前言
现在网上已经很多事件分发机制解析的文章了,很多文章讲的很详细。但是发现每次看完相关的文章后,当时看的挺明白,过后就忘,算了还是自己写篇文章记录一下,加深印象。加深理解。
储备知识
看本篇文章就默认的认为你已经掌握了以下几点:
1、事件分发相关的三个方法dispatchTouchEvent、onInterceptTouchEvent、onTouchEvent,其中默认情况下:ViewGroup中没有onTouchEvent方法;View中没有onInterceptTouchEvent方法;dispatchTouchEvent同时存在于ViewGroup和View中。
2、触摸事件包括按下(Down)、移动(Move)、抬起(Up)、取消(Cancel)等。
3、触摸事件第一次被处理是在Activity的dispatchTouchEvent方法
4、Window类的唯一实现类是PhoneWindow;DecorView继承自FrameLayout
下面从Activity开始分析。
源码
Activity#dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event)
/**
* Called to process touch screen events. You can override this to
* intercept all touch screen events before they are dispatched to the
* window. Be sure to call this implementation for touch screen events
* that should be handled normally.
*
* @param ev The touch screen event.
*
* @return boolean Return true if this event was consumed.
*/
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
onUserInteraction();//默认是个空方法,由用户自己实现,开发屏保相关的功能可以使用该方法
}
if (getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev)) {//如果为true,则不会再调用Activity的OnTouchEvent(ev)方法
return true;
}
return onTouchEvent(ev);
}
由储备知识点可以知道getWindow()获取的是PhoneWindow对象,所以看PhoneWindow的superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev)方法:
@Override
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return mDecor.superDispatchTouchEvent(event);
}
mDecor是DecorView类型对象,跟进去发现就是单纯的调用父类的方法dispatchTouchEvent,具体代码就不贴了、贴一下ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法:
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
//代码省略
boolean handled = false;
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(ev)) {
final int action = ev.getAction();
final int actionMasked = action & MotionEvent.ACTION_MASK;
//省略代码:down事件来的时候,就重置之前保存的各种状态
// Check for interception.
final boolean intercepted;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) {
//判断mGroupFlags是否设置了FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT,若设置了。则不拦截,默认不设置
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
if (!disallowIntercept) {
//注释1===调用onInterceptTouchEvent方法
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev);
ev.setAction(action); // restore action in case it was changed
} else {
intercepted = false;
}
} else {
// There are no touch targets and this action is not an initial down
// so this view group continues to intercept touches.
intercepted = true;
}
//省略部分带码
if (!canceled && !intercepted) {
// If the event is targeting accessiiblity focus we give it to the
// view that has accessibility focus and if it does not handle it
// we clear the flag and dispatch the event to all children as usual.
// We are looking up the accessibility focused host to avoid keeping
// state since these events are very rare.
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| (split && actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_HOVER_MOVE) {
final int childrenCount = mChildrenCount;
if (newTouchTarget == null && childrenCount != 0) {
//...
//遍历子view
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
final int childIndex = getAndVerifyPreorderedIndex(
childrenCount, i, customOrder);
final View child = getAndVerifyPreorderedView(
preorderedList, children, childIndex);
//省略
//判断触摸点是否在当前子view中、若不在继续遍历下一个子view
if (!canViewReceivePointerEvents(child)
|| !isTransformedTouchPointInView(x, y, child, null)) {
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
continue;
}
//省略
//注释2===判断当前子view是否消费点击事件 若消费掉、就调出循环不在遍历剩余子view
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {
// ...
mLastTouchDownX = ev.getX();
mLastTouchDownY = ev.getY();
newTouchTarget = addTouchTarget(child, idBitsToAssign);
alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget = true;
break;
}
// The accessibility focus didn't handle the event, so clear
// the flag and do a normal dispatch to all children.
ev.setTargetAccessibilityFocus(false);
}
if (preorderedList != null) preorderedList.clear();
}
//略。。
}
}
// Dispatch to touch targets.
//没有子view接受触摸事件、交给自己处理,注意第三个参数为null
//注释3
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {
// No touch targets so treat this as an ordinary view.
handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,
TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);
} else {//已有接收触摸Down事件的子view剩余事件均交给它
// Dispatch to touch targets, excluding the new touch target if we already
// dispatched to it. Cancel touch targets if necessary.
TouchTarget predecessor = null;
TouchTarget target = mFirstTouchTarget;
while (target != null) {
final TouchTarget next = target.next;
//已经传递过的事件、不再传递
if (alreadyDispatchedToNewTouchTarget && target == newTouchTarget) {
handled = true;
} else {
//分发剩余事件
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, cancelChild,
target.child, target.pointerIdBits)) {
handled = true;
}
//略
}
predecessor = target;
target = next;
}
}
}
return handled;
}
以上代码大致逻辑是Down事件进来后,先判断FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT是否禁止分发,一般为false,然后调用注释1处的onInterceptTouchEvent方法
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.isFromSource(InputDevice.SOURCE_MOUSE)
&& ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& ev.isButtonPressed(MotionEvent.BUTTON_PRIMARY)
&& isOnScrollbarThumb(ev.getX(), ev.getY())) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
默认返回false(不拦截)。然后回遍历子View、判断触摸点落在哪个子view内部,如果找到那个子View后调用注释2处的dispatchTransformedTouchEvent方法:
/**
* Transforms a motion event into the coordinate space of a particular child view,
* filters out irrelevant pointer ids, and overrides its action if necessary.
* If child is null, assumes the MotionEvent will be sent to this ViewGroup instead.
*/
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,
View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {
final boolean handled;
//略
// Perform any necessary transformations and dispatch.
//根据child是否为null 调用父类View或子View的dispatchTouchEvent方法
if (child == null) {
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
} else {
//略
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
}
return handled;
}
假如这里找到这里找到子View。那事件就会被分发到子View中。若果子View还是一个ViewGroup、那调用逻辑跟以上分析的一致。若子View不是ViewGroup。就会调用View的dispatchTouchEvent:
/**
* Pass the touch screen motion event down to the target view, or this
* view if it is the target.
*
* @param event The motion event to be dispatched.
* @return True if the event was handled by the view, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
//默认返回结果false 不消费事件
boolean result = false;
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
//noinspection SimplifiableIfStatement
//判断当前view是否设置了onTouchListener回调、若设置并返回true。则不再调用onTouchEvent方法
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
//若设置并返回true。则不再调用onTouchEvent方法
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
//略
return result;
}
在子view中onTouchEvent方法的调用受制于onTouchListener的设置及返回值、默认不设置、则会调用onTouchEvent
/**
* Implement this method to handle touch screen motion events.
* <p>
* If this method is used to detect click actions, it is recommended that
* the actions be performed by implementing and calling
* {@link #performClick()}. This will ensure consistent system behavior,
* including:
* <ul>
* <li>obeying click sound preferences
* <li>dispatching OnClickListener calls
* <li>handling {@link AccessibilityNodeInfo#ACTION_CLICK ACTION_CLICK} when
* accessibility features are enabled
* </ul>
*
* @param event The motion event.
* @return True if the event was handled, false otherwise.
*/
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (clickable || (viewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
boolean prepressed = (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PREPRESSED) != 0;
if ((mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_PRESSED) != 0 || prepressed) {
//在down中检查是否有长点击事件,若没有执行以下逻辑
if (!mHasPerformedLongPress && !mIgnoreNextUpEvent) {
// This is a tap, so remove the longpress check
removeLongPressCallback();
// Use a Runnable and post this rather than calling
// performClick directly. This lets other visual state
// of the view update before click actions start.
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
//使用一个runnable来处理点击事件,这让其他视图view在点击事件开始之前更新状态,如果post失败,再直接调用;performClick就是处理onClickListener的方法
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClick();
}
}
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
mHasPerformedLongPress = false;
if (!clickable) {
//检查长点击事件
checkForLongClick(0, x, y);
break;
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL:
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
break;
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
onTouchEvent对各个事件的处理有一个条件、就是clickable=true、若成立,则返回true、并处理其中的点击事件,若不成立则返回false、回到上一个方法。若是一个clickable==false的子view、则view的dispatchTouchEvent返回的为false表示没有分发此事件、继续往回返、返到dispatchTransformedTouchEvent方法也返回false、继续往回返回到viewgroup中对子view遍历调用都为false、没有找到消费该down事件的子view、该方法继续往下走、调用到注释3、调用dispatchTransformedTouchEvent但是此时传的child参数为null、所以调用super.dispatchTouchEvent,即view的dispatchTouchEvent方法、逻辑再走一遍、会走view的onTouchEvent方法、此viewgroup的clickable默认也为false、即返回false、然后一层层往上传回来、注释3处的handle为false。此事件就处理完毕、没有一个view消费此事件。
回过头来看、在viewgroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法的遍历子view调用dispatchTransformedTouchEvent那处代码、若有子view是clickable的,比如Button控件、则onTouchEvent返回true,所以dispatchTransformedTouchEvent返回true、说明找到消费此事件的子View了、然后在注释3出、就不会走第一个分支逻辑、会走第二个、把剩余的事件均交给此子View处理。讲到这里、只ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent方法中调用的onInterceptTouchEvent方法返回默认值false的情况。
如果onInterceptTouchEvent返回true,则下面的注释2中if判断那一堆逻辑就不会走了、不会遍历子View、而是直接进入注释3、调用dispatchTransformedTouchEvent,参数child为null、则直接调用view的dispatchTouchEvent方法。则会调用到自己的onTouchEvent方法
总结
- 事件分发从
Activity的dispatchTouchEvent开始、经历PhoneWindow----->DecorView----->ViewGroup#dispatchTouchEvent方法ViewGroup的dispatchTouchEvent----------调用------>ViewGroup的onInterceptTouchEvent。onInterceptTouchEvent:若返回false,则遍历子view,找到处理触摸事件的子view,并调用child.dispatchTouchEvent方法把触摸事件分发下去;若返回true,则不遍历子view,直接调用super.dispatchTouchEvent方法,自己处理触摸事件;默认返回false。3.1.
onInterceptTouchEvent返回false:
child.dispatchTouchEvent此方法中会判断onTouchListener是否不为null,且onTouch方法是否返回true。若不成立则调用自己的onTouchEvent方法;若成立,则不会执行自己的onTouchEvent方法3.1.1.
onTouchEvent返回true:
触摸事件被消费,接下来的move和up等事件均交由此view处理
3.1.2.onTouchEvent返回false:
最终会返回到第3点,遍历子view并判断是否有子view消费事件的那个逻辑,没有子view消费此事件3.2.
onInterceptTouchEvent返回true:
自己拦截触摸事件
- 第3.1.2和第3.2之后的逻辑都是需要自己询问自己是否拦截此触摸事件的逻辑,会调用
super.dispatchTouchEvent方法
5.在super.dispatchTouchEvent方法中(同3.1中child.dispatchTouchEvent),判断是否设置onTouchListener且
onTouch方法是否返回true,若不成立则调用自己的onTouchEvent方法;
最后来张流程图吧
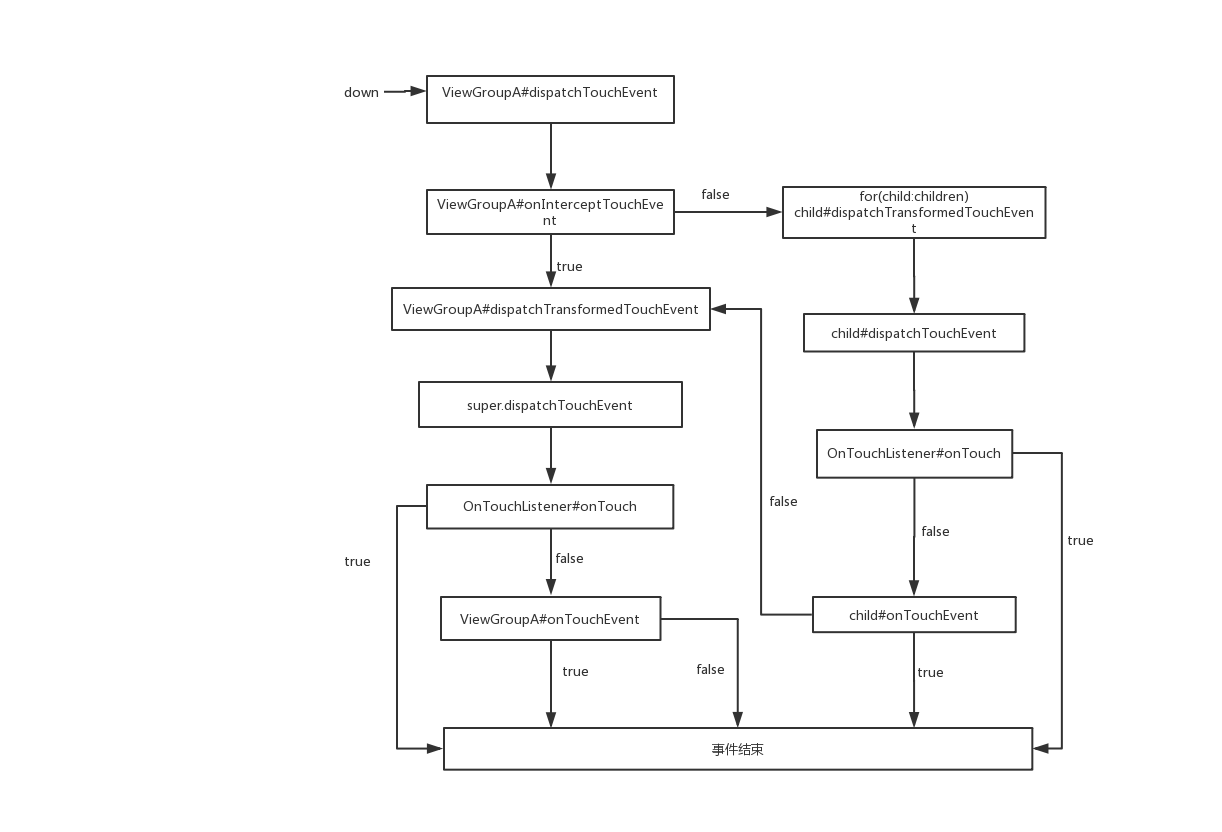
写的匆忙,如有不当的地方请指正
 Android事件分发机制详解
Android事件分发机制详解





 本文深入剖析Android事件分发机制,从Activity的dispatchTouchEvent开始,详细解释了事件如何在ViewGroup和View之间传递,包括onInterceptTouchEvent、onTouchEvent等关键方法的作用,以及事件在不同层级的消费和拦截逻辑。
本文深入剖析Android事件分发机制,从Activity的dispatchTouchEvent开始,详细解释了事件如何在ViewGroup和View之间传递,包括onInterceptTouchEvent、onTouchEvent等关键方法的作用,以及事件在不同层级的消费和拦截逻辑。
















 840
840

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








