尚硅谷课堂笔记:
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1BPdI_vDWW2M-1A0okF3Pww 提取码: 2333
视频的代码笔记和资料。
老师笔记中的某些内容不再赘叙
此笔记 针对以上笔记为基础 添加补充
主要目的为针对自己复习学习
AOP

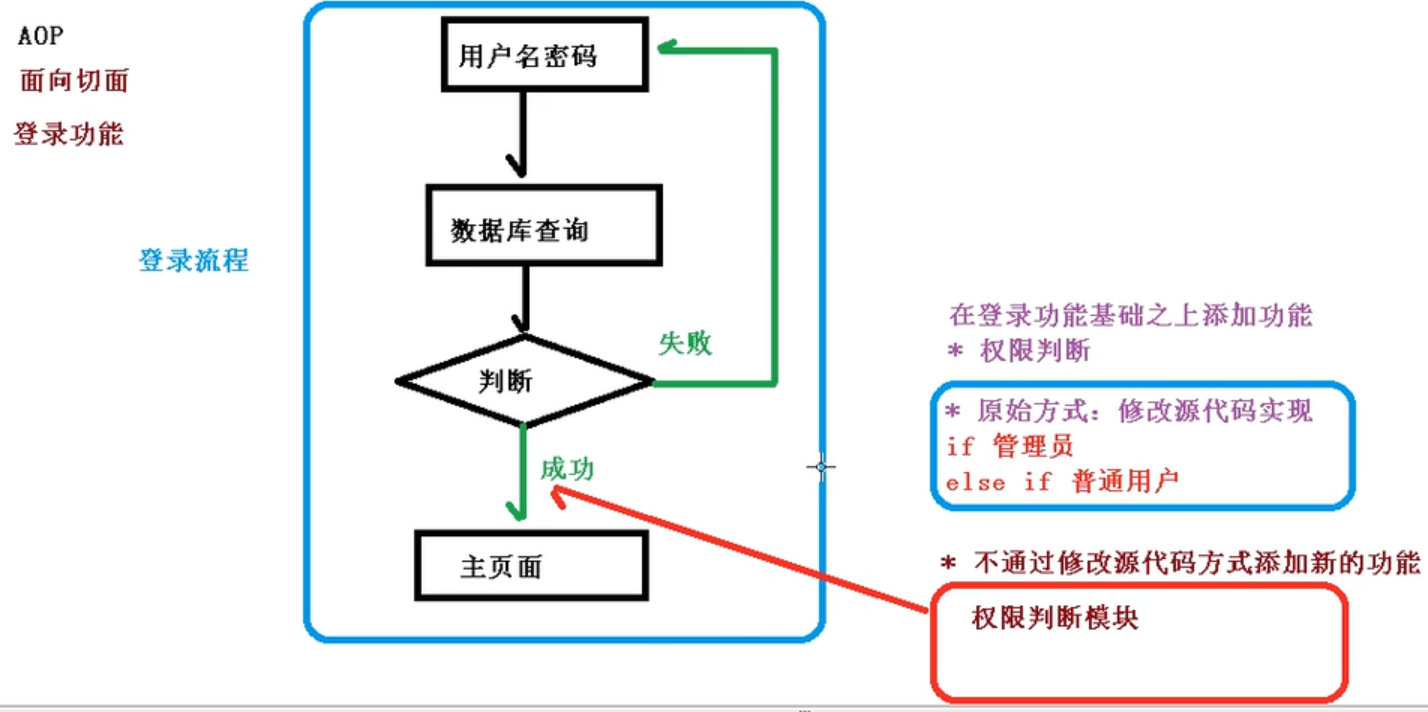
1.AOP底层原理
底层使用了 动态代理
知识补充: 静态代理,动态代理
代理类和被代理类实现同一个接口
静态代理
-
代理类 和 被代理类 编译期间已经确定下来啦
interface ClothFactory{ void produceCloth(); } //代理类 class ProxyClothFactory implements ClothFactory{ private ClothFactory factory;//用被代理类进行实例化 public ProxyClothFactory(ClothFactory factory) { this.factory = factory; } @Override public void produceCloth() { System.out.println("代理工厂准备工作代码"); factory.produceCloth(); System.out.println("代理工厂后续结尾代码"); } } //被代理类对象 class NikeClothFactory implements ClothFactory{ @Override public void produceCloth() { System.out.println("Nike工厂生产衣服"); } } public class StaticProxyTest { public static void main(String[] args) { NikeClothFactory nikeCloth = new NikeClothFactory(); ProxyClothFactory proxyClothFactory = new ProxyClothFactory(nikeCloth); proxyClothFactory.produceCloth(); //代理工厂准备工作代码 //Nike工厂生产衣服 //代理工厂后续结尾代码 } }动态代理

interface Human{
String getBelief();
void eat(String food);
}
//被代理类
class SuperMan implements Human{
@Override
public String getBelief() {
return "I believe I can fly!";
}
@Override
public void eat(String food) {
System.out.println("我喜欢吃"+food);
}
}
class proxyFactory{
// obj 就是创建的被代理的对象
//调用这个方法解决问题1
public static Object getProxyInstance(Object obj){
MyInvocationHandler handler = new MyInvocationHandler();
handler.bind(obj);
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(obj.getClass().getClassLoader(), obj.getClass().getInterfaces(),handler);
}
}
//匿名内部类也可以
class MyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler{
private Object obj;//需要使用被代理类的对象进行赋值
public void bind(Object obj){
this.obj =obj;
}
//当我们通过代理类的对象,调用方法a时,就会自动的调用如下的方法: invoke()
//里面已经封装好了 比如调eat方法时 会调用下面这个invoke方法
//这步很关键,那个参数是接口,接口无法实例化,通过它的实现类来实例化,实现类的对象“替代”了这个参数,多态的思想
/**
*
* @param proxy 就是上面那个getProxyInstance返回的对象
* @param method 代理类调的哪个方法 就是哪个方法(应该是被代理类的方法)
* @param args
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
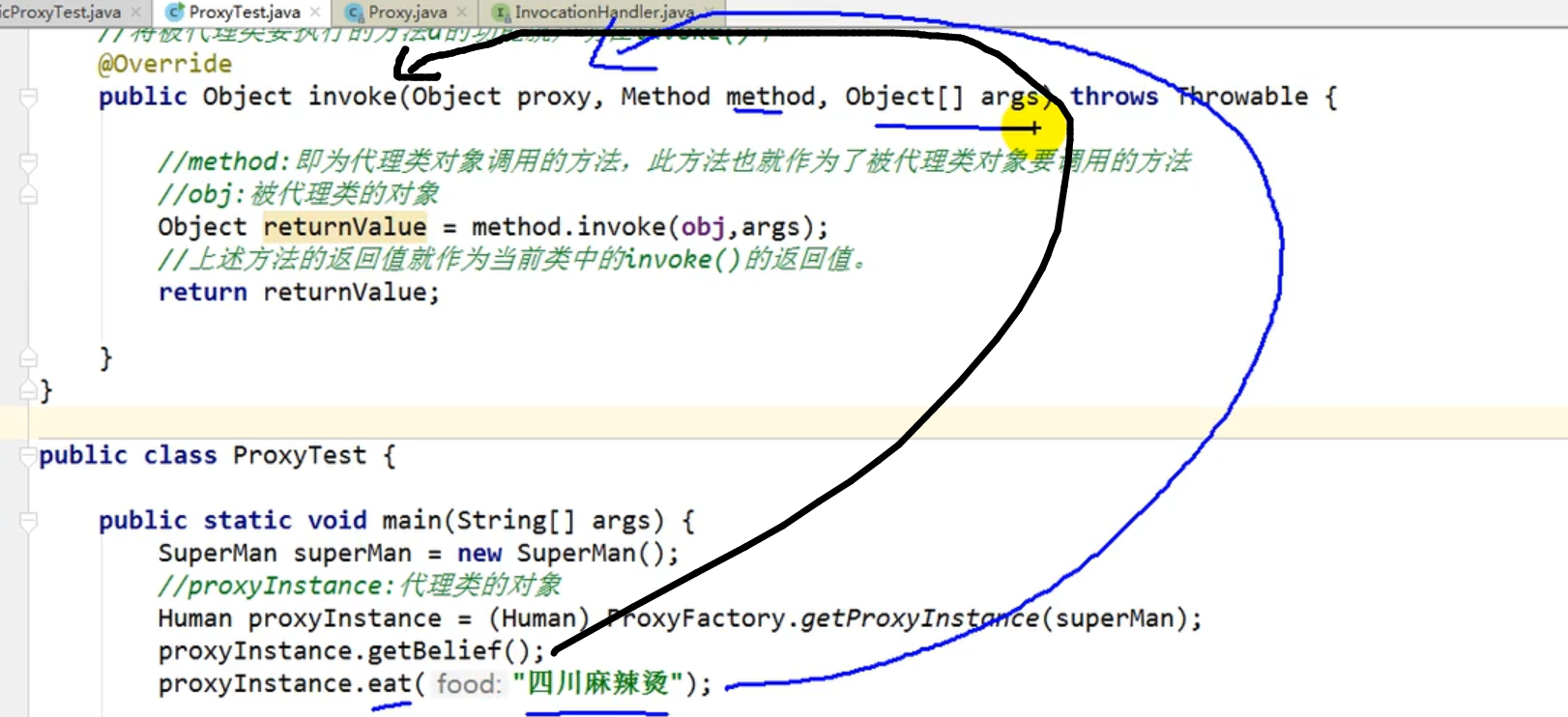
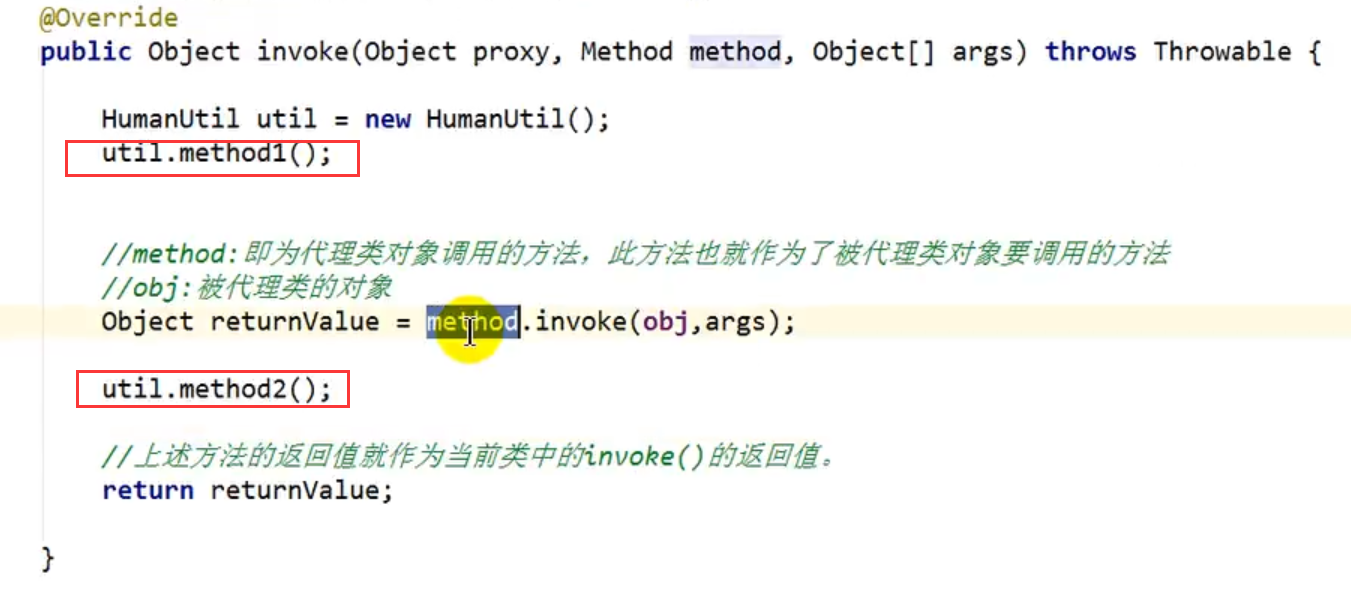
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//method:即为代理类对象调用的方法,此方法也就作为了被代理类对象要调用的方法
Object returnValue = method.invoke(obj, args);
//上述方法的返回值
return returnValue;
}
}
public class ProxyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SuperMan superMan = new SuperMan();
Human proxyInstance = (Human) ProxyFactory.getProxyInstance(superMan);
System.out.println(proxyInstance.getBelief());
proxyInstance.eat("麻辣烫");
System.out.println("-------------------------");
//动态性
ClothFactory proxyInstance1 = (ClothFactory) ProxyFactory.getProxyInstance(new NikeClothFactory());
proxyInstance1.produceCloth();
}
}
知识补充完毕
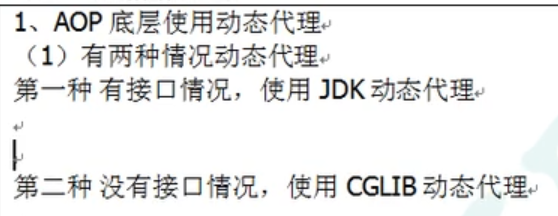
有接口的情况
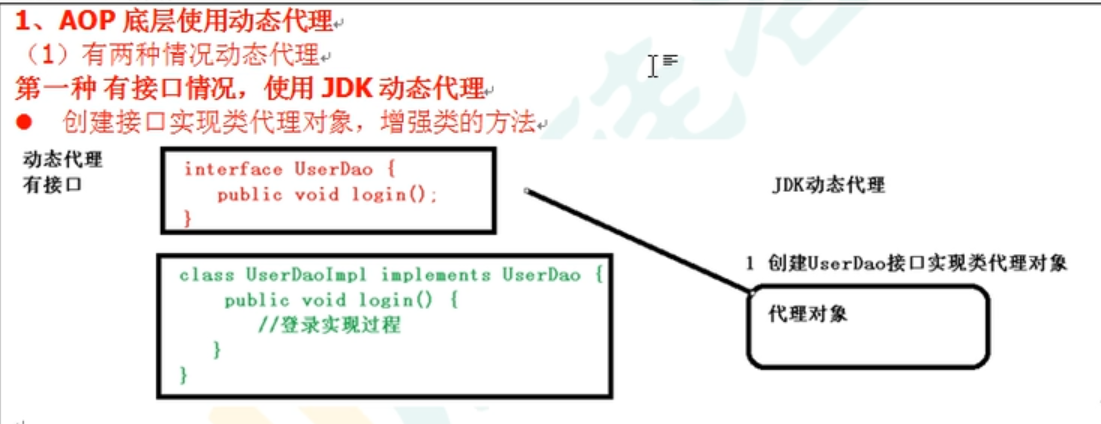

代码参考上面知识补充的即可
你调的是什么方法 就会增强什么方法
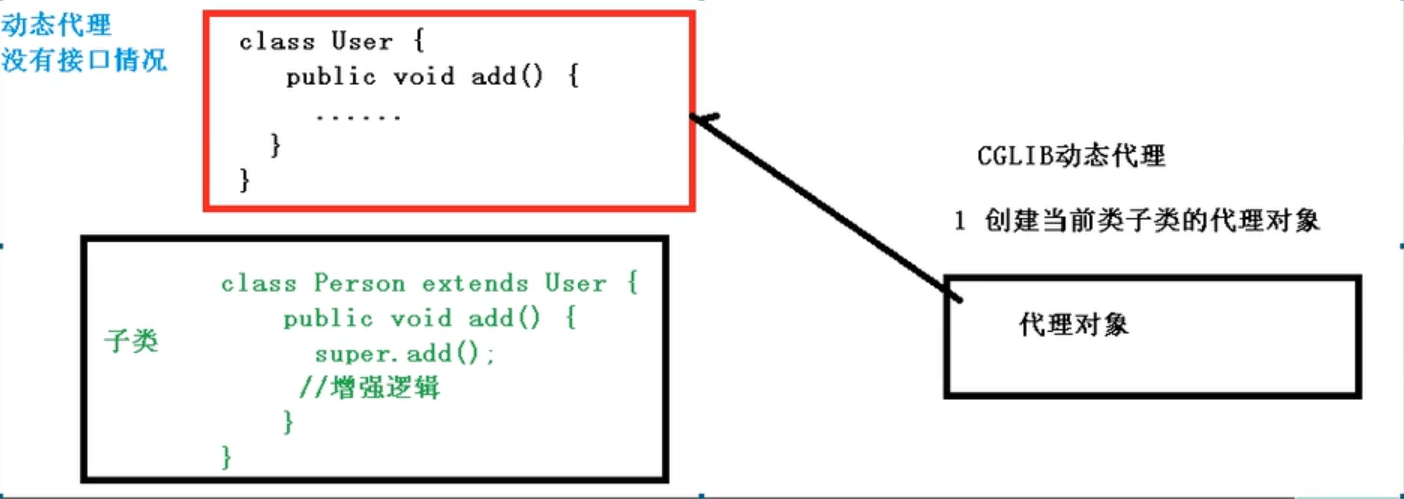
没有接口的情况
原始方法,利用子类继承发展功能

2.AOP操作的术语
- 连接点:可以被增强的方法;
- 切入点:实际被增强的方法
- 通知:增强的功能
- 切面: 是一个动作

3.AOP操作—准备


AOP相关依赖:
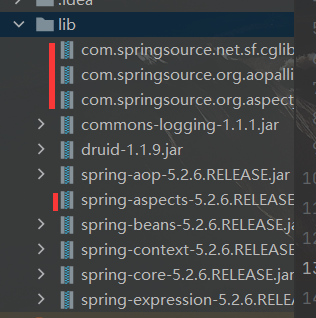
maven : spring-boot-starter-aop
4.切入点表达式



修饰符可以以省略,返回值不能省
*代表 任意返回类型
5.注解操作


对应的注解 在配置类上写 @EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Configuration //当前类作为配置类
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.company"})
//@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解等同于在xml中配置aspectj-autoproxy,表示开启spring对注解AOP的支持
//ture表示使用cglib代理 默认false表示用jdk代理 没接口应该使用cglib但是我的类测试false也行 可能高版本自己选择了
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class SpringConfig {
}

@Component
@Aspect
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class UserProxy {
@Before(value = "execution(* com.company.Spring5.AOP.Anno.User.add(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("Before...");
}
// 最终通知 不管有没有异常
@After("execution(* com.company.Spring5.AOP.Anno.User.add(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("After...");
}
//返回通知(后置通知) afterreturning只有正常返回才会执行, 发生异常不执行
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.company.Spring5.AOP.Anno.User.add(..))")
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("afterReturning...");
}
//异常通知 发生异常后执行
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.company.Spring5.AOP.Anno.User.add(..))")
public void afterThrowing(){
System.out.println("AfterThrowing...");
}
//环绕通知
@Around("execution(* com.company.Spring5.AOP.Anno.User.add(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("Around前...");
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
//发生异常后不执行 Around后
System.out.println("Around后...");
}
}
//被增强的类
@Component
public class User {
public void add(){
System.out.println("add...");
}
}
Around前…
Before…
add…
Around后…
After…
afterReturning…
这里方法里面的…代表适配所有方法,实际上参数是用来区分重载方法的
6.公共切入点提取
//相同切入点抽取
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.company.Spring5.AOP.Anno.User.add(..))")
public void pointDemo() {
}
@Before(value = "pointDemo")
public void before(){
System.out.println("Before...");
}
7.多个增强类对同一个类进行了增强 设置优先级

0开始
Before 永远在After前面
8.xml操作(了解)























 4574
4574

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








