鸿蒙NEXT开发实战往期必看文章:
一分钟了解”纯血版!鸿蒙HarmonyOS Next应用开发!
“非常详细的” 鸿蒙HarmonyOS Next应用开发学习路线!(从零基础入门到精通)
HarmonyOS NEXT应用开发案例实践总结合(持续更新......)
HarmonyOS NEXT应用开发性能优化实践总结(持续更新......)
1. 鸿蒙HTTP服务器可行性分析
看到这个题目,可能有的小伙伴会有一些疑问:
“鸿蒙API从9到12我都翻烂了,也没见提供HTTP服务器的接口啊”
“我BUG写得少,你可不要骗我”
的确,目前的鸿蒙API没有提供HTTP服务端的实现接口,但是我们知道,HTTP协议是基于TCP的,而鸿蒙API10提供了TCPSocketServer类,包含了如下几个关键接口:
listen(address: NetAddress): Promise<void>监听方法,绑定IP地址和端口,端口可以指定或由系统随机分配。成功调用该方法后,TCPSocketServer对象监听并接受与此套接字建立的TCPSocket连接。
on(type: 'connect', callback: Callback<TCPSocketConnection>): void订阅TCPSocketServer的连接事件,在新的客户端套接字连接上以后,会触发callback回调,在回调中包含TCPSocketConnection对象,该对象就表示TCPSocket客户端与服务端的连接。
TCPSocketConnection是服务端和客户端通讯的基础,提供了发送数据到客户端的方法:
send(options: TCPSendOptions): Promise<void>还提供了订阅客户端消息接收的事件:
on(type: 'message', callback: Callback<SocketMessageInfo>): void在这个事件的callback回调里,包含了SocketMessageInfo参数,该参数的属性message就是客户端发送过来的消息。
通过上述几个接口,我们就可以在服务端开启TCP监听,并且处理客户端的连接和消息收发。
再来说一下HTTP协议,众所周知,HTTP协议是一个简单的请求响应协议,根据RFC 9112,HTTP协议1.1版本的消息格式如下所示:
HTTP-message = start-line CRLF
*( field-line CRLF )
CRLF
[ message-body ]其中,start-line表示起始行,CRLF表示回车换行符号,field-line表示首部字段行,*( field-line CRLF )说明首部字段可以是零个或者多个,最后的[ message-body ]表示可选的消息正文;因为消息分为请求消息和应答消息,所以起始行又可以分为请求行和状态行,如下所示:
start-line = request-line / status-line当然,HTTP的协议还是有一点复杂的,这里就不展开了,不过我们明白,只要我们按照协议格式构造出了请求应答的文本,然后使用TCP协议作为传输层进行收发即可。
有了上面的API接口,加上HTTP协议的格式,就可以打造一个最简单的HTTP服务端了。
2. 实现HTTP服务器示例
本示例运行后的界面如下所示:
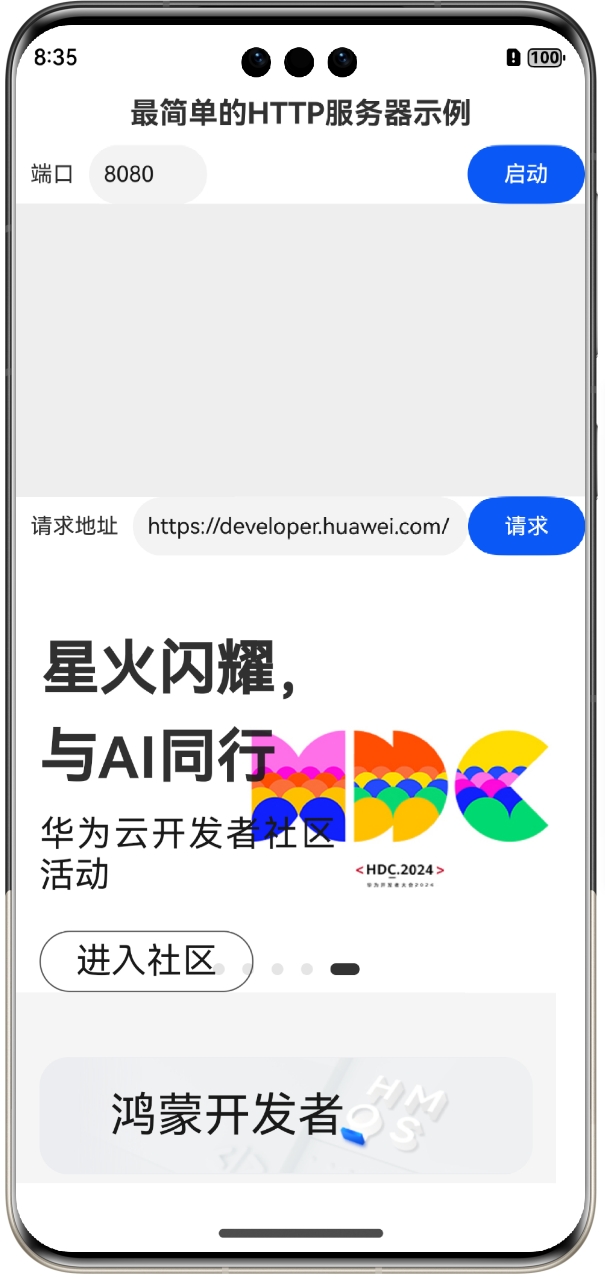
输入要监听的端口,然后单击“启动”按钮,即可在127.0.0.1上启动对端口的TCP协议监听了。然后在请求地址栏输入服务端地址,再单击“请求”按钮,既可请求刚创建的HTTP服务器,效果如图所示:
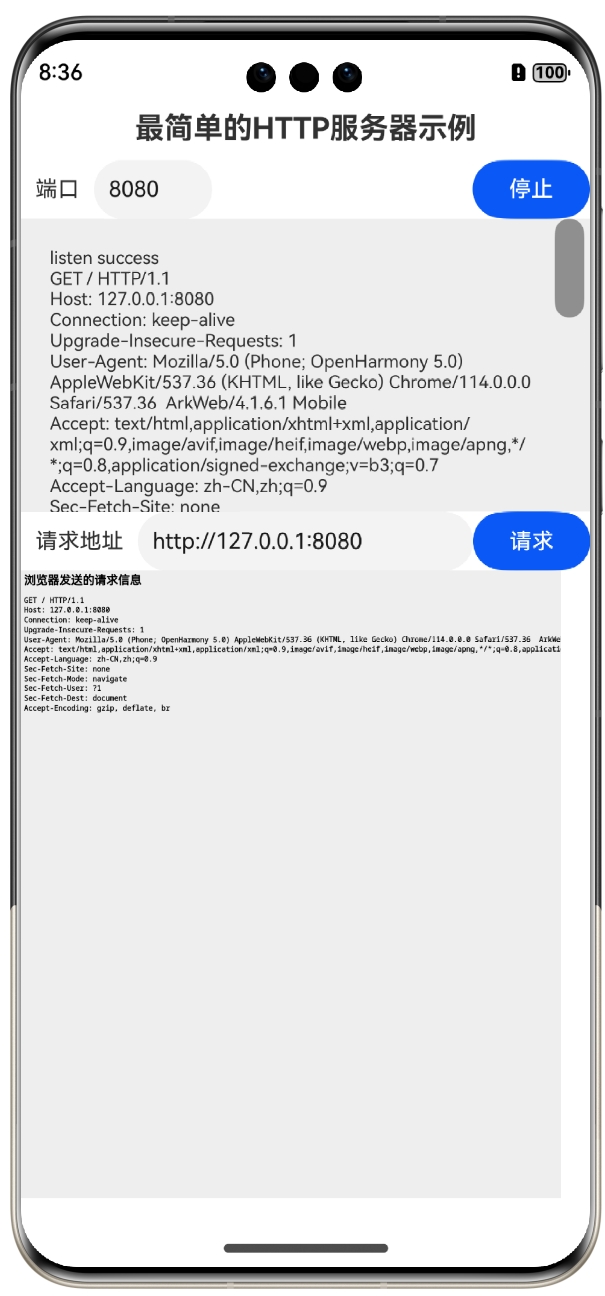
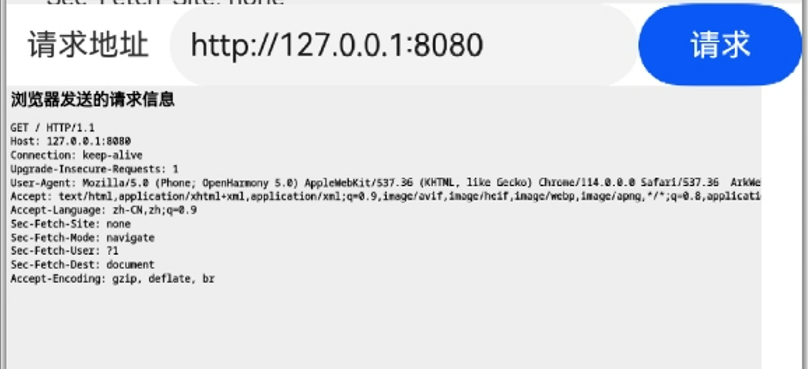
这里实现的HTTP服务器是这样的,接收到客户端的请求后,会把客户端发送的信息作为网页的内容反馈给客户端,也就是上图中看到的这些内容:
下面详细介绍创建该应用的步骤。
步骤1:创建Empty Ability项目。
步骤2:在module.json5配置文件加上对权限的声明:
"requestPermissions": [
{
"name": "ohos.permission.INTERNET"
}
]这里添加了获取互联网信息的权限。
步骤3:在Index.ets文件里添加如下的代码:
import { socket } from '@kit.NetworkKit';
import { BusinessError } from '@kit.BasicServicesKit';
import { util } from '@kit.ArkTS';
import { webview } from '@kit.ArkWeb';
let tcpServer: socket.TCPSocketServer = socket.constructTCPSocketServerInstance();
@Entry
@Component
struct Index {
@State message: string = '最简单的HTTP服务器示例';
@State port: number = 8080
@State running: boolean = false
@State msgHistory: string = ''
@State webUrl: string = "https://developer.huawei.com/"
scroller: Scroller = new Scroller()
webScroller: Scroller = new Scroller()
controller: webview.WebviewController = new webview.WebviewController()
build() {
RelativeContainer() {
Text(this.message)
.id('txtTitle')
.fontSize(20)
.fontWeight(FontWeight.Bold)
.alignRules({
middle: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.Center },
top: { anchor: '__container__', align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.padding(10)
Text("端口")
.id('txtPort')
.fontSize(15)
.height(40)
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: 'txtTitle', align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.padding(10)
TextInput({ text: this.port.toString() })
.onChange((value) => {
this.port = parseInt(value)
})
.type(InputType.Number)
.width(80)
.height(40)
.id('txtInputPort')
.fontSize(15)
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: 'txtPort', align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: 'txtPort', align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.padding(10)
Button(this.running ? "停止" : "启动")
.onClick(() => {
this.running = !this.running
if (this.running) {
this.start()
} else {
this.stop()
}
})
.height(40)
.width(80)
.id('butRun')
.fontSize(15)
.alignRules({
right: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: 'txtPort', align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.padding(10)
Scroll(this.scroller) {
Text(this.msgHistory)
.textAlign(TextAlign.Start)
.padding(10)
.width('100%')
.fontSize(12)
.backgroundColor(0xeeeeee)
}
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: 'butRun', align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.align(Alignment.Top)
.backgroundColor(0xeeeeee)
.height(200)
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Vertical)
.scrollBar(BarState.On)
.scrollBarWidth(20)
.padding(10)
.id('scrollHis')
Text("请求地址")
.id('txtUrl')
.fontSize(15)
.height(40)
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: 'scrollHis', align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.padding(10)
TextInput({ text: this.webUrl.toString() })
.onChange((value) => {
this.webUrl = value
})
.height(40)
.id('txtInputWebUrl')
.fontSize(15)
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: 'txtUrl', align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: 'txtUrl', align: VerticalAlign.Top },
right: { anchor: 'butWeb', align: HorizontalAlign.Start }
})
.padding(10)
Button("请求")
.onClick(() => {
this.controller.loadUrl(this.webUrl)
})
.height(40)
.width(80)
.id('butWeb')
.fontSize(15)
.alignRules({
right: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.End },
top: { anchor: 'txtUrl', align: VerticalAlign.Top }
})
.padding(10)
Scroll(this.webScroller) {
Web({ src: this.webUrl, controller: this.controller })
.padding(10)
.width('100%')
.backgroundColor(0xeeeeee)
.textZoomRatio(200)
}
.alignRules({
left: { anchor: '__container__', align: HorizontalAlign.Start },
top: { anchor: 'txtUrl', align: VerticalAlign.Bottom },
bottom: { anchor: '__container__', align: VerticalAlign.Bottom }
})
.backgroundColor(0xeeeeee)
.scrollable(ScrollDirection.Vertical)
.scrollBar(BarState.On)
.scrollBarWidth(20)
}
.height('100%')
.width('100%')
}
start() {
this.webUrl = "http://127.0.0.1:" + this.port.toString()
let listenAddr: socket.NetAddress = {
address: '0.0.0.0',
port: this.port,
family: 1
}
tcpServer.listen(listenAddr, (err: BusinessError) => {
if (err) {
this.msgHistory += "listen fail \r\n";
return;
}
this.msgHistory += "listen success \r\n";
})
tcpServer.on('connect', (clientSocket: socket.TCPSocketConnection) => {
clientSocket.on('message', (msgInfo: socket.SocketMessageInfo) => {
let requestMsg = buf2String(msgInfo.message)
this.msgHistory += requestMsg + "\r\n"
let resp = buildRespString(requestMsg)
clientSocket.send({ data: resp })
})
});
}
stop() {
tcpServer.off('connect')
}
}
//构造给客户端的应答内容
function buildRespString(content: string) {
let result: string = ""
let bodyContent = "<html>"
bodyContent += "<head>"
bodyContent += "<title>"
bodyContent += "HTTP服务器模拟"
bodyContent += "</title>"
bodyContent += "</head>"
bodyContent += "<body>"
bodyContent += "<h1>"
bodyContent += "浏览器发送的请求信息"
bodyContent += "</h1>"
bodyContent += "<pre><h2>"
bodyContent += content
bodyContent += "</h2></pre>"
bodyContent += "</body>"
bodyContent += "</html>"
let textEncoder = new util.TextEncoder();
let contentBuf = textEncoder.encodeInto(bodyContent)
result += "HTTP/1.1 200 OK \r\n"
result += "Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8 \r\n"
result += `Content-Length: ${contentBuf.length} \r\n`
result += "\r\n"
result += bodyContent
return result
}
//ArrayBuffer转utf8字符串
function buf2String(buf: ArrayBuffer) {
let msgArray = new Uint8Array(buf);
let textDecoder = util.TextDecoder.create("utf-8");
return textDecoder.decodeWithStream(msgArray)
}步骤4:编译运行,可以使用模拟器或者真机,因为当前还处于内测期间,只能使用模拟器。
步骤5:具体的操作过程上面讲过了,就不再赘述了。
3. 关键功能分析
比较关键的代码如下:
tcpServer.on('connect', (clientSocket: socket.TCPSocketConnection) => {
clientSocket.on('message', (msgInfo: socket.SocketMessageInfo) => {
let requestMsg = buf2String(msgInfo.message)
this.msgHistory += requestMsg + "\r\n"
let resp = buildRespString(requestMsg)
clientSocket.send({ data: resp })
})
});这里连接后得到了clientSocket对象,然后继续订阅clientSocket对象的收到客户端消息事件,把消息转换为字符串,然后写入到历史日志msgHistory里。这里buildRespString函数是创建返回给客户端的信息的,最后通过clientSocket的send方法发送给客户端。
虽然本示例比较简单,但是具备了HTTP服务端的基本功能,可以接收客户端的输入,并且可以对客户端的输入进行处理,最后再发送给客户端。

























 1058
1058

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








