一 抽象类
- 不能被实例化
- 其他该有的都能有
- 静态代码块
- 实例代码块
- 构造方法
- …
- 其他该有的都能有
- 可以被继承
- 多了一层 代码是否重写的校验
- 普通类继承抽象类
- 要重写里面所有的的继承方法
- 可以不重写 设计为抽象类(出来混迟早要还)??
- abstract 修饰类
- 有抽象方法的类必是抽象类
- 抽象方法
- abstract 修饰方法
- 不需要具体实现
- 不能static private final 修饰
- 抽象方法
- 是抽象类 不一定有抽象方法
- 有抽象方法的类必是抽象类
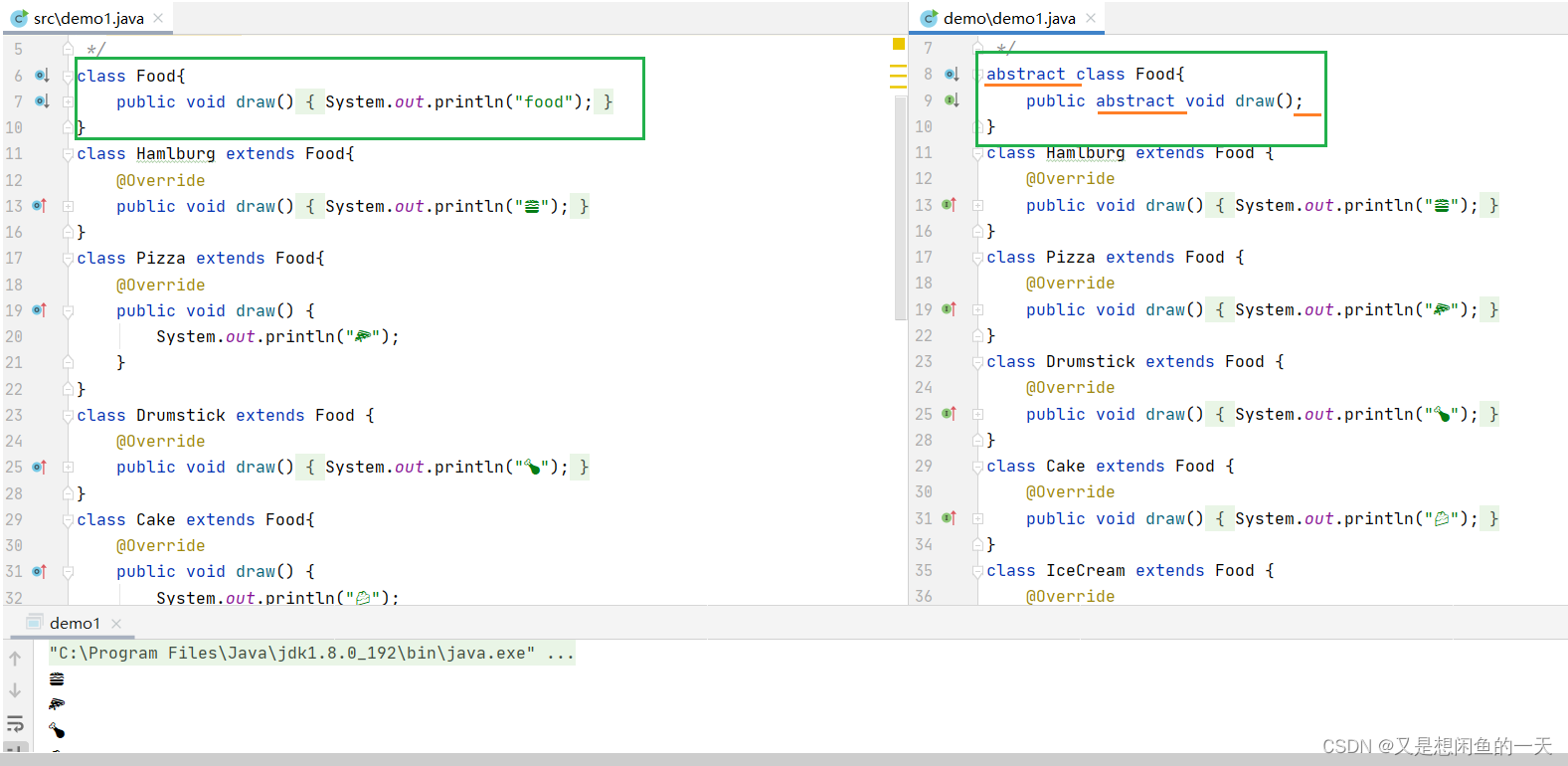
来个代码look,look~
abstract class Food{
public abstract void draw();
}
class Hamlburg extends Food {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("??");
}
}
class Pizza extends Food {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("??");
}
}
class Drumstick extends Food {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("??");
}
}
class Cake extends Food {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("??");
}
}
class IceCream extends Food {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("??");
}
}
public class demo1 {
public static void foodMap(Food food){
food.draw();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
foodMap(new Hamlburg());
foodMap(new Pizza());
foodMap(new Drumstick());
foodMap(new Cake());
foodMap(new IceCream());
}
}
二 接口
-
interface 类名(前I)
-
成员变量默认为
- public static final修饰
-
成员方法默认为
- public stract
-
抽象方法
-
不能具体实现
- 普通成员方法
-
能具体实现
-
default修饰(普通成员方法
-
静态成员方法
-
-
-
- public stract
-
不能实例化
-
class 类 implements 接口
-
重写接口里的方法(这次要写public)
-
一个接口可以引用 具体实现类的(向上转型)
-
-
不能有静态代码块 构造方法
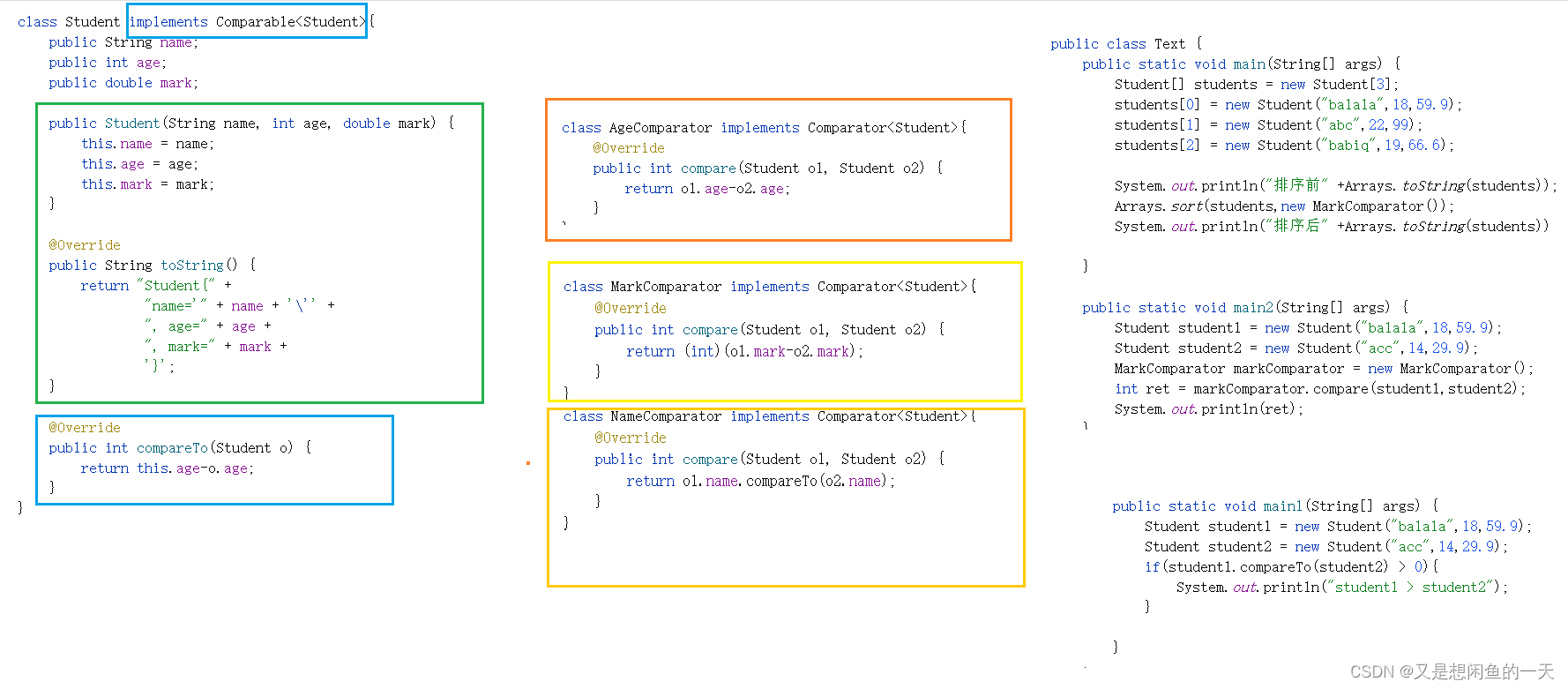
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
public String name;
public int age;
public double mark;
public Student(String name, int age, double mark) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.mark = mark;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", age=" + age +
", mark=" + mark +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.age-o.age;
}
}
class AgeComparator implements Comparator<Student>{
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.age-o2.age;
}
}
class MarkComparator implements Comparator<Student>{
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return (int)(o1.mark-o2.mark);
}
}
class NameComparator implements Comparator<Student>{
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.name.compareTo(o2.name);
}
}
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student[] students = new Student[3];
students[0] = new Student("balala",18,59.9);
students[1] = new Student("abc",22,99);
students[2] = new Student("babiq",19,66.6);
System.out.println("排序前" +Arrays.toString(students));
Arrays.sort(students,new MarkComparator());
System.out.println("排序后" +Arrays.toString(students));
}
public static void main2(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student("balala",18,59.9);
Student student2 = new Student("acc",14,29.9);
MarkComparator markComparator = new MarkComparator();
int ret = markComparator.compare(student1,student2);
System.out.println(ret);
}
public static void main1(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student("balala",18,59.9);
Student student2 = new Student("acc",14,29.9);
if(student1.compareTo(student2) > 0){
System.out.println("student1 > student2");
}
}
}

abstract class Animal{
public String name;
public int age;
public abstract void eat();
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"name='" + name + ''' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
interface IFly{
void fly();
}
interface ISpeak{
void speak();
}
class Bird extends Animal implements IFly,ISpeak{
public int wing;
public Bird(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(name+" 正在吃虫子~");
}
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println(name+" 有翅膀的鸟在飞~~");
}
@Override
public void speak() {
System.out.println(name+" 在学人说话!");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal implements ISpeak{
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(name+" 在被无情的吃狗粮");
}
@Override
public void speak() {
System.out.println(name+" 在汪汪汪的大叫!!");
}
}
public class demo2{
public static void speak(ISpeak iSpeak){
iSpeak.speak();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
speak(new Dog("狗子",3));
speak(new Bird("小鸟",2));
}
public static void main1(String[] args) {
Bird bird = new Bird("lala",2);
bird.fly();
bird.eat();
bird.speak();
Dog dog = new Dog("狗子",3);
dog.eat();
dog.speak();
}
}























 2474
2474

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








