The Maximum Number of Strong Kings
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 2010 | Accepted: 934 |
Description
A tournament can be represented by a complete graph in which each vertex denotes a player and a directed edge is from vertex x to vertex y if player x beats player y. For a player x in a tournament T, the score of x is the number of players beaten by x. The
score sequence of T, denoted by S(T) = (s1, s2, . . . , sn), is a non-decreasing list of the scores of all the players in T. It can be proved that S(T) = (s1, s2, . . . , sn) is a score sequence of T if and only if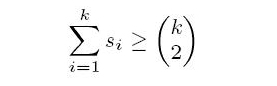
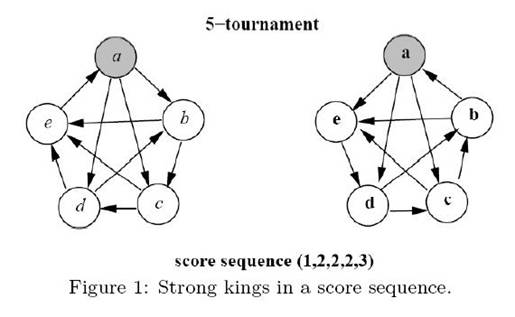
for k = 1, 2, . . . , n and equality holds when k = n. A player x in a tournament is a strong king if and only if x beats all of the players whose scores are greater than the score of x. For a score sequence S, we say that a tournament T realizes S if S(T) = S. In particular, T is a heavy tournament realizing S if T has the maximum number of strong kings among all tournaments realizing S. For example, see T2 in Figure 1. Player a is a strong king since the score of player a is the largest score in the tournament. Player b is also a strong king since player b beats player a who is the only player having a score larger than player b. However, players c, d and e are not strong kings since they do not beat all of the players having larger scores.
The purpose of this problem is to find the maximum number of strong kings in a heavy tournament after a score sequence is given. For example,Figure 1 depicts two possible tournaments on five players with the same score sequence (1, 2, 2, 2, 3). We can see that there are at most two strong kings in any tournament with the score sequence (1, 2, 2, 2, 3) since the player with score 3 can be beaten by only one other player. We can also see that T2 contains two strong kings a and b. Thus, T2 is one of heavy tournaments. However, T1 is not a heavy tournament since there is only one strong king in T1. Therefore, the answer of this example is 2.
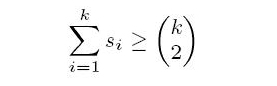
for k = 1, 2, . . . , n and equality holds when k = n. A player x in a tournament is a strong king if and only if x beats all of the players whose scores are greater than the score of x. For a score sequence S, we say that a tournament T realizes S if S(T) = S. In particular, T is a heavy tournament realizing S if T has the maximum number of strong kings among all tournaments realizing S. For example, see T2 in Figure 1. Player a is a strong king since the score of player a is the largest score in the tournament. Player b is also a strong king since player b beats player a who is the only player having a score larger than player b. However, players c, d and e are not strong kings since they do not beat all of the players having larger scores.
The purpose of this problem is to find the maximum number of strong kings in a heavy tournament after a score sequence is given. For example,Figure 1 depicts two possible tournaments on five players with the same score sequence (1, 2, 2, 2, 3). We can see that there are at most two strong kings in any tournament with the score sequence (1, 2, 2, 2, 3) since the player with score 3 can be beaten by only one other player. We can also see that T2 contains two strong kings a and b. Thus, T2 is one of heavy tournaments. However, T1 is not a heavy tournament since there is only one strong king in T1. Therefore, the answer of this example is 2.

Input
The first line of the input file contains an integer m, m <= 10, which represents the number of test cases. The following m lines contain m score sequences in which each line contains a score sequence. Note that each score sequence contains at most ten scores.
Output
The maximum number of strong kings for each test case line by line.
Sample Input
5 1 2 2 2 3 1 1 3 4 4 4 4 3 3 4 4 4 4 5 6 6 6 0 3 4 4 4 5 5 5 6 0 3 3 3 3 3
Sample Output
2 4 5 3 5题意:有m个测试样例,每个测试样例给出n个人的分数(注意是赢的分数!!保持非递减,这里以为是输的分数调了一晚上,真是哔了狗了...),明明样例解释的是输的分数
问最多有几个strong king (分数全场最高之一,或者打赢了所有分数比他高的人)
思路:看这位大神的,写的十分详细。
http://blog.youkuaiyun.com/sdj222555/article/details/7797257
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define N 1000
#define INF 99999999
struct Edge
{
int v,next,cap;
} edge[N*N];
char a[100];
int num[15],n,m;
int ma[15][15],vis[15][15],head[N],cnt,d[N];
void init()
{
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
cnt=0;
}
void addedge(int u,int v,int cap)
{
edge[cnt].v=v,edge[cnt].cap=cap;
edge[cnt].next=head[u],head[u]=cnt++;
edge[cnt].v=u,edge[cnt].cap=0;
edge[cnt].next=head[v],head[v]=cnt++;
}
int bfs(int s,int t)
{
memset(d,-1,sizeof(d));
d[s]=0;
queue<int>q;
q.push(s);
while(!q.empty())
{
int u=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=head[u]; i!=-1; i=edge[i].next)
{
int v=edge[i].v,cap=edge[i].cap;
if(d[v]==-1&&cap>0)
{
d[v]=d[u]+1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return d[t]!=-1;
}
int dfs(int s,int t,int f)
{
if(s==t||f==0) return f;
int flow=0;
for(int i=head[s]; i!=-1; i=edge[i].next)
{
int v=edge[i].v,cap=edge[i].cap;
if(d[v]==d[s]+1&&cap>0)
{
int x=min(f-flow,cap);
x=dfs(v,t,x);
flow+=x;
edge[i].cap-=x;
edge[i^1].cap+=x;
}
}
if(!flow) d[s]=-2;
return flow;
}
int Dinic(int s,int t)
{
int flow=0,f;
while(bfs(s,t))
{
while(f=dfs(s,t,INF))
flow+=f;
}
return flow;
}
int ans(int k)
{
init();
int s=0,t=n+m+1;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
addedge(s,i,num[i]);
for(int i=n+1;i<=n+m;i++)
addedge(i,t,1);
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=n-k+1; i<=n; i++)
for(int j=i+1; j<=n; j++)
if(num[i]<num[j])
{
addedge(i,ma[i][j],1);
vis[i][j]=1;
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(int j=i+1; j<=n; j++)
if(!vis[i][j])
{
addedge(i,ma[i][j],1);
addedge(j,ma[i][j],1);
}
return Dinic(s,t);
}
void solve()
{
for(int i=n;; i--)
if(ans(i)==n*(n-1)/2)
{
printf("%d\n",i);
return;
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
getchar();
while(T--)
{
gets(a);
n=m=0;
for(int i=0; i<strlen(a); i++)
{
if(a[i]>='0'&&a[i]<='9')
{
num[++n]=a[i]-'0';
if(i<strlen(a)-1&&a[i+1]>='0'&&a[i+1]<='9')
{
num[n]=num[n]*10+a[i+1]-'0';
i++;
}
}
}
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++)
for(int j=i+1; j<=n; j++)
ma[i][j]=ma[j][i]=n+(++m);
solve();
}
return 0;
}





















 1287
1287

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








