虽然要写这篇文章,但是有些地方仍然没有了解,比如对TimeBank-Dense。因为以后没有用这个语料的可能性,所以就直接忽略了。
这篇论文是2017ACL上的一篇短文,作者为来自日本国立情报学研究所的Fei Cheng和Yusuke Miyao。
在引言部分,作者介绍了这篇论文的任务。时间关系抽取主要是判别时间实体对之间是否存在某种关系。实体有两种,events和temporal expressions。能组成关系的有event-event(E-E), event-time(E-T)和event-DCT(document creation time, E-D)。论文在没有利用外部知识和人工标注的实体属性的情况下取得了较好的性能。
在方法部分,作者介绍了跨句子在语料中所占比例还是很大的,并且因为作者采用了基于依存路径的输入,一般依存路径都是以一句话为单位的,所以如何表示跨句子实体间的依存路径是一个挺大的障碍。于是了作者假设两个相邻的句子共享一个“common root”,这样就可以表示了,具体如下图所示: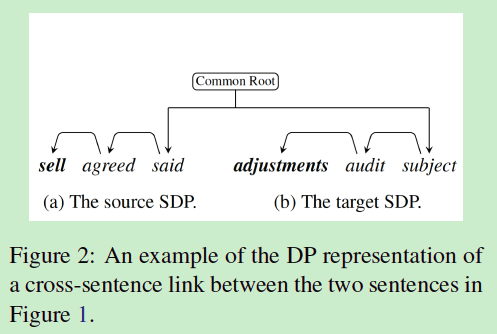
从这个图可以很清楚的看出,首先两个句子都表示为依存路径,然后共享一个“common root”。这样就成功解决了跨句子的问题。依存路径由Stanford CoreNLP工具进行解析得到。输入的词向量为词向量、词性向量和依存关系向量的拼接。
E-E,E-T使用同一个分类器,从源目标词到common root和从目的目标词到common root各自使用一个双向的LSTM。E-D包含一个事件依存路径分支,只使用了一个分支的双向LSTM。具体看下图就能了解: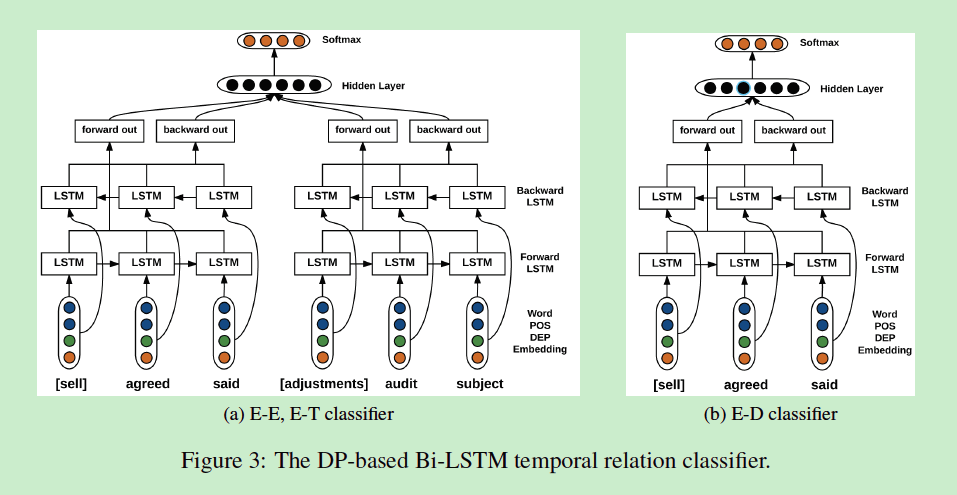
实验部分没详细了解,这也是前面我说的没有了解的地方。以后有机会去做的话还是需要认真了解的。
这篇论文的介绍到这里就结束了,如有理解错误的地方,欢迎批评指正。




 本文介绍了一种在跨句子场景下进行时间关系抽取的方法,该方法由日本国立情报学研究所的Fei Cheng和Yusuke Miyao提出。通过引入‘common root’概念,解决了基于依存路径表示的跨句实体间关系抽取难题。实验未详细探讨,但论文在不依赖外部知识和人工标注实体属性的情况下,取得了良好效果。
本文介绍了一种在跨句子场景下进行时间关系抽取的方法,该方法由日本国立情报学研究所的Fei Cheng和Yusuke Miyao提出。通过引入‘common root’概念,解决了基于依存路径表示的跨句实体间关系抽取难题。实验未详细探讨,但论文在不依赖外部知识和人工标注实体属性的情况下,取得了良好效果。

















 950
950

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








