Richardson–Lucy deconvolution
The Richardson–Lucy algorithm, also known as Lucy–Richardson deconvolution, is an iterative procedure for recovering a latent image that has been blurred by a known point spread function.[1][2]
Pixels in the observed image can be represented in terms of the point spread function and the latent image as
where 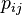 is the point spread function (the fraction of light coming from true location
is the point spread function (the fraction of light coming from true location 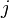 that is observed at position
that is observed at position 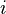 ),
),  is the pixel value at location
is the pixel value at location 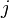 in the latent image, and
in the latent image, and  is the observed value at pixel location
is the observed value at pixel location 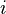 . The statistics are performed under the assumption that
. The statistics are performed under the assumption that 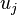 are Poisson distributed, which is appropriate for photon noise in the data.
are Poisson distributed, which is appropriate for photon noise in the data.
The basic idea is to calculate the most likely 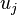 given the observed
given the observed 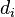 and known
and known 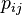 . This leads to an equation for
. This leads to an equation for 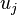 which can be solved iteratively according to
which can be solved iteratively according to
where
It has been shown empirically that if this iteration converges, it converges to the maximum likelihood solution for 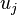 .[3]
.[3]
In problems where the point spread function 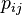 is dependent on one or more unknown parameters, the Richardson–Lucy algorithm cannot be used. A later and more general class of algorithms, theexpectation-maximization algorithms,[4] have been applied to this type of problem with great success
is dependent on one or more unknown parameters, the Richardson–Lucy algorithm cannot be used. A later and more general class of algorithms, theexpectation-maximization algorithms,[4] have been applied to this type of problem with great success
[edit]References
- ^ Richardson, William Hadley (1972). "Bayesian-Based Iterative Method of Image Restoration". JOSA 62 (1): 55–59. doi:10.1364/JOSA.62.000055.
- ^ Lucy, L. B. (1974). "An iterative technique for the rectification of observed distributions". Astronomical Journal 79 (6): 745–754. doi:10.1086/111605.
- ^ Shepp, L. A.; Vardi, Y. (1982), "Maximum Likelihood Reconstruction for Emission Tomography", IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 1: 113, doi:10.1109/TMI.1982.4307558
- ^ A.P. Dempster, N.M. Laird, D.B. Rubin, 1977, Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm, J. Royal Stat. Soc. Ser. B, 39 (1), pp. 1–38








 本文深入探讨了Richardson-Lucy去模糊算法的核心原理,包括其数学公式、迭代过程及适用条件,特别关注了算法在解决模糊图像恢复问题时的实际应用。
本文深入探讨了Richardson-Lucy去模糊算法的核心原理,包括其数学公式、迭代过程及适用条件,特别关注了算法在解决模糊图像恢复问题时的实际应用。
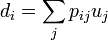
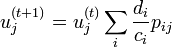

















 8494
8494

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








