哦我们要写界面该如何做?
SpringBoot提供了几种模板引擎:FreeMarker,Velocity,Thymeleaf,Groovy,JSP。
在resources 下面建立两个目录:static和templates。static目录用于存放静态资源,比如CSS,JS,HTML等。templates目录用于存放模板引擎文件。





 本文深入探讨SpringBoot与SpringCloud在微服务架构中的应用,比较了SpringCloud与Dubbo的区别,详细介绍了SpringBoot的配置与启动过程,以及如何通过注解实现微服务的自动化配置。
本文深入探讨SpringBoot与SpringCloud在微服务架构中的应用,比较了SpringCloud与Dubbo的区别,详细介绍了SpringBoot的配置与启动过程,以及如何通过注解实现微服务的自动化配置。
















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








