几种基础的排序算法
文章目录
一、冒泡排序BubbleSort
static void bubbleSort(int[] arr){
for(int i = 0;i<arr.length-1;i++){
for(int j = 0;j <arr.length-i-1;j++){
if(arr[j]>arr[j+1]){
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
二、快速排序QuickSort
基本思路:
- 将数组划分为两个子数组A[start,end-1] A[start+1,end],使得A[start]为大小居中的数,左侧都小于A[start],右侧都大于A[end],通过递归调用快速排序对子数组进行排序。
- 1.需要形参有开头start和结尾end
- 2.如果start < end就递归自己
- 3.把下标为0(也可以是其他下标)的值设为标准值
- 把开头和结束分别设置为低位(low)和高位(high)
- 4.当low<high时循环执行
- 1.(low<high时)高位的值大于标准值,把高位减一位,直到小于时把当前高位的值赋值给低位
- 2.(low<high时)低位的值小于标准值,把低位减一位,直到大于时把当前低位的值赋值给高位
- 5.执行完后此时的高位和低位相等,把标准值赋值给低位or高位的值
- (low<high时)保证高位一定等于低位出循环
- 6.此时的数组分为(low右边)大于标准值和(low左边)小于标准值
- 然后分两边递归调用自己
- 7.直到start >= end(low >= high)不会递归下去
具体实现:
static void QuickSort(int[] arr,int start,int end){
if(start < end){
int low = start;
int high = end;
int standard = arr[low];
while(low < high){
while(low < high && standard < arr[high])high--;
if(low < high)arr[low++] = arr[high];
while(low < high && standard > arr[low])low++;
if(low < high)arr[high--] = arr[low];
}
arr[low] = standard;
QuickSort(arr, start, low-1);
QuickSort(arr, low + 1,end);
}
}
三、基础版插入排序InsertSort
static void insertSort(int[] arr){
for(int i = 1;i<arr.length;i++){
int target = arr[i];
int j = i-1;
while(j>-1&&target<arr[j]){
arr[j+1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j+1] = target;
}
}
四、希尔排序ShellSort
基本思路:设定一个间隔值,分成一个个小的插入排序
static void ShellSort(int[] arr){
for(int interval = arr.length/2;interval>0;interval/=2){
for(int i = interval;i<arr.length;i++){
int target = arr[i];
int j = i-interval;
while(j>-1&&target<arr[j]){
arr[j+interval] = arr[j];
j -= interval;
}
arr[j+interval] = target;
}
}
}
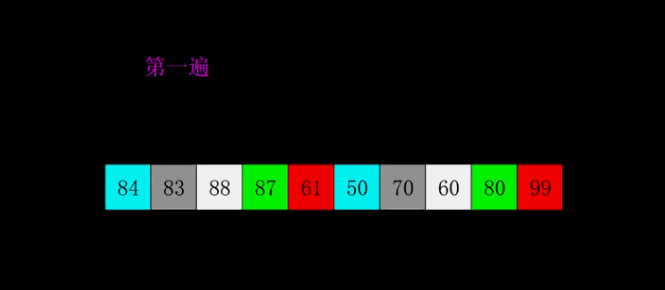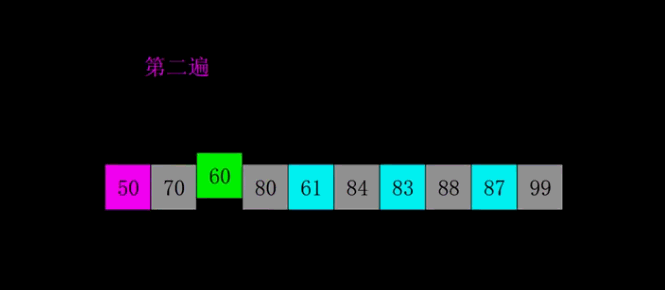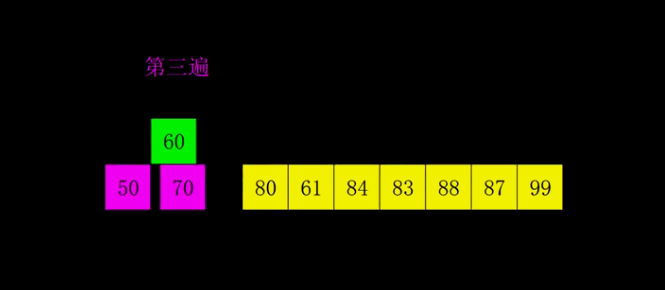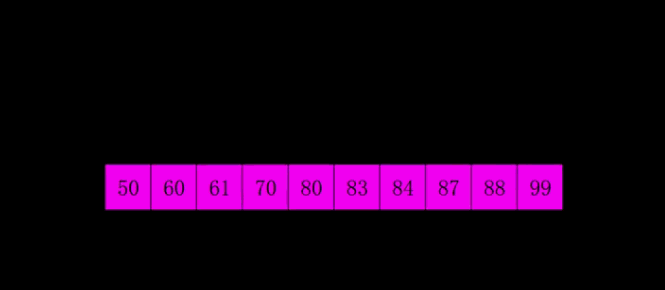
五、选择排序SelectSort
static void selectSort(int[] arr){
int min = 0;
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<arr.length;i++){
min = arr[i];
count = 0;
for(int j = i;j<arr.length-1;j++){
if(min>arr[j+1]){
min = arr[j+1];
count = j+1;
}
}
if(min == arr[i])continue;
int temp = arr[count];
arr[count] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
并查集
#include <bits\stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int pa[1000005];
int find(int x) {
int x_root = x;
while(x_root != pa[x_root]) {
//在find查询中嵌入一个路径压缩操作
pa[x_root]=pa[pa[x_root]];
//p元素不再选择原来的父亲节点,而是直接选择父亲节点的父亲节点来做为自己新的一个父亲节点
//这样的操作使得树的层数被压缩了
x_root=pa[x_root];//p压缩完毕后且p并不是根节点,p变成p新的父节点继续进行查找和压缩的同时操作
}
return x_root;
}
void merge(int x,int y)//推断x,y是否连通。若不连通。则使其连通。
{
int fx,fy;
fx=find(x);
fy=find(y);
if(fx!=fy)
pa[fx]=fy;
}
set<int> s;
int main() {
for(int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
pa[i] = i;
}
int n;
cin >> n;
int zong = 0;
while(n--) {
int t, x;
cin >> t;
cin >> x;
s.insert(x);
for(int i = 0; i < t - 1; i++) {
int k;
cin >> k;
s.insert(k);
merge(x, k);
}
}
int buluo = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= s.size(); i++) {
if(pa[i] == i) {
buluo++;
}
}
cout << s.size() <<" " << buluo <<endl;
int q;
cin >> q;
while(q--) {
int xx, yy;
cin >> xx >> yy;
if(find(xx) == find(yy)) {
cout << "Y" << endl;
} else {
cout <<"N" <<endl;
}
}
二分查找
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main{
static int BinarySearch(int a[],int x, int left, int right) {
while(left <= right) {
int mid = (left - right) / 2 + right;
if(a[mid] < x) {
left = mid + 1;
} else if (a[mid] > x) {
right = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = new int[10000];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
}
System.out.println(BinarySearch(arr,9,1,10));
System.out.println(Arrays.binarySearch(arr,9));
}
}
快速幂
public class Main{
static long fastpow(int a, int b) {
// 求 a 的 b 次方
long ans = 1;
while(b>=1) {
if((b & 1)>=1) ans *= a;
a *= a;
b >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int[] arr = new int[10000];
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
arr[i] = i;
}
System.out.println(fastpow(3,70));
}
}
全排列
public void Permutation(char chs[],int start )
{
if(start==chs.length-1)
{
Arrays.toString(chs);
//如果已经到了数组的最后一个元素,前面的元素已经排好,输出。
}
for(int i=start;i<=chs.length-1;i++)
{
//把第一个元素分别与后面的元素进行交换,递归的调用其子数组进行排序
Swap(chs,i,start);
Permutation(chs,start+1);
Swap(chs,i,start);
//子数组排序返回后要将第一个元素交换回来。
//如果不交换回来会出错,比如说第一次1、2交换,第一个位置为2,子数组排序返回后如果不将1、2
//交换回来第二次交换的时候就会将2、3交换,因此必须将1、2交换使1还是在第一个位置
}
}
public void Swap(char chs[],int i,int j)
{
char temp;
temp=chs[i];
chs[i]=chs[j];
chs[j]=temp;
}
DFS
全排列:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main{
static int n;
static boolean used[] = new boolean[10];
static int ans[] = new int[10];
static void dfs(int u){
if(u == n+1){
for (int i = 1; i <=n ; i++) {
System.out.print(ans[i]);
}
System.out.println();
return;
}
for (int i = 1; i <=n; i++) {
if(!used[i]){
ans[u] = i;
used[i] = true;
dfs(u+1);
used[i] = false;//回溯
}
}
return;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
n = input.nextInt();
dfs(1);
}
}
模板:
void dfs()//参数用来表示状态
{
if(到达终点状态)
{
...//根据题意添加
return;
}
if(越界或者是不合法状态)
return;
if(特殊状态)//剪枝
return ;
for(扩展方式)
{
if(扩展方式所达到状态合法)
{
修改操作;//根据题意来添加
标记;
dfs();
(还原标记);
//是否还原标记根据题意
//如果加上(还原标记)就是 回溯法
}
}
}
n;
}
if(越界或者是不合法状态)
return;
if(特殊状态)//剪枝
return ;
for(扩展方式)
{
if(扩展方式所达到状态合法)
{
修改操作;//根据题意来添加
标记;
dfs();
(还原标记);
//是否还原标记根据题意
//如果加上(还原标记)就是 回溯法
}
}
}


























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










