cp16_Model Sequential_Output_Hidden_Recurrent NNs_LSTM_aclImdb_IMDb_Embed_token_py_function_GRU_Gate:
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/Linli522362242/article/details/113846940
from tensorflow.keras.layers import GRU
model = Sequential()
model.add( Embedding(10000,32) )
model.add( GRU(32, return_sequences=True) )
model.add( GRU(32) )
model.add(Dense(1))
model.summary()
Building an RNN model for the sentiment analysis task
Since we have very long sequences, we are going to use an LSTM(Long short-term memory) layer to account for long-term effects. In addition, we will put the LSTM layer inside a Bidirectional([ˌbaɪdɪˈrɛkʃənəl]双向的) wrapper, which will make the recurrent layers pass through the input sequences from both directions, start to end, as well as the reverse direction:
A Bidirectional LSTM, or biLSTM, is a sequence processing model that consists of two LSTMs: one taking the input in a forward direction, and the other in a backwards direction. BiLSTMs effectively increase the amount of information available to the network, improving the context available to the algorithm (e.g. knowing what words immediately follow and precede a word in a sentence)
Bidirectional layer wrapper provides the implementation of Bidirectional LSTMs in Keras
tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(
layer, merge_mode="concat", weights=None, backward_layer=None, **kwargs
)Bidirectional wrapper for RNNs.
Arguments
- layer:
keras.layers.RNNinstance, such askeras.layers.LSTMorkeras.layers.GRU. It could also be akeras.layers.Layerinstance that meets the following criteria:- Be a sequence-processing layer (accepts 3D+ inputs).
- Have a
go_backwards,return_sequencesandreturn_stateattribute (with the same semantics as for theRNNclass). - Have an
input_specattribute. - Implement serialization via
get_config()andfrom_config(). Note that the recommended way to create new RNN layers is to write a custom RNN cell and use it withkeras.layers.RNN, instead of subclassingkeras.layers.Layerdirectly.
- merge_mode: Mode by which outputs of the forward and backward RNNs will be combined. One of {'sum', 'mul', 'concat', 'ave', None}. If None, the outputs will not be combined, they will be returned as a list. Default value is 'concat'.
- backward_layer: Optional
keras.layers.RNN, orkeras.layers.Layerinstance to be used to handle backwards input processing. Ifbackward_layeris not provided, the layer instance passed as thelayerargument will be used to generate the backward layer automatically. Note that the providedbackward_layerlayer should have properties matching those of thelayerargument, in particular it should have the same values forstateful,return_states,return_sequence, etc. In addition,backward_layerandlayershould have differentgo_backwardsargument values. AValueErrorwill be raised if these requirements are not met
It takes a recurrent layer (first LSTM layer) as an argument and you can also specify the merge mode, that describes how forward and backward outputs should be merged before being passed on to the coming layer. The options are:
– ‘sum‘: The results are added together.
– ‘mul‘: The results are multiplied together.
– ‘concat‘(the default): The results are concatenated together ,providing double the number of outputs to the next layer.
– ‘ave‘: The average of the results is taken.
###################
embedding_dim:

###################
embedding_dim = 20
vocab_size = len( token_counts ) + 2 # Vocab-size: 87007
tf.random.set_seed(1)
# build the model
bi_lstm_model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(
input_dim = vocab_size, # n+2
output_dim = embedding_dim, #use a vector of length=embedding_dim to represent each word
name = 'embed-layer'
),# Output Shape ==> (None_batch_size, None_each_input_length, output_dim=20)
tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(
# lstm-layer:
# return_sequences=False == many-to-one: (None_each_input_length, output_dim=64)==>(64)
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64, name='lstm-layer'),
name = 'bidir-lstm', # default merge_mode='concat' ==> (64)==>(128)
),# Output Shape ==> (None_batch_size, output_dim=128)
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
bi_lstm_model.summary()(None_batch_size, None_each_input_length, output_dim=20) ==>2 x LSTM(return_sequences=False) ==> 2x (None_batch_size, output_dim=64)==>2x(64) ==>Bidirectional(merge_mode='concat') ==>(128)


# compile and train:
bi_lstm_model.compile(
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-3),
loss = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy( from_logits=False),
metrics=['accuracy']
)
history = bi_lstm_model.fit(
train_data,
validation_data = valid_data,
epochs=10
)# compile and train:
bi_lstm_model.compile(
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-3),
loss = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy( from_logits=False),
metrics=['accuracy']
)
history = bi_lstm_model.fit(
train_data,
validation_data = valid_data,
epochs=10
)... ...
##################################################################since my computer runs previous code very slowly, so I use colab
Left figure is from colab without gpu, right figure is from my computer

colab with gpu
 ==>
==>
!pip install -U -q PyDrive
from pydrive.auth import GoogleAuth
from pydrive.drive import GoogleDrive
from google.colab import auth
from oauth2client.client import GoogleCredentials
# Authenticate and create the PyDrive client.
auth.authenticate_user()
gauth = GoogleAuth()
gauth.credentials = GoogleCredentials.get_application_default()
drive = GoogleDrive(gauth)
##############################################
link : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gClJCGP-l3Byp2y1p6lEGbq3q2rIKMZg/view?usp=sharing
OR https://github.com/rasbt/python-machine-learning-book-3rd-edition/blob/master/ch08/movie_data.csv.gz
!wget https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gClJCGP-l3Byp2y1p6lEGbq3q2rIKMZg/view?usp=sharing so, I use following code
so, I use following code
!pip install PyDrive googledrivedownloader
from google_drive_downloader import GoogleDriveDownloader
link='https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gClJCGP-l3Byp2y1p6lEGbq3q2rIKMZg/view?usp=sharing'
GoogleDriveDownloader.download_file_from_google_drive(file_id=link,
dest_path="./movie_data.csv.gz",
unzip=True)
Unzipping...
/usr/local/lib/python3.7/dist-packages/google_drive_downloader/google_drive_downloader.py:78: UserWarning: Ignoring `unzip` since "https://drive.google.com/file/d/1gClJCGP-l3Byp2y1p6lEGbq3q2rIKMZg/view?usp=sharing" does not look like a valid zip file warnings.warn('Ignoring `unzip` since "{}" does not look like a valid zip file'.format(file_id))
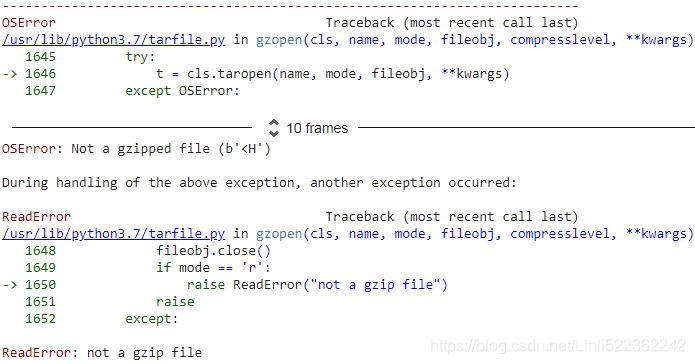
import tarfile
if not os.path.isdir('movie_data.csv'):
with tarfile.open('movie_data.csv.gz', 'r:gz') as tar:
tar.extractall()ReadError: not a gzip file
import os
import gzip
import shutil
import pandas as pd
with gzip.open('movie_data.csv.gz', 'rb') as f_in, open ('movie_data.csv', 'wb') as f_out:
shutil.copyfileobj(f_in, f_out)
##############################################
Solution : download the movie_data.csv.gz file then upzip it by using your tools(e.g. WinRAR or 7zip), upload to google drive

link = 'https://drive.google.com/file/d/17AYKouLCv7oOxloZ52COW0kEpVLRZikS/view?usp=sharing'
import pandas as pd
# to get the id part of the file
# link.split("/")
# ['https:',
# '',
# 'drive.google.com',
# 'file',
# 'd',
# '17AYKouLCv7oOxloZ52COW0kEpVLRZikS',
# 'view?usp=sharing']
id = link.split("/")[-2] #==>'17AYKouLCv7oOxloZ52COW0kEpVLRZikS'
downloaded = drive.CreateFile({'id':id})
downloaded.GetContentFile('movie_data.csv')
df = pd.read_csv('movie_data.csv', encoding='utf-8')
df.tail()
import tensorflow as tf
# Step 1: Create a dataset
target = df.pop('sentiment') #series # key: [value_list]
ds_raw = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(
(df.values, # array([ [...string...], [...string...], ...]
target.values)
)# <TensorSliceDataset shapes: ((1,), ()), types: (tf.string, tf.int64)>
## inspection:
for item in ds_raw.take(3):
# item[0].numpy() : array([...string...])
tf.print( item[0].numpy()[0][:50], item[1] )![]()
A -- An alternative way to get the dataset: using tensorflow_datasets
imdb_bldr = tfds.builder('imdb_reviews')
print(imdb_bldr.info)
imdb_bldr.download_and_prepare()
datasets = imdb_bldr.as_dataset(shuffle_files=False)
datasets.keys()
imdb_test = datasets['test'] # 25000,
imdb_train_valid = datasets['train'] # 25000,
# ## inspection:
for item in imdb_train_valid.take(1):
tf.print( item ) 
prefetchDataset
imdb_test = datasets['test'] # 25000,
imdb_train_valid = datasets['train'] # 25000,
# tf.random.set_seed(1)
# ds_raw = imdb_train_valid.take(25000).shuffle(
# 25000, reshuffle_each_iteration=False
# ) # 25000 <== 0~24999
def transform_prefetchDataset(prefetchDataset):
textList=[]
labelList=[]
for example in prefetchDataset:
textList.append( example['text'].numpy() )
labelList.append( example['label'].numpy() )
textArr=np.array(textList)
labelArr=np.array(labelList)
return tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices( ( textArr[..., np.newaxis],
labelArr
) )
ds_raw_train_valid = transform_prefetchDataset(imdb_train_valid)
ds_raw_test = transform_prefetchDataset(imdb_test)
ds_raw_train = ds_raw_train_valid.take(20000)
ds_raw_valid = ds_raw_train_valid.skip(20000)
# ## inspection:
for item in ds_raw_train.take(3):
tf.print( item[0].numpy()[0][:50], item[1] )![]()
###############################################
tf.random.set_seed(1)
ds_raw = ds_raw.shuffle(
50000, reshuffle_each_iteration=False
) # 50000 <== 0~49999
ds_raw_test = ds_raw.take(25000)
ds_raw_train_valid = ds_raw.skip(25000)
ds_raw_train = ds_raw_train_valid.take(20000)
ds_raw_valid = ds_raw_train_valid.skip(20000)
# Step 2: find unique tokens (words)
from collections import Counter
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
token_counts = Counter()
tokenizer = tfds.features.text.Tokenizer() ##########################
for example in ds_raw_train:
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(example[0].numpy()[0])#numpy()[0] get first element in arr
token_counts.update(tokens)
print('Vocab-size:', len(token_counts))
AttributeError: module 'tensorflow_datasets.core.features' has no attribute 'text'
###############################################
solutions: tokenizer = tfds.deprecated.text.Tokenizer()
tf.random.set_seed(1)
ds_raw = ds_raw.shuffle(
50000, reshuffle_each_iteration=False
) # 50000 <== 0~49999
ds_raw_test = ds_raw.take(25000)
ds_raw_train_valid = ds_raw.skip(25000)
ds_raw_train = ds_raw_train_valid.take(20000)
ds_raw_valid = ds_raw_train_valid.skip(20000)
# Step 2: find unique tokens (words)
from collections import Counter
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
token_counts = Counter()
tokenizer = tfds.deprecated.text.Tokenizer()
for example in ds_raw_train:
tokens = tokenizer.tokenize(example[0].numpy()[0])#numpy()[0] get first element in arr
token_counts.update(tokens)
print('Vocab-size:', len(token_counts))![]() is different with Vocab-size: 87007, since I take data from buffer twice.
is different with Vocab-size: 87007, since I take data from buffer twice.
solutions: re-run your code from link = 'https://drive.google.com/file/d/17AYKouLCv7oOxloZ52COW0kEpVLRZikS/view?usp=sharing'![]()
# Step 3: encoding each unique token into integers
######encoder = tfds.features.text.TokenTextEncoder( token_counts )
encoder = tfds.deprecated.text.TokenTextEncoder( token_counts )
# Step 3-A: define the function for transformation
# function will treat the input tensors as if the eager execution mode is enabled
def encode(text_tensor, label):
text = text_tensor.numpy()[0]
encoded_text = encoder.encode(text) # encoder = tfds.features.text.TokenTextEncoder( token_counts )
return encoded_text, label
# Step 3-B: wrap the encode function to a TF Op that executes it eagerly
def encode_map_fn( text, label ):
return tf.py_function( encode, inp=[text, label],
Tout=(tf.int64, tf.int64))
ds_train = ds_raw_train.map( encode_map_fn ) # during mapping: the eager execution will be disabled
ds_valid = ds_raw_valid.map( encode_map_fn ) # so wrap the encode function to a TF operator that executes it eagerly
ds_test = ds_raw_test.map( encode_map_fn )
tf.random.set_seed(1)
for example in ds_train.shuffle(1000).take(5):
print('Sequence length:', example[0].shape)
example
# batching the datasets
train_data = ds_train.padded_batch(
32, padded_shapes=([-1], # batch_size, here is 32
[]) # unset, all dimensions of all components are padded to the maximum size in the batch
)
valid_data = ds_valid.padded_batch(
32, padded_shapes=([-1],
[])
)
test_data = ds_test.padded_batch(
32, padded_shapes=([-1],
[])
)
from tensorflow.keras import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Embedding
from tensorflow.keras.layers import SimpleRNN
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense
embedding_dim = 20
vocab_size = len( token_counts ) + 2 # Vocab-size: 87007
tf.random.set_seed(1)
# build the model
bi_lstm_model = tf.keras.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Embedding(
input_dim = vocab_size, # n+2
output_dim = embedding_dim, #use a vector of length=embedding_dim to represent each word
name = 'embed-layer'
),# Output Shape ==> (None_batch_size, None_each_input_length, output_dim=20)
tf.keras.layers.Bidirectional(
# lstm-layer:
# return_sequences=False == many-to-one: (None_each_input_length, output_dim=64)==>(64)
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(64, name='lstm-layer'),
name = 'bidir-lstm', # default merge_mode='concat' ==> (64)==>(128)
),# Output Shape ==> (None_batch_size, output_dim=128)
tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
])
bi_lstm_model.summary() 
# compile and train:
bi_lstm_model.compile(
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-3),
loss = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy( from_logits=False),
metrics=['accuracy']
)
history = bi_lstm_model.fit(
train_data,
validation_data = valid_data,
epochs=10
)
# evaluate on the test data
test_results = bi_lstm_model.evaluate( test_data )
print( 'Test Acc.: {:.2f}%'.format(test_results[1]*100) ) ![]()
After training this model for 10 epochs, evaluation on the test data shows 82 percent accuracy. (Note that this result is not the best when compared to the state-of-the-art
methods used on the IMDb dataset. The goal was simply to show how RNN works.)
# if not os.path.exists('models'):
# os.mkdir('models')
!mkdir models
bi_lstm_model.save('models/Birdir-LSTM-full-length-seq.h5')
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/gdrive') ==>
==>





 本文介绍了RNN及LSTM在情感分析任务中的应用,并实现了一个完整的文本生成项目。此外,还深入探讨了Transformer模型及其核心机制——自注意力机制。
本文介绍了RNN及LSTM在情感分析任务中的应用,并实现了一个完整的文本生成项目。此外,还深入探讨了Transformer模型及其核心机制——自注意力机制。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 813
813

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










