1.LinkedList全面说明
- LinkedList底层实现了双向链表和双端队列
- 可以添加任意元素(元素可以重复)包括null
- 线程不安全 没有实现同步
2.LinkedList底层操作机制
- LinkedList底层维护了一个双向链表
- LinkedList中维护了两个属性first和last,分别指向首节点和尾节点
- 每个节点(Node对象),里面又维护了prev、next、item三个属性,其中通过prev指向前一个,通过next指向后一个节点,最终实现双向链表
- 所以LinkedList的元素的添加和删除,不是通过数组完成的,相对来说效率较高。
简单双向链表模拟
package com.logic.list_;
/**
* @author logic
* @version 1.0
*/
public class LinkedList01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//moni
Node logic = new Node("L0g1c");
Node jack = new Node("jack");
Node you = new Node("You");
logic.next = jack;
jack.next = you;
you.pre = jack;
jack.pre = logic;
Node first = logic;
Node last = you;
System.out.println("===从头到尾遍历===");
while (true) {
if (first == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(first);
first = first.next;
}
System.out.println("===从尾到头遍历===");
while (true) {
if (last == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(last);
last = last.pre;
}
Node smith = new Node("smith");
smith.next = you;
smith.pre = jack;
jack.next = smith;
you.pre = smith;
first = logic;
last = you;
System.out.println("===从头到尾遍历===");
while (true) {
if (first == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(first);
first = first.next;
}
System.out.println("===从尾到头遍历===");
while (true) {
if (last == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(last);
last = last.pre;
}
}
}
class Node {
public Object item;
public Node next;
public Node pre;
public Node(Object item) {
this.item = item;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"item=" + item +
'}';
}
}
3.LinkedList的增删改查
package com.logic.list_;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* @author logic
* @version 1.0
*/
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class LinkedListCRUD_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.add(1);
linkedList.add(2);
linkedList.add(3);
System.out.println("linkedList=" + linkedList);
//演示一个删除结点的
linkedList.remove(); // 这里默认删除的是第一个结点
//linkedList.remove(2);
System.out.println("linkedList=" + linkedList);
//修改某个结点对象
linkedList.set(1, 999);
System.out.println("linkedList=" + linkedList);
//得到某个结点对象
//get(1) 是得到双向链表的第二个对象
Object o = linkedList.get(1);
System.out.println(o);//999
//因为LinkedList 是 实现了List接口, 遍历方式
System.out.println("===LinkeList遍历迭代器====");
Iterator iterator = linkedList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Object next = iterator.next();
System.out.println("next=" + next);
}
System.out.println("===LinkeList遍历增强for====");
for (Object o1 : linkedList) {
System.out.println("o1=" + o1);
}
System.out.println("===LinkeList遍历普通for====");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));
}
//源码解读
/* 1. LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
public LinkedList() {}
2. 这时 linkeList 的属性 first = null last = null
3. 执行 添加
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
4.将新的结点,加入到双向链表的最后
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
*/
/*
读源码 linkedList.remove(); // 这里默认删除的是第一个结点
1. 执行 removeFirst
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
2. 执行
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
3. 执行 unlinkFirst, 将 f 指向的双向链表的第一个结点拿掉
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
// assert f == first && f != null;
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
*/
}
}
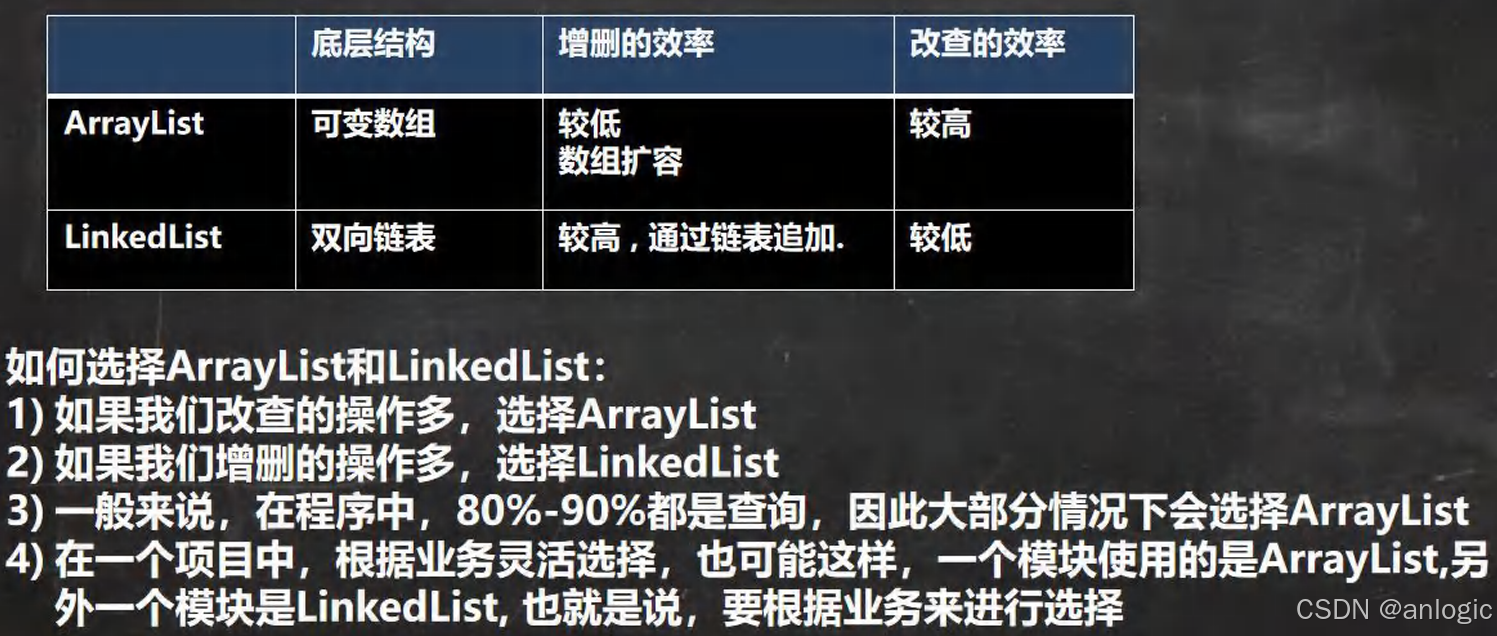
4.ArrayList和LinkedList比较






















 6401
6401

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








