- 内核 启动后回去调用第一个程序init、给用户提供操作界面的shell程序 、应用程序所依赖的库文件。这些必须的基本的文件合起来称为根文件系统,他们存放在一个分区中,Linux系统启动之后首先挂载这个分区,称为挂载根文件系统,其他的分区上的所有的目录、文件的集合,也称之为文件系统。
- linux系统中没有C、D、E等盘的概念,linux中以树状管理所有的文件目录,其他的分区挂载在这个目录上,这个目录被称之为挂载点或者安装点,然后可以通过这个分区来访问这个分区上的文件了,比如根文件系统被挂载在根目录’/‘上之后,就可以在’/'看到根目录下的文件了\
- 在一个分区上存储文件时需要遵循一定的格式,这种格式称之为文件系统,比如fat16、ntfs、wxt2、ext3、jffs2、yaffs2等,除了这几个拥有实实在在的存储分区的文件系统之外,linux还有几个虚拟的文件系统类型,比如proc、yaffs等,他们的文件并不存在实际的设备上,而是访问他们时有linux内核临时的生成。
- /etc下的文件
export 用来配置NFS文件系统
fstab 用来指明执行"mount -a"时的需要挂载的文件系统
mtab 用来显示已经加载的文件系统,通常是/proc/mounts的链接文件
ftpusers 启动FTP服务时,用来配置用户的访问权限
group 用户的组文件
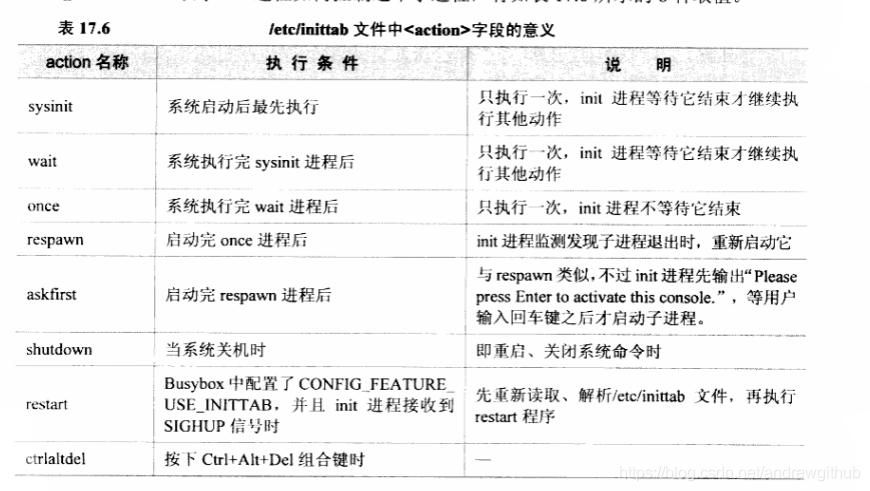
inittab init进程的配置文件
ld.so.conf 其它共享库的路径
passed 密码文件 - /proc目录
proc可以为空,linux内核创建的临时文件,proc文件系统,是一个虚拟的文件系统,他没有实际的存储设备,里面的目录、文件都是内核临时生成的,用来表示系统的运行状态,也可已操作其中的文件控制系统。
系统启动之后使用以下命令挂载proc文件系统(常在/etc/fstab进行设置以自动挂载)
#mount -t proc none /proc
- /tmp用于存放临时文件,减少系统对flash的操作,所以/tmp目录必须保证可以访问到。可使用以下命令记性==进行挂载
# mount -t tmpfs none /tmp
linux文件类型
- 普通文件
- 目录文件
- 字符设备文件
- 块设备文件
- FIFO
- 套接字
- 连接文件
启动第一个程序init
文件在linux源码的init/main.c中
/* This is a non __init function. Force it to be noinline otherwise gcc
* makes it inline to init() and it becomes part of init.text section
*/
//若果使用的是 __attribute__(noinline)的话代表的是,返回的出错将被当成警告处理
static int noinline init_post(void)
{
free_initmem();
unlock_kernel();
mark_rodata_ro();
system_state = SYSTEM_RUNNING;
numa_default_policy();
if (sys_open((const char __user *) "/dev/console", O_RDWR, 0) < 0)
printk(KERN_WARNING "Warning: unable to open an initial console.\n");
(void) sys_dup(0);
(void) sys_dup(0);
//因为是linux内核刚刚启动所以打开的文件描述符是0、1、2,并且使用sys_dup将0、1、2都连接到打开的额console上
//> 之后就能实现将标准输入标准输出和标注错误输出重定向到console上。
if (ramdisk_execute_command) {
run_init_process(ramdisk_execute_command);
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to execute %s\n",
ramdisk_execute_command);
}
/*
* We try each of these until one succeeds.
*
* The Bourne shell can be used instead of init if we are
* trying to recover a really broken machine.
*/
// execute_command ==> init = /linuxrc
//因为这种函数都是死循环的样式进行的,所以无论是 /linuxrc还是
// /sbin/init 等程序都是只能执行一个
if (execute_command) {
run_init_process(execute_command);
printk(KERN_WARNING "Failed to execute %s. Attempting "
"defaults...\n", execute_command);
}
run_init_process("/sbin/init");
run_init_process("/etc/init");
run_init_process("/bin/init");
run_init_process("/bin/sh");
panic("No init found. Try passing init= option to kernel.");
}
busybox的init程序对应代码中的init/init.c文件
执行的过程如下:
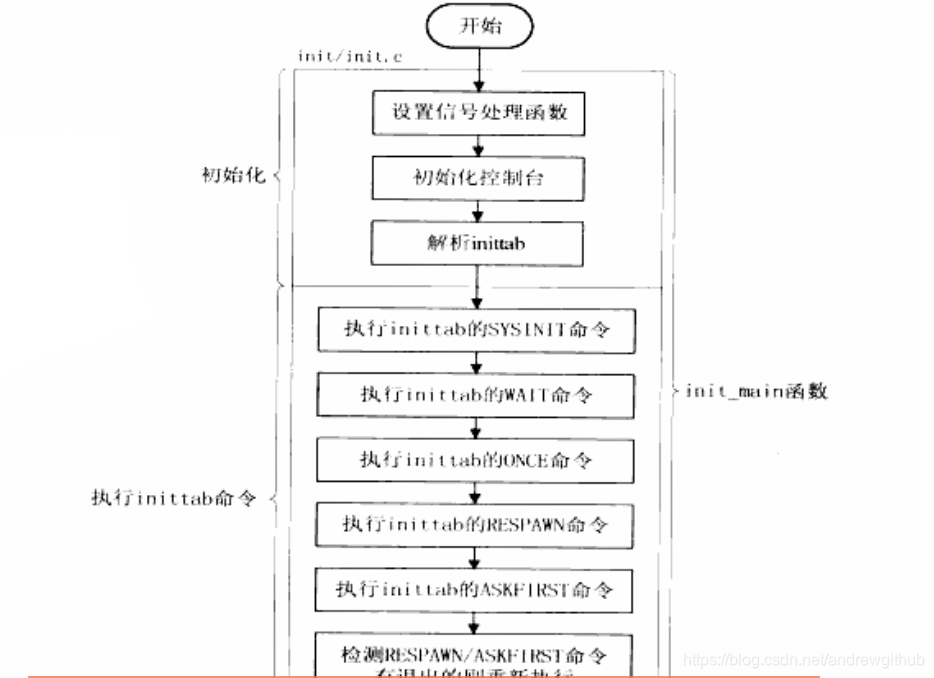
busybox的inittab配置文件

上图中的-/bin/sh中的 '-'代表程序是交互的方式启动,这时就会弹出交互式shell窗口,嵌入式设备中是使用串口
下面是我的开发板上的inittab配置文件
# /etc/inittab init(8) configuration for BusyBox
#
# Copyright (C) 1999-2004 by Erik Andersen <andersen@codepoet.org>
#
#
# Note, BusyBox init doesn't support runlevels. The runlevels field is
# completely ignored by BusyBox init. If you want runlevels, use sysvinit.
#
#
# Format for each entry: <id>:<runlevels>:<action>:<process>
#
# <id>: WARNING: This field has a non-traditional meaning for BusyBox init!
#
# The id field is used by BusyBox init to specify the controlling tty for
# the specified process to run on. The contents of this field are
# appended to "/dev/" and used as-is. There is no need for this field to
# be unique, although if it isn't you may have strange results. If this
# field is left blank, it is completely ignored. Also note that if
# BusyBox detects that a serial console is in use, then all entries
# containing non-empty id fields will be ignored. BusyBox init does
# nothing with utmp. We don't need no stinkin' utmp.
#
# <runlevels>: The runlevels field is completely ignored.
#
# <action>: Valid actions include: sysinit, respawn, askfirst, wait, once,
# restart, ctrlaltdel, and shutdown.
#
# Note: askfirst acts just like respawn, but before running the specified
# process it displays the line "Please press Enter to activate this
# console." and then waits for the user to press enter before starting
# the specified process.
#
# Note: unrecognised actions (like initdefault) will cause init to emit
# an error message, and then go along with its business.
#
# <process>: Specifies the process to be executed and it's command line.
#
# Note: BusyBox init works just fine without an inittab. If no inittab is
# found, it has the following default behavior:
# ::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS
# ::askfirst:/bin/sh
# ::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot
# ::shutdown:/sbin/swapoff -a
# ::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r
# ::restart:/sbin/init
#
# if it detects that /dev/console is _not_ a serial console, it will
# also run:
# tty2::askfirst:/bin/sh
# tty3::askfirst:/bin/sh
# tty4::askfirst:/bin/sh
#
# Boot-time system configuration/initialization script.
# This is run first except when booting in single-user mode.
#
::sysinit:/etc/init.d/rcS
# /bin/sh invocations on selected ttys
#
# Note below that we prefix the shell commands with a "-" to indicate to the
# shell that it is supposed to be a login shell. Normally this is handled by
# login, but since we are bypassing login in this case, BusyBox lets you do
# this yourself...
#
# Start an "askfirst" shell on the console (whatever that may be)
::askfirst:-/bin/sh
# Start an "askfirst" shell on /dev/tty2-4
new_init_action(ASKFIRST, bb_default_login_shell, "");
new_init_action(ASKFIRST, bb_default_login_shell, VC_2);
new_init_action(ASKFIRST, bb_default_login_shell, VC_3);
new_init_action(ASKFIRST, bb_default_login_shell, VC_4);
VC_2 ==> tty2
ASKFIRST ==> askfirst
-/bin/sh ==> bb_default_login_shell
tty2::askfirst:-/bin/sh
tty3::askfirst:-/bin/sh
tty4::askfirst:-/bin/sh
# /sbin/getty invocations for selected ttys
tty4::respawn:/sbin/getty 38400 tty5
tty5::respawn:/sbin/getty 38400 tty6
# Example of how to put a getty on a serial line (for a terminal)
#::respawn:/sbin/getty -L ttyS0 9600 vt100
#::respawn:/sbin/getty -L ttyS1 9600 vt100
#
# Example how to put a getty on a modem line.
#::respawn:/sbin/getty 57600 ttyS2
# Stuff to do when restarting the init process
::restart:/sbin/init
# Stuff to do before rebooting
::ctrlaltdel:/sbin/reboot
::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r
::shutdown:/sbin/swapoff -a

























 935
935












