// SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0-only
// Copyright (c) 2024 MediaTek Inc.
/*
* virtio transport for vsock
*
* Copyright (C) 2013-2015 Red Hat, Inc.
* Author: Asias He <asias@redhat.com>
* Stefan Hajnoczi <stefanha@redhat.com>
*
* Some of the code is take from Gerd Hoffmann <kraxel@redhat.com>'s
* early virtio-vsock proof-of-concept bits.
*/
#include <linux/spinlock.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/atomic.h>
#include <linux/virtio.h>
#include <linux/virtio_ids.h>
#include <linux/virtio_config.h>
#include <linux/virtio_vsock.h>
#include <linux/of_irq.h>
#include <net/sock.h>
#include <linux/mutex.h>
#include <net/af_vsock.h>
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <uapi/linux/sched/types.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/kthread.h>
static struct workqueue_struct *virtio_vsock_workqueue;
static struct virtio_vsock __rcu *the_virtio_vsock;
static DEFINE_MUTEX(the_virtio_vsock_mutex); /* protects the_virtio_vsock */
static struct virtio_transport virtio_transport; /* forward declaration */
struct virtio_vsock {
struct virtio_device *vdev;
struct virtqueue *vqs[VSOCK_VQ_MAX];
/* Virtqueue processing is deferred to a workqueue */
struct work_struct tx_work;
struct work_struct rx_work;
struct work_struct event_work;
/* The following fields are protected by tx_lock. vqs[VSOCK_VQ_TX]
* must be accessed with tx_lock held.
*/
struct mutex tx_lock;
bool tx_run;
struct work_struct send_pkt_work;
spinlock_t send_pkt_list_lock;
struct list_head send_pkt_list;
atomic_t queued_replies;
/* The following fields are protected by rx_lock. vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX]
* must be accessed with rx_lock held.
*/
struct mutex rx_lock;
bool rx_run;
int rx_buf_nr;
int rx_buf_max_nr;
/* The following fields are protected by event_lock.
* vqs[VSOCK_VQ_EVENT] must be accessed with event_lock held.
*/
struct mutex event_lock;
bool event_run;
struct virtio_vsock_event event_list[8];
u32 guest_cid;
bool seqpacket_allow;
int num_hwirq_vq;
int kick_irq[VSOCK_VQ_MAX];
int notify_irq[VSOCK_VQ_MAX];
};
#include <linux/arm-smccc.h>
#define SMC_FC_NBL_VHM_REQ 0xB4000100
#define SMC_HYP_SECURE_ID 1 /* SMC call for hypervisor */
static void virtio_vsock_hw_irq_notify(uint32_t irq)
{
struct arm_smccc_res res;
unsigned long r7 = SMC_HYP_SECURE_ID << 16;
arm_smccc_smc(SMC_FC_NBL_VHM_REQ, 0, irq, 0, 0, 0, 0, r7, &res);
}
static void virtio_vsock_notify(struct virtio_vsock *vsock, int qidx) {
struct virtqueue *vq = vsock->vqs[qidx];
int notify_irq = vsock->notify_irq[qidx];
if (notify_irq) {
if (virtqueue_kick_prepare(vq))
virtio_vsock_hw_irq_notify(notify_irq);
} else {
virtqueue_kick(vq);
}
}
static u32 virtio_transport_get_local_cid(void)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock;
u32 ret;
rcu_read_lock();
vsock = rcu_dereference(the_virtio_vsock);
if (!vsock) {
ret = VMADDR_CID_ANY;
goto out_rcu;
}
ret = vsock->guest_cid;
out_rcu:
rcu_read_unlock();
return ret;
}
static void
virtio_transport_send_pkt_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock =
container_of(work, struct virtio_vsock, send_pkt_work);
struct virtqueue *vq;
bool added = false;
bool restart_rx = false;
mutex_lock(&vsock->tx_lock);
if (!vsock->tx_run)
goto out;
vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_TX];
for (;;) {
struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt;
struct scatterlist hdr, buf, *sgs[2];
int ret, in_sg = 0, out_sg = 0;
bool reply;
spin_lock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
if (list_empty(&vsock->send_pkt_list)) {
spin_unlock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
break;
}
pkt = list_first_entry(&vsock->send_pkt_list,
struct virtio_vsock_pkt, list);
list_del_init(&pkt->list);
spin_unlock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
virtio_transport_deliver_tap_pkt(pkt);
reply = pkt->reply;
sg_init_one(&hdr, &pkt->hdr, sizeof(pkt->hdr));
sgs[out_sg++] = &hdr;
if (pkt->buf) {
sg_init_one(&buf, pkt->buf, pkt->len);
sgs[out_sg++] = &buf;
}
ret = virtqueue_add_sgs(vq, sgs, out_sg, in_sg, pkt, GFP_KERNEL);
/* Usually this means that there is no more space available in
* the vq
*/
if (ret < 0) {
spin_lock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
list_add(&pkt->list, &vsock->send_pkt_list);
spin_unlock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
break;
}
if (reply) {
struct virtqueue *rx_vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX];
int val;
val = atomic_dec_return(&vsock->queued_replies);
/* Do we now have resources to resume rx processing? */
if (val + 1 == virtqueue_get_vring_size(rx_vq))
restart_rx = true;
}
added = true;
}
if (added)
virtio_vsock_notify(vsock, VSOCK_VQ_TX);
out:
mutex_unlock(&vsock->tx_lock);
if (restart_rx)
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->rx_work);
}
static int
virtio_transport_send_pkt(struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock;
int len = pkt->len;
rcu_read_lock();
vsock = rcu_dereference(the_virtio_vsock);
if (!vsock) {
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
len = -ENODEV;
goto out_rcu;
}
if (le64_to_cpu(pkt->hdr.dst_cid) == vsock->guest_cid) {
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
len = -ENODEV;
goto out_rcu;
}
if (pkt->reply)
atomic_inc(&vsock->queued_replies);
spin_lock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
list_add_tail(&pkt->list, &vsock->send_pkt_list);
spin_unlock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->send_pkt_work);
out_rcu:
rcu_read_unlock();
return len;
}
static int
virtio_transport_cancel_pkt(struct vsock_sock *vsk)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock;
struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt, *n;
int cnt = 0, ret;
LIST_HEAD(freeme);
rcu_read_lock();
vsock = rcu_dereference(the_virtio_vsock);
if (!vsock) {
ret = -ENODEV;
goto out_rcu;
}
spin_lock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
list_for_each_entry_safe(pkt, n, &vsock->send_pkt_list, list) {
if (pkt->vsk != vsk)
continue;
list_move(&pkt->list, &freeme);
}
spin_unlock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
list_for_each_entry_safe(pkt, n, &freeme, list) {
if (pkt->reply)
cnt++;
list_del(&pkt->list);
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
}
if (cnt) {
struct virtqueue *rx_vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX];
int new_cnt;
new_cnt = atomic_sub_return(cnt, &vsock->queued_replies);
if (new_cnt + cnt >= virtqueue_get_vring_size(rx_vq) &&
new_cnt < virtqueue_get_vring_size(rx_vq))
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->rx_work);
}
ret = 0;
out_rcu:
rcu_read_unlock();
return ret;
}
static void virtio_vsock_rx_fill(struct virtio_vsock *vsock)
{
int buf_len = VIRTIO_VSOCK_DEFAULT_RX_BUF_SIZE;
struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt;
struct scatterlist hdr, buf, *sgs[2];
struct virtqueue *vq;
int ret;
vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX];
do {
pkt = kzalloc(sizeof(*pkt), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pkt)
break;
pkt->buf = kmalloc(buf_len, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pkt->buf) {
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
break;
}
pkt->buf_len = buf_len;
pkt->len = buf_len;
sg_init_one(&hdr, &pkt->hdr, sizeof(pkt->hdr));
sgs[0] = &hdr;
sg_init_one(&buf, pkt->buf, buf_len);
sgs[1] = &buf;
ret = virtqueue_add_sgs(vq, sgs, 0, 2, pkt, GFP_KERNEL);
if (ret) {
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
break;
}
vsock->rx_buf_nr++;
} while (vq->num_free);
if (vsock->rx_buf_nr > vsock->rx_buf_max_nr)
vsock->rx_buf_max_nr = vsock->rx_buf_nr;
virtio_vsock_notify(vsock, VSOCK_VQ_RX);
}
static void virtio_transport_tx_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock =
container_of(work, struct virtio_vsock, tx_work);
struct virtqueue *vq;
bool added = false;
vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_TX];
mutex_lock(&vsock->tx_lock);
if (!vsock->tx_run)
goto out;
do {
struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt;
unsigned int len;
virtqueue_disable_cb(vq);
while ((pkt = virtqueue_get_buf(vq, &len)) != NULL) {
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
added = true;
}
} while (!virtqueue_enable_cb(vq));
out:
mutex_unlock(&vsock->tx_lock);
if (added)
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->send_pkt_work);
}
/* Is there space left for replies to rx packets? */
static bool virtio_transport_more_replies(struct virtio_vsock *vsock)
{
struct virtqueue *vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX];
int val;
smp_rmb(); /* paired with atomic_inc() and atomic_dec_return() */
val = atomic_read(&vsock->queued_replies);
return val < virtqueue_get_vring_size(vq);
}
/* event_lock must be held */
static int virtio_vsock_event_fill_one(struct virtio_vsock *vsock,
struct virtio_vsock_event *event)
{
struct scatterlist sg;
struct virtqueue *vq;
vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_EVENT];
sg_init_one(&sg, event, sizeof(*event));
return virtqueue_add_inbuf(vq, &sg, 1, event, GFP_KERNEL);
}
/* event_lock must be held */
static void virtio_vsock_event_fill(struct virtio_vsock *vsock)
{
size_t i;
for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(vsock->event_list); i++) {
struct virtio_vsock_event *event = &vsock->event_list[i];
virtio_vsock_event_fill_one(vsock, event);
}
virtio_vsock_notify(vsock, VSOCK_VQ_EVENT);
}
static void virtio_vsock_reset_sock(struct sock *sk)
{
/* vmci_transport.c doesn't take sk_lock here either. At least we're
* under vsock_table_lock so the sock cannot disappear while we're
* executing.
*/
sk->sk_state = TCP_CLOSE;
sk->sk_err = ECONNRESET;
sk_error_report(sk);
}
static void virtio_vsock_update_guest_cid(struct virtio_vsock *vsock)
{
struct virtio_device *vdev = vsock->vdev;
__le64 guest_cid;
vdev->config->get(vdev, offsetof(struct virtio_vsock_config, guest_cid),
&guest_cid, sizeof(guest_cid));
vsock->guest_cid = le64_to_cpu(guest_cid);
}
/* event_lock must be held */
static void virtio_vsock_event_handle(struct virtio_vsock *vsock,
struct virtio_vsock_event *event)
{
switch (le32_to_cpu(event->id)) {
case VIRTIO_VSOCK_EVENT_TRANSPORT_RESET:
virtio_vsock_update_guest_cid(vsock);
vsock_for_each_connected_socket(&virtio_transport.transport,
virtio_vsock_reset_sock);
break;
}
}
static void virtio_transport_event_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock =
container_of(work, struct virtio_vsock, event_work);
struct virtqueue *vq;
vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_EVENT];
mutex_lock(&vsock->event_lock);
if (!vsock->event_run)
goto out;
do {
struct virtio_vsock_event *event;
unsigned int len;
virtqueue_disable_cb(vq);
while ((event = virtqueue_get_buf(vq, &len)) != NULL) {
if (len == sizeof(*event))
virtio_vsock_event_handle(vsock, event);
virtio_vsock_event_fill_one(vsock, event);
}
} while (!virtqueue_enable_cb(vq));
virtio_vsock_notify(vsock, VSOCK_VQ_EVENT);
out:
mutex_unlock(&vsock->event_lock);
}
static void virtio_vsock_event_done(struct virtqueue *vq)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = vq->vdev->priv;
if (!vsock)
return;
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->event_work);
}
static void virtio_vsock_tx_done(struct virtqueue *vq)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = vq->vdev->priv;
if (!vsock)
return;
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->tx_work);
}
static void virtio_vsock_rx_done(struct virtqueue *vq)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = vq->vdev->priv;
if (!vsock)
return;
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->rx_work);
}
static bool virtio_transport_seqpacket_allow(u32 remote_cid);
static struct virtio_transport virtio_transport = {
.transport = {
.module = THIS_MODULE,
.get_local_cid = virtio_transport_get_local_cid,
.init = virtio_transport_do_socket_init,
.destruct = virtio_transport_destruct,
.release = virtio_transport_release,
.connect = virtio_transport_connect,
.shutdown = virtio_transport_shutdown,
.cancel_pkt = virtio_transport_cancel_pkt,
.dgram_bind = virtio_transport_dgram_bind,
.dgram_dequeue = virtio_transport_dgram_dequeue,
.dgram_enqueue = virtio_transport_dgram_enqueue,
.dgram_allow = virtio_transport_dgram_allow,
.stream_dequeue = virtio_transport_stream_dequeue,
.stream_enqueue = virtio_transport_stream_enqueue,
.stream_has_data = virtio_transport_stream_has_data,
.stream_has_space = virtio_transport_stream_has_space,
.stream_rcvhiwat = virtio_transport_stream_rcvhiwat,
.stream_is_active = virtio_transport_stream_is_active,
.stream_allow = virtio_transport_stream_allow,
.seqpacket_dequeue = virtio_transport_seqpacket_dequeue,
.seqpacket_enqueue = virtio_transport_seqpacket_enqueue,
.seqpacket_allow = virtio_transport_seqpacket_allow,
.seqpacket_has_data = virtio_transport_seqpacket_has_data,
.notify_poll_in = virtio_transport_notify_poll_in,
.notify_poll_out = virtio_transport_notify_poll_out,
.notify_recv_init = virtio_transport_notify_recv_init,
.notify_recv_pre_block = virtio_transport_notify_recv_pre_block,
.notify_recv_pre_dequeue = virtio_transport_notify_recv_pre_dequeue,
.notify_recv_post_dequeue = virtio_transport_notify_recv_post_dequeue,
.notify_send_init = virtio_transport_notify_send_init,
.notify_send_pre_block = virtio_transport_notify_send_pre_block,
.notify_send_pre_enqueue = virtio_transport_notify_send_pre_enqueue,
.notify_send_post_enqueue = virtio_transport_notify_send_post_enqueue,
.notify_buffer_size = virtio_transport_notify_buffer_size,
},
.send_pkt = virtio_transport_send_pkt,
};
static bool virtio_transport_seqpacket_allow(u32 remote_cid)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock;
bool seqpacket_allow;
seqpacket_allow = false;
rcu_read_lock();
vsock = rcu_dereference(the_virtio_vsock);
if (vsock)
seqpacket_allow = vsock->seqpacket_allow;
rcu_read_unlock();
return seqpacket_allow;
}
static void virtio_transport_rx_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock =
container_of(work, struct virtio_vsock, rx_work);
struct virtqueue *vq;
vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX];
mutex_lock(&vsock->rx_lock);
if (!vsock->rx_run)
goto out;
do {
virtqueue_disable_cb(vq);
for (;;) {
struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt;
unsigned int len;
if (!virtio_transport_more_replies(vsock)) {
/* Stop rx until the device processes already
* pending replies. Leave rx virtqueue
* callbacks disabled.
*/
goto out;
}
pkt = virtqueue_get_buf(vq, &len);
if (!pkt) {
break;
}
vsock->rx_buf_nr--;
/* Drop short/long packets */
if (unlikely(len < sizeof(pkt->hdr) ||
len > sizeof(pkt->hdr) + pkt->len)) {
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
continue;
}
pkt->len = len - sizeof(pkt->hdr);
virtio_transport_deliver_tap_pkt(pkt);
virtio_transport_recv_pkt(&virtio_transport, pkt);
}
} while (!virtqueue_enable_cb(vq));
out:
if (vsock->rx_buf_nr < vsock->rx_buf_max_nr / 2)
virtio_vsock_rx_fill(vsock);
mutex_unlock(&vsock->rx_lock);
}
typedef irqreturn_t (*irq_handler_t)(int irq, void *data);
static irqreturn_t virtio_vsock_tx_irq_handler(int irq, void *data)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = data;
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->tx_work);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static irqreturn_t virtio_vsock_rx_irq_handler(int irq, void *data)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = data;
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->rx_work);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static irqreturn_t virtio_vsock_event_irq_handler(int irq, void *data)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = data;
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->event_work);
return IRQ_HANDLED;
}
static void virtio_vsock_init_hw_irq(struct virtio_vsock *vsock,
irq_handler_t handlers[], size_t num_vq)
{
struct device_node *irq_node;
struct irq_desc *desc;
int irq;
int ret;
int vq_idx;
cpumask_t mask;
cpumask_clear(&mask);
cpumask_set_cpu(5, &mask);
irq_node = of_find_compatible_node(NULL, NULL, "nbl,virtio_vsock_irq");
if (irq_node == NULL) {
return;
}
vsock->num_hwirq_vq = num_vq;
for (vq_idx = 0; vq_idx < num_vq; vq_idx++) {
irq = of_irq_get(irq_node, vq_idx * 2 + 1);
BUG_ON(irq == 0);
ret = request_irq(irq, handlers[vq_idx],
IRQF_TRIGGER_HIGH | IRQF_NO_SUSPEND, "vritio-vsock", vsock);
BUG_ON(ret != 0);
vsock->kick_irq[vq_idx] = ret;
irq_set_affinity_hint(irq, &mask);
irq = of_irq_get(irq_node, vq_idx * 2);
BUG_ON(irq == 0);
desc = irq_to_desc(irq);
BUG_ON(desc == NULL);
vsock->notify_irq[vq_idx] = desc->irq_data.hwirq;
}
}
static void virtio_vsock_release_hw_irq(struct virtio_vsock *vsock) {
int vq_idx;
for (vq_idx = 0; vq_idx < vsock->num_hwirq_vq; vq_idx++) {
free_irq(vsock->kick_irq[vq_idx], vsock);
}
}
static int virtio_vsock_vqs_init(struct virtio_vsock *vsock)
{
struct virtio_device *vdev = vsock->vdev;
static const char * const names[] = {
"rx",
"tx",
"event",
};
vq_callback_t *callbacks[] = {
virtio_vsock_rx_done,
virtio_vsock_tx_done,
virtio_vsock_event_done,
};
irq_handler_t hwirq_vq_handlers[] = {
virtio_vsock_rx_irq_handler,
virtio_vsock_tx_irq_handler,
virtio_vsock_event_irq_handler,
};
int ret;
ret = virtio_find_vqs(vdev, VSOCK_VQ_MAX, vsock->vqs, callbacks, names,
NULL);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
virtio_vsock_update_guest_cid(vsock);
virtio_vsock_init_hw_irq(vsock, hwirq_vq_handlers, /*num_vq=*/2);
virtio_device_ready(vdev);
return 0;
}
static void virtio_vsock_vqs_start(struct virtio_vsock *vsock)
{
mutex_lock(&vsock->tx_lock);
vsock->tx_run = true;
mutex_unlock(&vsock->tx_lock);
mutex_lock(&vsock->rx_lock);
virtio_vsock_rx_fill(vsock);
vsock->rx_run = true;
mutex_unlock(&vsock->rx_lock);
mutex_lock(&vsock->event_lock);
virtio_vsock_event_fill(vsock);
vsock->event_run = true;
mutex_unlock(&vsock->event_lock);
/* virtio_transport_send_pkt() can queue packets once
* the_virtio_vsock is set, but they won't be processed until
* vsock->tx_run is set to true. We queue vsock->send_pkt_work
* when initialization finishes to send those packets queued
* earlier.
* We don't need to queue the other workers (rx, event) because
* as long as we don't fill the queues with empty buffers, the
* host can't send us any notification.
*/
queue_work(virtio_vsock_workqueue, &vsock->send_pkt_work);
}
static void virtio_vsock_vqs_del(struct virtio_vsock *vsock)
{
struct virtio_device *vdev = vsock->vdev;
struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt;
/* Reset all connected sockets when the VQs disappear */
vsock_for_each_connected_socket(&virtio_transport.transport,
virtio_vsock_reset_sock);
/* Stop all work handlers to make sure no one is accessing the device,
* so we can safely call virtio_reset_device().
*/
mutex_lock(&vsock->rx_lock);
vsock->rx_run = false;
mutex_unlock(&vsock->rx_lock);
mutex_lock(&vsock->tx_lock);
vsock->tx_run = false;
mutex_unlock(&vsock->tx_lock);
mutex_lock(&vsock->event_lock);
vsock->event_run = false;
mutex_unlock(&vsock->event_lock);
/* Flush all device writes and interrupts, device will not use any
* more buffers.
*/
virtio_reset_device(vdev);
mutex_lock(&vsock->rx_lock);
while ((pkt = virtqueue_detach_unused_buf(vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX])))
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
mutex_unlock(&vsock->rx_lock);
mutex_lock(&vsock->tx_lock);
while ((pkt = virtqueue_detach_unused_buf(vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_TX])))
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
mutex_unlock(&vsock->tx_lock);
spin_lock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
while (!list_empty(&vsock->send_pkt_list)) {
pkt = list_first_entry(&vsock->send_pkt_list,
struct virtio_vsock_pkt, list);
list_del(&pkt->list);
virtio_transport_free_pkt(pkt);
}
spin_unlock_bh(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
virtio_vsock_release_hw_irq(vsock);
/* Delete virtqueues and flush outstanding callbacks if any */
vdev->config->del_vqs(vdev);
}
static int virtio_vsock_probe(struct virtio_device *vdev)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = NULL;
int ret;
ret = mutex_lock_interruptible(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex);
if (ret)
return ret;
/* Only one virtio-vsock device per guest is supported */
if (rcu_dereference_protected(the_virtio_vsock,
lockdep_is_held(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex))) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
vsock = kzalloc(sizeof(*vsock), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!vsock) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto out;
}
vsock->vdev = vdev;
vsock->rx_buf_nr = 0;
vsock->rx_buf_max_nr = 0;
atomic_set(&vsock->queued_replies, 0);
mutex_init(&vsock->tx_lock);
mutex_init(&vsock->rx_lock);
mutex_init(&vsock->event_lock);
spin_lock_init(&vsock->send_pkt_list_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&vsock->send_pkt_list);
INIT_WORK(&vsock->rx_work, virtio_transport_rx_work);
INIT_WORK(&vsock->tx_work, virtio_transport_tx_work);
INIT_WORK(&vsock->event_work, virtio_transport_event_work);
INIT_WORK(&vsock->send_pkt_work, virtio_transport_send_pkt_work);
if (virtio_has_feature(vdev, VIRTIO_VSOCK_F_SEQPACKET))
vsock->seqpacket_allow = true;
vdev->priv = vsock;
ret = virtio_vsock_vqs_init(vsock);
if (ret < 0)
goto out;
rcu_assign_pointer(the_virtio_vsock, vsock);
virtio_vsock_vqs_start(vsock);
mutex_unlock(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex);
return 0;
out:
kfree(vsock);
mutex_unlock(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex);
return ret;
}
static void virtio_vsock_remove(struct virtio_device *vdev)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = vdev->priv;
mutex_lock(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex);
vdev->priv = NULL;
rcu_assign_pointer(the_virtio_vsock, NULL);
synchronize_rcu();
virtio_vsock_vqs_del(vsock);
/* Other works can be queued before 'config->del_vqs()', so we flush
* all works before to free the vsock object to avoid use after free.
*/
flush_work(&vsock->rx_work);
flush_work(&vsock->tx_work);
flush_work(&vsock->event_work);
flush_work(&vsock->send_pkt_work);
mutex_unlock(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex);
kfree(vsock);
}
#define CONFIG_PM_SLEEP 1
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
static int virtio_vsock_freeze(struct virtio_device *vdev)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = vdev->priv;
mutex_lock(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex);
rcu_assign_pointer(the_virtio_vsock, NULL);
synchronize_rcu();
virtio_vsock_vqs_del(vsock);
//add by konggc
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = virtio_get_drvdata(vdev);
struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt, *tmp;
unsigned long flags;
vsock->suspended = true;
cancel_work_sync(&vsock->rx_fill_work); // 取消未执行的工作
// 释放所有pkt和缓冲区
spin_lock_irqsave(&vsock->rx_lock, flags);
list_for_each_entry_safe(pkt, tmp, &vsock->rx_pkts, list) {
list_del(&pkt->list);
virtqueue_detach_unused_buf(vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX], pkt);
kfree(pkt->buf);
kfree(pkt);
}
vsock->rx_buf_nr = 0;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&vsock->rx_lock, flags);
//end of add by konggc
mutex_unlock(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex);
return 0;
}
static int virtio_vsock_restore(struct virtio_device *vdev)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = vdev->priv;
int ret;
mutex_lock(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex);
/* Only one virtio-vsock device per guest is supported */
if (rcu_dereference_protected(the_virtio_vsock,
lockdep_is_held(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex))) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
ret = virtio_vsock_vqs_init(vsock);
if (ret < 0)
goto out;
rcu_assign_pointer(the_virtio_vsock, vsock);
virtio_vsock_vqs_start(vsock);
out:
mutex_unlock(&the_virtio_vsock_mutex);
return ret;
}
#endif /* CONFIG_PM_SLEEP */
static struct virtio_device_id id_table[] = {
{ VIRTIO_ID_VSOCK, VIRTIO_DEV_ANY_ID },
{ 0 },
};
static unsigned int features[] = {
VIRTIO_VSOCK_F_SEQPACKET
};
static struct virtio_driver virtio_vsock_driver = {
.feature_table = features,
.feature_table_size = ARRAY_SIZE(features),
.driver.name = KBUILD_MODNAME,
.driver.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.id_table = id_table,
.probe = virtio_vsock_probe,
.remove = virtio_vsock_remove,
#ifdef CONFIG_PM_SLEEP
.freeze = virtio_vsock_freeze,
.restore = virtio_vsock_restore,
#endif
};
static int __init virtio_vsock_init(void)
{
int ret;
virtio_vsock_workqueue = alloc_workqueue("virtio_vsock", 0, 0);
if (!virtio_vsock_workqueue)
return -ENOMEM;
ret = vsock_core_register(&virtio_transport.transport,
VSOCK_TRANSPORT_F_G2H);
if (ret)
goto out_wq;
ret = register_virtio_driver(&virtio_vsock_driver);
if (ret)
goto out_vci;
return 0;
out_vci:
vsock_core_unregister(&virtio_transport.transport);
out_wq:
destroy_workqueue(virtio_vsock_workqueue);
return ret;
}
static void __exit virtio_vsock_exit(void)
{
unregister_virtio_driver(&virtio_vsock_driver);
vsock_core_unregister(&virtio_transport.transport);
destroy_workqueue(virtio_vsock_workqueue);
}
module_init(virtio_vsock_init);
module_exit(virtio_vsock_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");
MODULE_AUTHOR("Asias He");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("virtio transport for vsock");
MODULE_DEVICE_TABLE(virtio, id_table);
上述是原来的代码,下面是做了优先通过工作队列将分配逻辑延迟到进程上下文,保留GFP_KERNEL的高效分配;强化休眠 / 唤醒阶段的资源管理(提前释放、延迟分配),降低内存竞争风险的相关代码#include <linux/virtio.h>
#include <linux/virtio_vsock.h>
#include <linux/workqueue.h>
#include <linux/spinlock.h>
#include <linux/list.h>
#include <linux/pm.h>
// 扩展VSOCK数据包结构体,添加链表成员用于资源跟踪
struct virtio_vsock_pkt {
struct virtio_vsock_hdr hdr;
void *buf;
size_t buf_len;
size_t len;
struct list_head list; // 用于链表跟踪所有分配的pkt
};
// 扩展VSOCK设备结构体,添加工作队列和资源管理成员
struct virtio_vsock {
struct virtqueue *vqs[VSOCK_VQ_NUM];
unsigned int rx_buf_nr;
unsigned int rx_buf_max_nr;
struct list_head rx_pkts; // 跟踪所有分配的pkt
spinlock_t rx_lock; // 保护rx_pkts的自旋锁
struct work_struct rx_fill_work; // 工作队列项(延迟分配)
bool suspended; // 标记设备是否处于休眠状态
};
// 工作队列处理函数(运行在进程上下文)
static void virtio_vsock_rx_fill_work(struct work_struct *work)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = container_of(work, struct virtio_vsock, rx_fill_work);
// 仅在非休眠状态下执行分配
if (!vsock->suspended) {
virtio_vsock_rx_fill(vsock);
}
}
// 改进后的接收缓冲区填充函数(在进程上下文执行)
static void virtio_vsock_rx_fill(struct virtio_vsock *vsock)
{
int buf_len = VIRTIO_VSOCK_DEFAULT_RX_BUF_SIZE;
struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt;
struct scatterlist hdr, buf, *sgs[2];
struct virtqueue *vq;
int ret;
vq = vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX];
if (!vq)
return;
do {
// 1. 分配pkt结构体(进程上下文,安全使用GFP_KERNEL)
pkt = kzalloc(sizeof(*pkt), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pkt)
break;
// 2. 分配数据缓冲区
pkt->buf = kmalloc(buf_len, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!pkt->buf) {
kfree(pkt);
break;
}
// 3. 初始化pkt元信息
pkt->buf_len = buf_len;
pkt->len = buf_len;
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&pkt->list);
// 4. 初始化scatterlist并添加到虚拟队列
sg_init_one(&hdr, &pkt->hdr, sizeof(pkt->hdr));
sgs[0] = &hdr;
sg_init_one(&buf, pkt->buf, buf_len);
sgs[1] = &buf;
ret = virtqueue_add_sgs(vq, sgs, 0, 2, pkt, GFP_KERNEL);
if (ret) {
kfree(pkt->buf);
kfree(pkt);
break;
}
// 5. 将pkt加入跟踪链表(带锁保护)
spin_lock(&vsock->rx_lock);
list_add(&pkt->list, &vsock->rx_pkts);
vsock->rx_buf_nr++;
spin_unlock(&vsock->rx_lock);
} while (vq->num_free > 0);
// 更新最大缓冲区计数
if (vsock->rx_buf_nr > vsock->rx_buf_max_nr)
vsock->rx_buf_max_nr = vsock->rx_buf_nr;
// 通知设备接收队列已准备好
virtio_vsock_notify(vsock, VSOCK_VQ_RX);
}
// 休眠回调:释放所有资源
static int virtio_vsock_suspend(struct device *dev)
{
struct virtio_device *vdev = container_of(dev, struct virtio_device, dev);
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = virtio_get_drvdata(vdev);
struct virtio_vsock_pkt *pkt, *tmp;
unsigned long flags;
vsock->suspended = true;
cancel_work_sync(&vsock->rx_fill_work); // 取消未执行的工作
// 释放所有pkt和缓冲区
spin_lock_irqsave(&vsock->rx_lock, flags);
list_for_each_entry_safe(pkt, tmp, &vsock->rx_pkts, list) {
list_del(&pkt->list);
virtqueue_detach_unused_buf(vsock->vqs[VSOCK_VQ_RX], pkt);
kfree(pkt->buf);
kfree(pkt);
}
vsock->rx_buf_nr = 0;
spin_unlock_irqrestore(&vsock->rx_lock, flags);
return 0;
}
// 唤醒回调:调度工作队列重建缓冲区
static int virtio_vsock_resume(struct device *dev)
{
struct virtio_device *vdev = container_of(dev, struct virtio_device, dev);
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = virtio_get_drvdata(vdev);
vsock->suspended = false;
// 调度工作队列在进程上下文重建缓冲区
if (!work_pending(&vsock->rx_fill_work)) {
queue_work(system_wq, &vsock->rx_fill_work);
}
return 0;
}
// 电源管理操作结构体
static const struct dev_pm_ops virtio_vsock_pm_ops = {
SET_SYSTEM_SLEEP_PM_OPS(virtio_vsock_suspend, virtio_vsock_resume)
};
// 设备初始化函数
static int virtio_vsock_probe(struct virtio_device *vdev)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock;
int ret;
vsock = kzalloc(sizeof(*vsock), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!vsock)
return -ENOMEM;
// 初始化虚拟队列(原有逻辑)
ret = virtio_vsock_init_vqs(vdev, vsock);
if (ret) {
kfree(vsock);
return ret;
}
// 初始化资源跟踪与工作队列
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&vsock->rx_pkts);
spin_lock_init(&vsock->rx_lock);
INIT_WORK(&vsock->rx_fill_work, virtio_vsock_rx_fill_work);
vsock->suspended = false;
virtio_set_drvdata(vdev, vsock);
return 0;
}
// 设备移除函数
static void virtio_vsock_remove(struct virtio_device *vdev)
{
struct virtio_vsock *vsock = virtio_get_drvdata(vdev);
// 清理逻辑(释放资源等)
cancel_work_sync(&vsock->rx_fill_work);
virtio_vsock_cleanup_vqs(vsock);
kfree(vsock);
}
// VSOCK设备驱动结构体
static struct virtio_driver virtio_vsock_driver = {
.driver = {
.name = "virtio-vsock",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.pm = &virtio_vsock_pm_ops,
},
.probe = virtio_vsock_probe,
.remove = virtio_vsock_remove,
// 其他驱动回调(如feature_table等)
};
module_virtio_driver(virtio_vsock_driver);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("VirtIO VSOCK driver with suspend/resume optimization");
现在需要将两份代码进行合并
最新发布
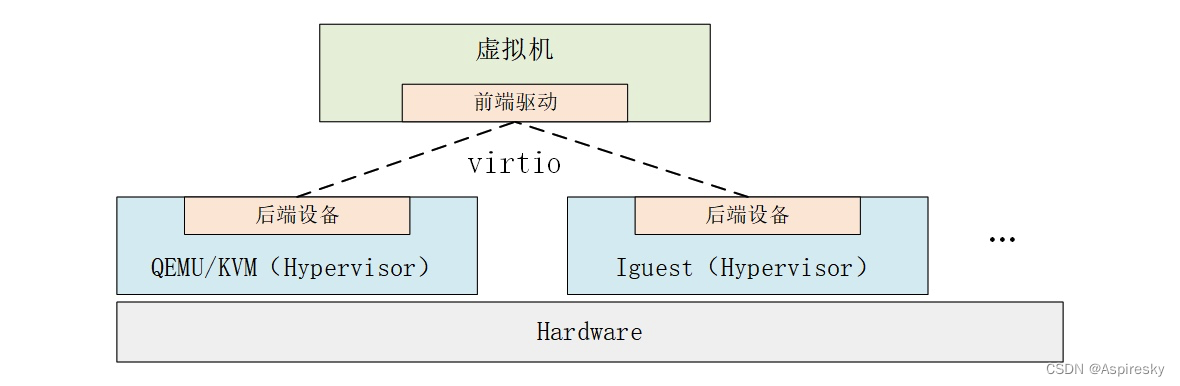










 virtio是主流的IO设备半虚拟化解决方案,提供统一通信框架和编程接口。介绍了virtio协议,包括版本、架构(前端驱动、后端设备、传输层),还阐述了其工作机制,通过前后端通信模型和虚拟队列进行数据交互。
virtio是主流的IO设备半虚拟化解决方案,提供统一通信框架和编程接口。介绍了virtio协议,包括版本、架构(前端驱动、后端设备、传输层),还阐述了其工作机制,通过前后端通信模型和虚拟队列进行数据交互。
















 1053
1053

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








