Mybatis是如何实现日志功能的呢?市面上又有非常多的日志框架,比如:log4j、slf4j、logback等......
Mybatis提供了一个灵活的日志模块,支持多种日志框架。通过配置日志框架,可以方便地记录 MyBatis 的运行日志,帮助调试和监控应用程序。
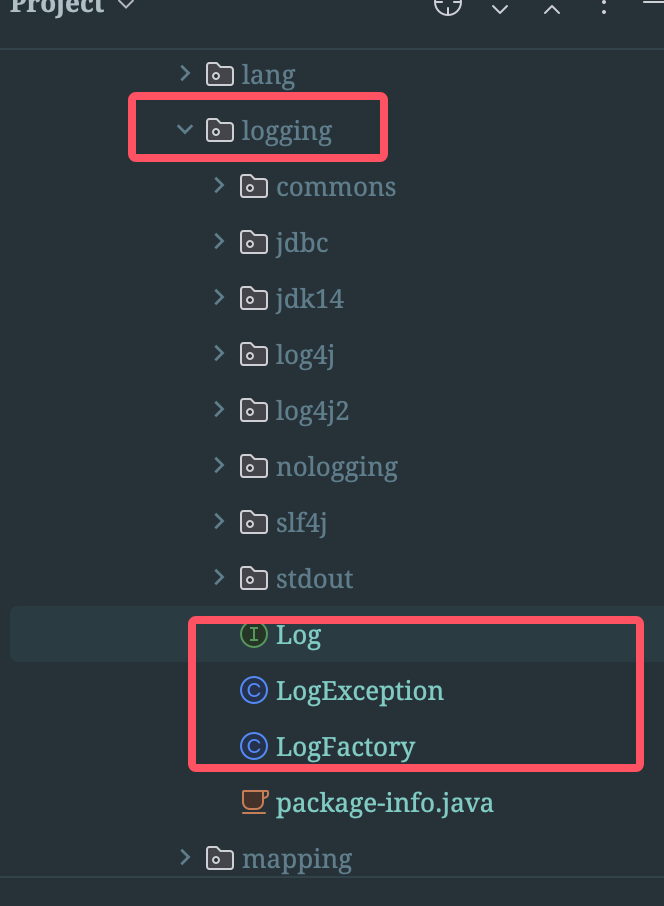
1. Mybatis的日志工作原理
1.1. Log接口
MyBatis 的日志模块通过一个抽象的 org.apache.ibatis.logging.Log 接口来实现日志记录功能。MyBatis 提供了多个实现类,每个实现类对应一个具体的日志框架。在初始化 MyBatis 时,会根据配置选择合适的日志实现
public interface Log {
boolean isDebugEnabled();
boolean isTraceEnabled();
void error(String s, Throwable e);
void error(String s);
void debug(String s);
void trace(String s);
void warn(String s);
支持的日志框架
- Log4j
- SLF4J
- Logback
- Java Util Logging
- Commons Logging
- No Logging(不记录日志)
1.2. LogFactory
LogFactory 类负责创建 Log 接口的具体实现。它会根据配置和可用的日志框架选择合适的实现类。
public final class LogFactory {
/**
* Marker to be used by logging implementations that support markers.
*/
public static final String MARKER = "MYBATIS";
//Log实现类的构造器
private static Constructor<? extends Log> logConstructor;
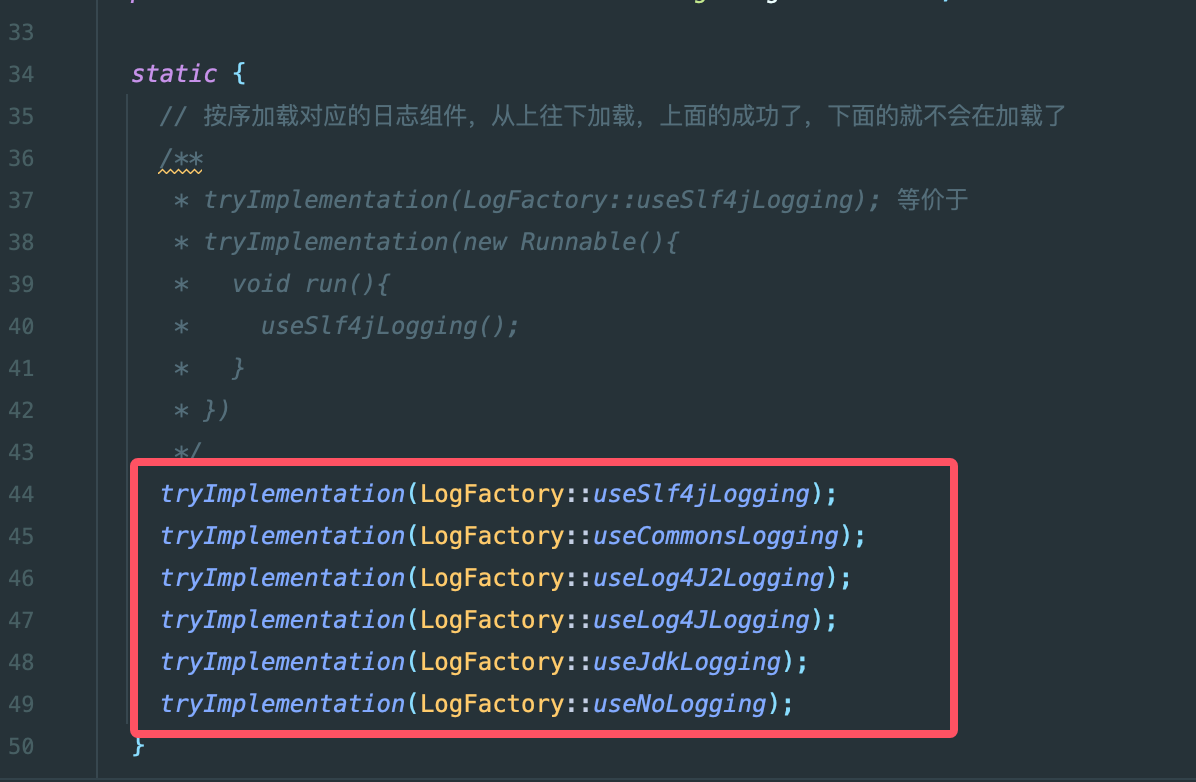
static {
// 按序加载对应的日志组件,从上往下加载,上面的成功了,下面的就不会在加载了
/**
* tryImplementation(LogFactory::useSlf4jLogging); 等价于
* tryImplementation(new Runnable(){
* void run(){
* useSlf4jLogging();
* }
* })
*/
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useSlf4jLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useCommonsLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useLog4J2Logging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useLog4JLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useJdkLogging);
tryImplementation(LogFactory::useNoLogging);
}
private LogFactory() {
// disable construction
}
public static Log getLog(Class<?> aClass) {
return getLog(aClass.getName());
}
public static Log getLog(String logger) {
try {
return logConstructor.newInstance(logger);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error creating logger for logger " + logger + ". Cause: " + t, t);
}
}
public static synchronized void useCustomLogging(Class<? extends Log> clazz) {
setImplementation(clazz);
}
public static synchronized void useSlf4jLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.slf4j.Slf4jImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useCommonsLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.commons.JakartaCommonsLoggingImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useLog4JLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.log4j.Log4jImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useLog4J2Logging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.log4j2.Log4j2Impl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useJdkLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.jdk14.Jdk14LoggingImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useStdOutLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl.class);
}
public static synchronized void useNoLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.nologging.NoLoggingImpl.class);
}
private static void tryImplementation(Runnable runnable) {
if (logConstructor == null) {
try {
runnable.run();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// ignore
}
}
}
private static void setImplementation(Class<? extends Log> implClass) {
try {
// 获取指定适配器的构造方法
Constructor<? extends Log> candidate = implClass.getConstructor(String.class);
// 实例化适配器
Log log = candidate.newInstance(LogFactory.class.getName());
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Logging initialized using '" + implClass + "' adapter.");
}
// 初始化 logConstructor 字段
logConstructor = candidate;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error setting Log implementation. Cause: " + t, t);
}
}
}重点关注它的静态代码块,可以发现会在静态代码块中按顺序加载日志的适配类,加载到第一个成功了就不会继续加载其他的实现类了
private static void tryImplementation(Runnable runnable) {
//不为空才会加载
if (logConstructor == null) {
try {
runnable.run();
} catch (Throwable t) {
// ignore
}
}
}public static synchronized void useSlf4jLogging() {
setImplementation(org.apache.ibatis.logging.slf4j.Slf4jImpl.class);
}private static void setImplementation(Class<? extends Log> implClass) {
try {
// 获取指定适配器的构造方法
Constructor<? extends Log> candidate = implClass.getConstructor(String.class);
// 实例化适配器
Log log = candidate.newInstance(LogFactory.class.getName());
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Logging initialized using '" + implClass + "' adapter.");
}
// 初始化 logConstructor 字段
logConstructor = candidate;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error setting Log implementation. Cause: " + t, t);
}
}2. 日志配置加载
在Mybatis使用中,如果我们想要指定Mybatis的日志实现类,应该怎么做呢?
1、先在配置文件的settings标签中指定日志实现类
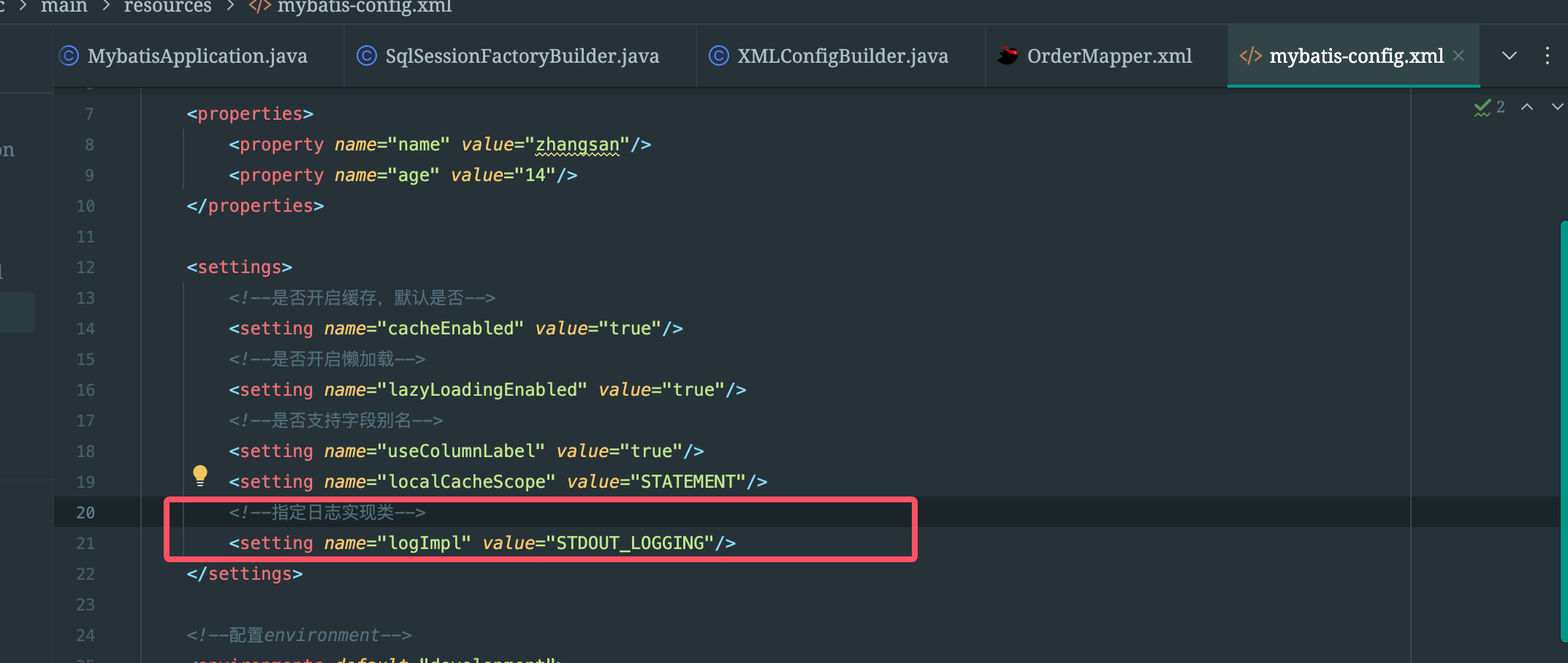
这个日志实现类的别名是怎么来的?还是在Configuration的无参构造中默认加载的
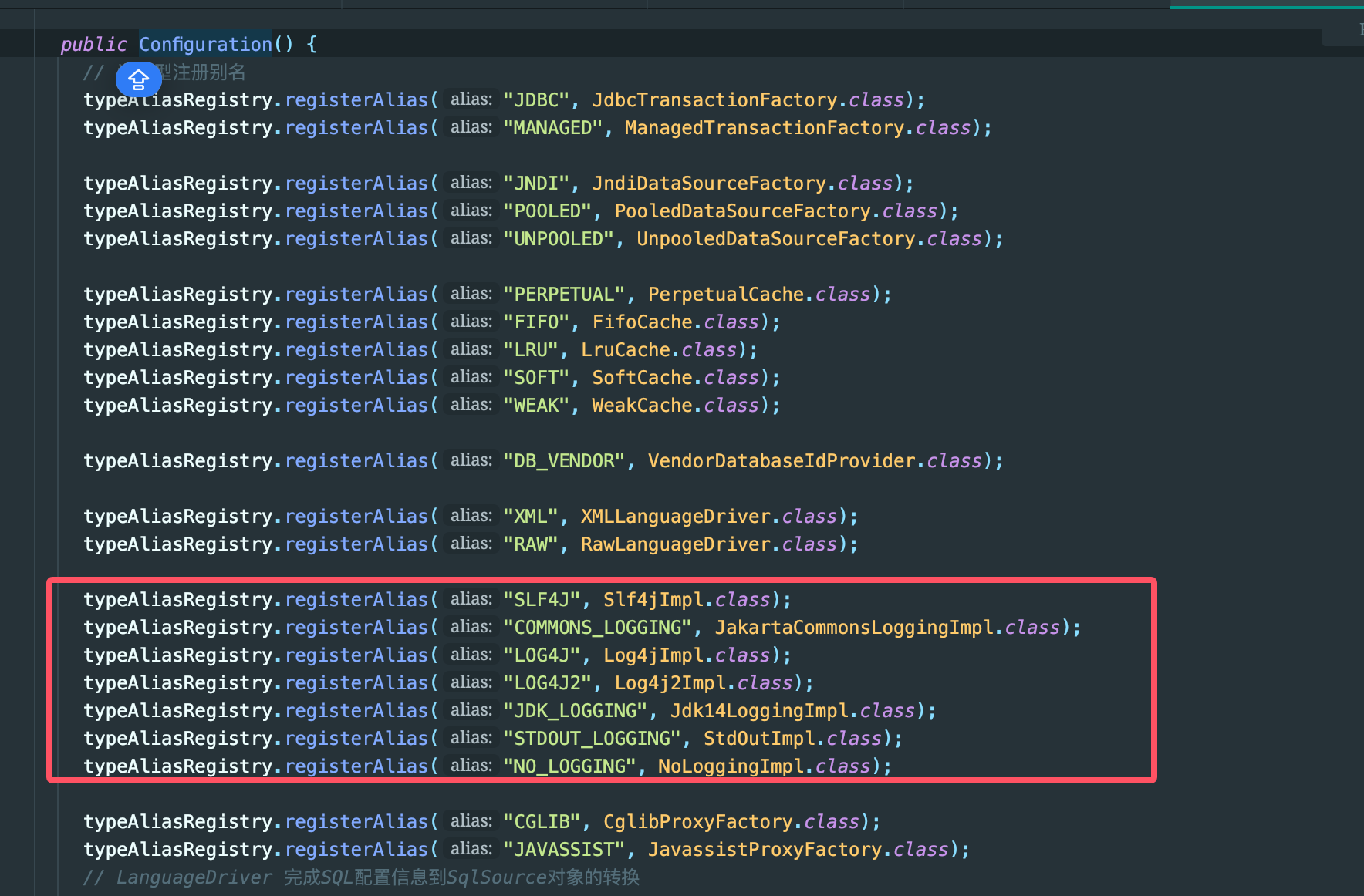
加载日志配置类,肯定是找配置解析,settings标签附近
配置解析咱就不说了,前面已经说过很多遍了,直接定位到日志配置的地方
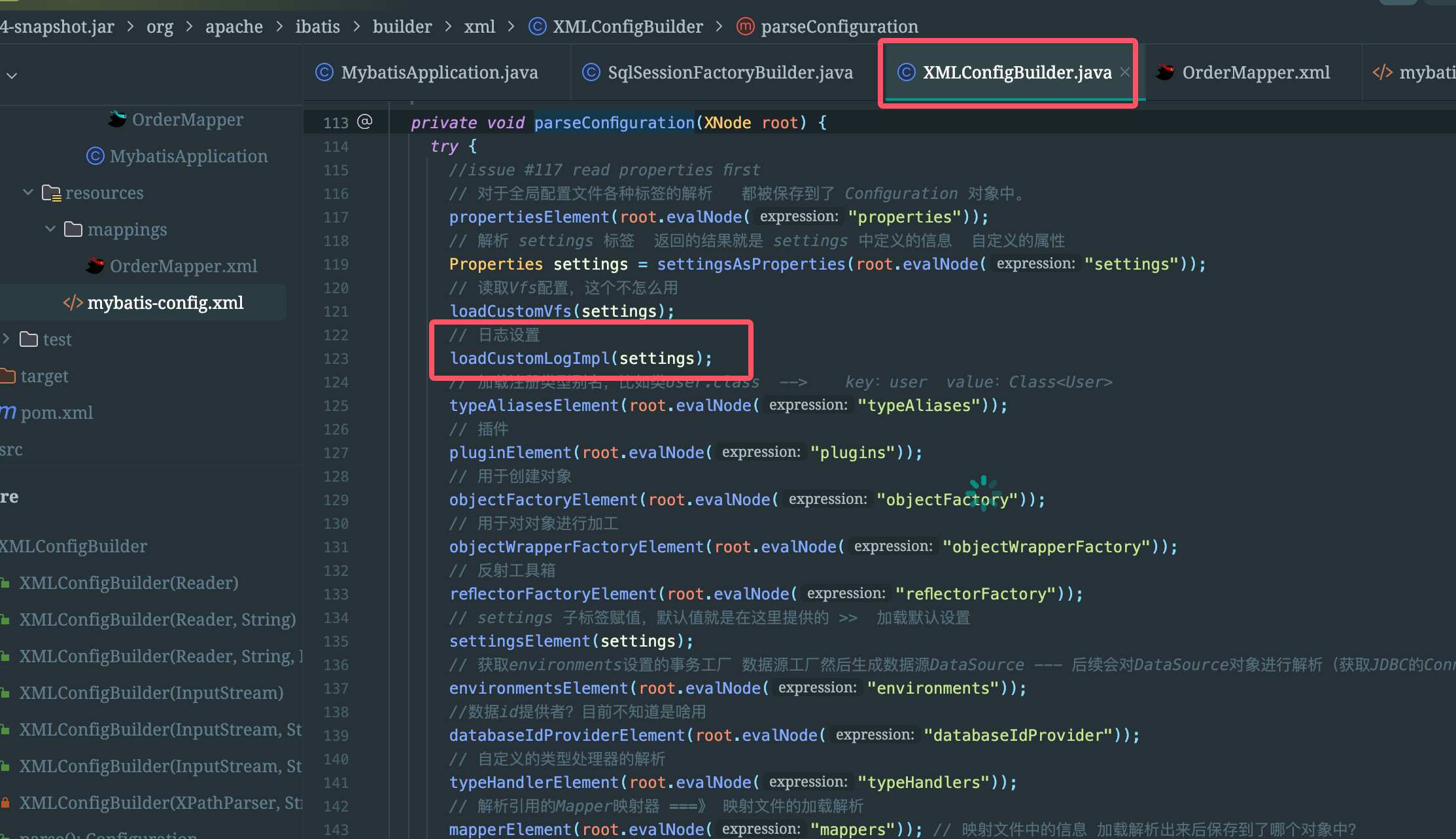
private void loadCustomLogImpl(Properties props) {
// 获取 logImpl设置的 日志 类型
Class<? extends Log> logImpl = resolveClass(props.getProperty("logImpl"));
// 设置日志 这块代码是我们后面分析 日志 模块的 关键代码
configuration.setLogImpl(logImpl);
}public void setLogImpl(Class<? extends Log> logImpl) {
if (logImpl != null) {
this.logImpl = logImpl; // 记录日志的类型
// 设置 适配选择
LogFactory.useCustomLogging(this.logImpl);
}
}public static synchronized void useCustomLogging(Class<? extends Log> clazz) {
setImplementation(clazz);
}这个方法有没有感觉很熟悉,对了,其实就是上面说过的LogFactory的静态代码块也有此方法
private static void setImplementation(Class<? extends Log> implClass) {
try {
// 获取指定适配器的构造方法
Constructor<? extends Log> candidate = implClass.getConstructor(String.class);
// 实例化适配器
Log log = candidate.newInstance(LogFactory.class.getName());
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Logging initialized using '" + implClass + "' adapter.");
}
// 初始化 logConstructor 字段
logConstructor = candidate;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw new LogException("Error setting Log implementation. Cause: " + t, t);
}
}这个方法就是直接设置我们指定的日志实现类了,至此,LogFactory和具体的logConstructor已经完成绑定,并且会输出日志log.debug("Logging initialized using '" + implClass + "' adapter.");
我们可以启动Mybatis项目的时候验证一下,是否输出这句语句。

成功输出我们配置的控制台输出方式的日志配置
3. 日志执行
Mybatis的日志在哪些地方会执行呢?
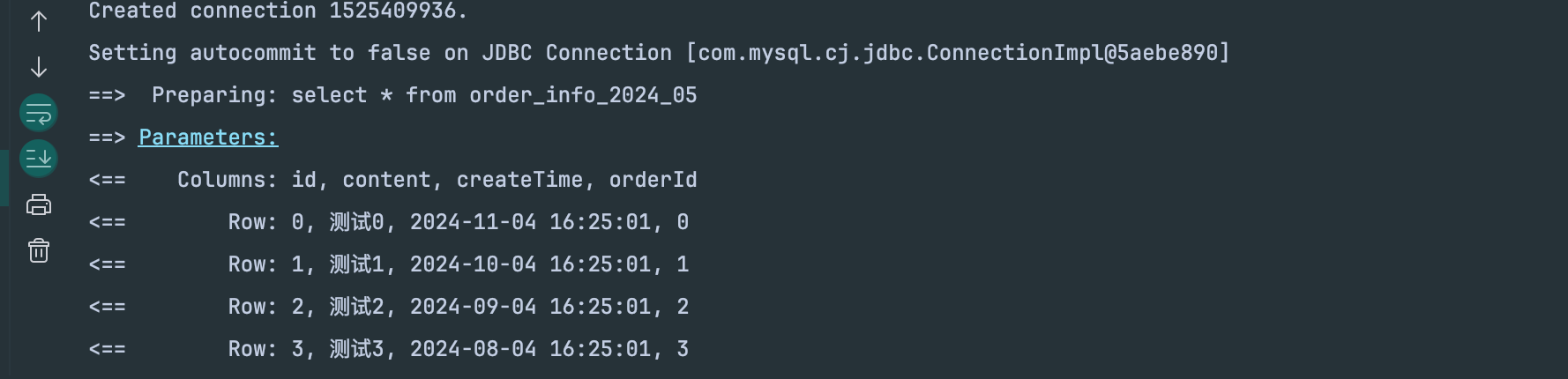
获取Connection连接
执行sql的时候就会打印对应的sql语句、参数、返回值
输出条数等
接下来我们就要去找,哪个地方会调用日志模块,应该是找sql执行的地方了。
sql执行的源码流程可以看前面的章节,这里直接定位到SimpleExecutor.doQuery()方法
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 注意,已经来到SQL处理的关键对象 StatementHandler >> 同时会完成 parameterHandler和resultSetHandler的实例化
// 默认创建的是 PreparedStatementHandler
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 获取一个 Statement对象 对占位符处理
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行查询
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
// 用完就关闭
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}之前一直觉得日志打印就在具体操作sql的方法,所以一直去handler.query()方法,但是没发现有日志打印的线索。
其实Mybatis又是用了动态代理的功能,实现Connection类和PreparedStatement、ResultSet,封装了一层日志打印的功能。
所有应该去获取Connection的地方找。
也就是代码 stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt;
// 放开了日志 会创建 Connection 的代理对象
Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);
// 获取 Statement 对象 ==》 PreparedStatement对象 Statement 如果放开了日志 则会创建 Statement 对应的代理对象
stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());
// 为 Statement 设置参数 如果是Prepare dStatement处理则会对 对应的占位符赋值
handler.parameterize(stmt);
return stmt;
}进去getConnection方法,不看不知道🙈 一看吓一跳
protected Connection getConnection(Log statementLog) throws SQLException {
// 获取到了真正的 Connection 对象 ? 如果有连接池管理 在此处获取的是PooledConnection 是Connection的代理对象
Connection connection = transaction.getConnection();
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
// 创建Connection的日志代理对象
return ConnectionLogger.newInstance(connection, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
// 返回的是真正的Connection 没有走代理的方式
return connection;
}
}这里会先获取到原始的Connection对象
判断当前的mapperStatmement的statementLog对象是否开启debug日志功能
是的话会创建动态代理对象
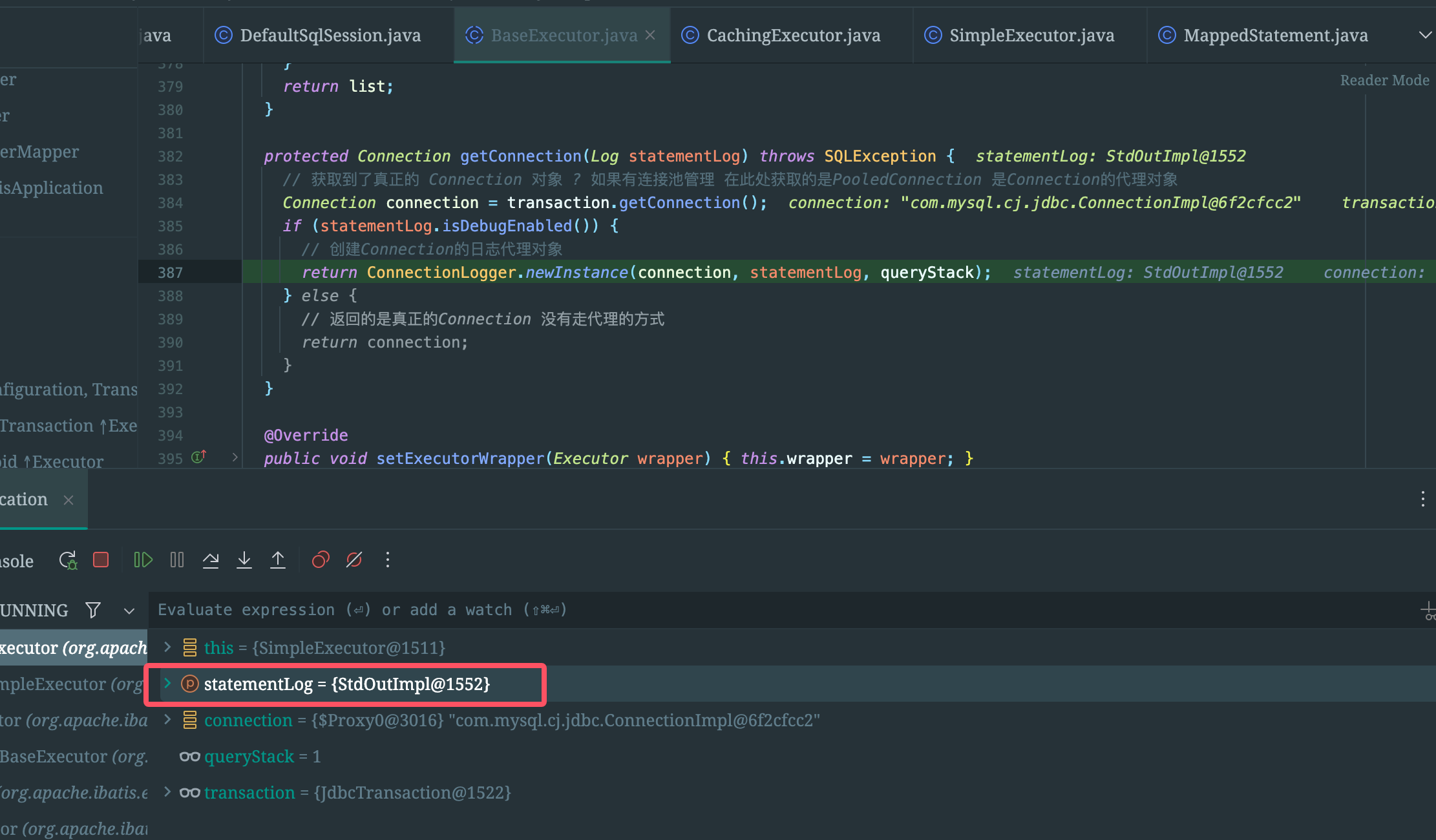
疑问❓这里的statementLog哪里来的?而且还是StdOutImpl对象,就是我们配置的日志类
可以自己去找一下,应该就在加载CRUD标签时,拿到LogFactory,顺便初始化到mapperStatement中
public static Connection newInstance(Connection conn, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new ConnectionLogger(conn, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = Connection.class.getClassLoader();
// 创建了 Connection的 代理对象 目的是 增强 Connection对象 给他添加了日志功能
return (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{Connection.class}, handler);
}这里的代码就很熟悉了,就是jdk的动态代理。看到动态代理,就得看对应InvocationHandler类的invoke方法,看看到底是增强了什么。
jdbc目录是对应Mybatis执行日志的实现地方。用了jdk的动态代理
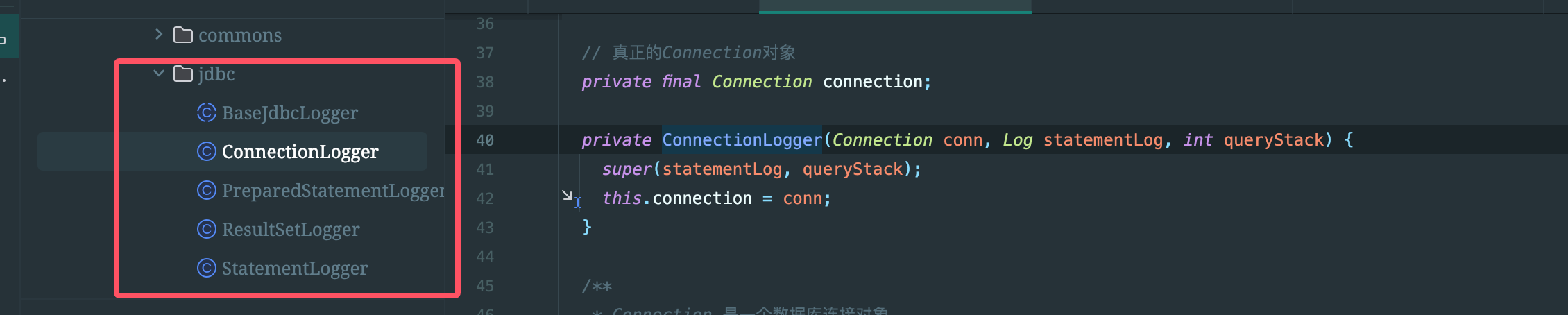
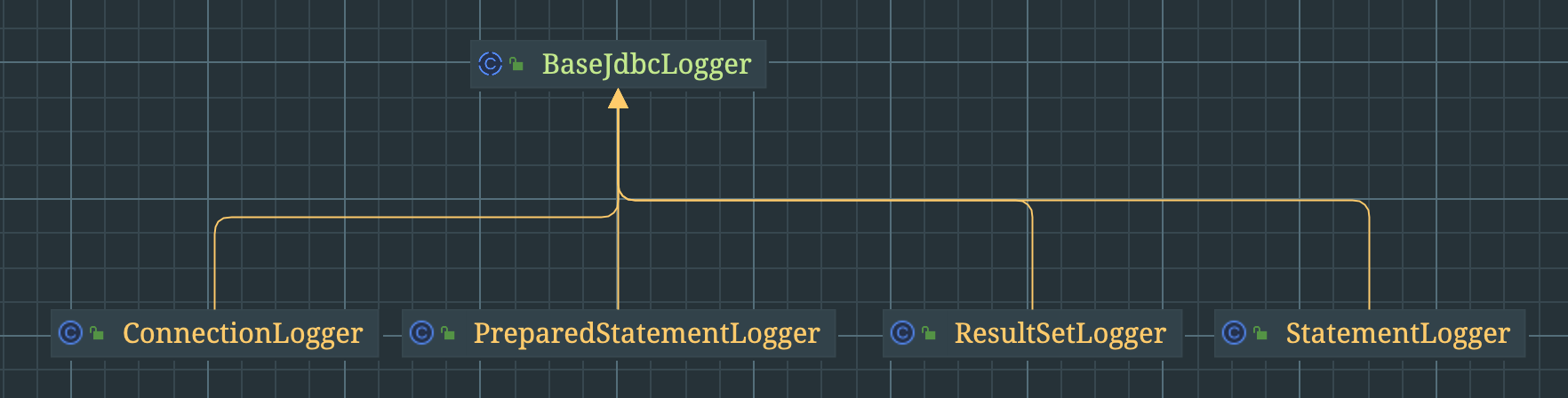
可以看到这里有对Connection、PreparedStatment、ResultSet和Statment的代理类,对的上jdbc的代码执行
BaseJdbcLogger没什么,就是存储了一下set方法名称(对应jdbc的PreparedStatment的setInt、SetNull等方法),executor方法名称(jdbc的execute、executeUpdate方法等)。
public abstract class BaseJdbcLogger {
// 记录 PreparedStatement 接口中定义的常用的set*() 方法
protected static final Set<String> SET_METHODS;
// 记录了 Statement 接口和 PreparedStatement 接口中与执行SQL语句有关的方法
protected static final Set<String> EXECUTE_METHODS = new HashSet<>();
// 记录了PreparedStatement.set*() 方法设置的键值对
private final Map<Object, Object> columnMap = new HashMap<>();
// 记录了PreparedStatement.set*() 方法设置的键 key
private final List<Object> columnNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 记录了PreparedStatement.set*() 方法设置的值 Value
private final List<Object> columnValues = new ArrayList<>();
protected final Log statementLog;// 用于日志输出的Log对象
protected final int queryStack; // 记录了SQL的层数,用于格式化输出SQL
/*
* Default constructor
*/
public BaseJdbcLogger(Log log, int queryStack) {
this.statementLog = log;
if (queryStack == 0) {
this.queryStack = 1;
} else {
this.queryStack = queryStack;
}
}
static {
SET_METHODS = Arrays.stream(PreparedStatement.class.getDeclaredMethods())
.filter(method -> method.getName().startsWith("set"))
.filter(method -> method.getParameterCount() > 1)
.map(Method::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
EXECUTE_METHODS.add("execute");
EXECUTE_METHODS.add("executeUpdate");
EXECUTE_METHODS.add("executeQuery");
EXECUTE_METHODS.add("addBatch");
}
protected void setColumn(Object key, Object value) {
columnMap.put(key, value);
columnNames.add(key);
columnValues.add(value);
}
protected Object getColumn(Object key) {
return columnMap.get(key);
}
protected String getParameterValueString() {
List<Object> typeList = new ArrayList<>(columnValues.size());
for (Object value : columnValues) {
if (value == null) {
typeList.add("null");
} else {
typeList.add(objectValueString(value) + "(" + value.getClass().getSimpleName() + ")");
}
}
final String parameters = typeList.toString();
return parameters.substring(1, parameters.length() - 1);
}
protected String objectValueString(Object value) {
if (value instanceof Array) {
try {
return ArrayUtil.toString(((Array) value).getArray());
} catch (SQLException e) {
return value.toString();
}
}
return value.toString();
}
protected String getColumnString() {
return columnNames.toString();
}
protected void clearColumnInfo() {
columnMap.clear();
columnNames.clear();
columnValues.clear();
}
protected String removeBreakingWhitespace(String original) {
StringTokenizer whitespaceStripper = new StringTokenizer(original);
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
while (whitespaceStripper.hasMoreTokens()) {
builder.append(whitespaceStripper.nextToken());
builder.append(" ");
}
return builder.toString();
}
protected boolean isDebugEnabled() {
return statementLog.isDebugEnabled();
}
protected boolean isTraceEnabled() {
return statementLog.isTraceEnabled();
}
protected void debug(String text, boolean input) {
if (statementLog.isDebugEnabled()) {
statementLog.debug(prefix(input) + text);
}
}
protected void trace(String text, boolean input) {
if (statementLog.isTraceEnabled()) {
statementLog.trace(prefix(input) + text);
}
}
private String prefix(boolean isInput) {
char[] buffer = new char[queryStack * 2 + 2];
Arrays.fill(buffer, '=');
buffer[queryStack * 2 + 1] = ' ';
if (isInput) {
buffer[queryStack * 2] = '>';
} else {
buffer[0] = '<';
}
return new String(buffer);
}
}重点关注下面的invoke方法,jdk的动态代理执行的时候会回调这个方法进行增强
public final class ConnectionLogger extends BaseJdbcLogger implements InvocationHandler {
// 真正的Connection对象
private final Connection connection;
private ConnectionLogger(Connection conn, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
super(statementLog, queryStack);
this.connection = conn;
}
/**
* Connection 是一个数据库连接对象
* 通过 Connection 的下一步是创建 Statement 对象
* Statement包含对应的子类 PreparedStatement
*
* 日志记录 Connection 创建 Statement 的过程
* 同时会创建 Statement 的代理对象类增强 Statement
*
* @param proxy
* @param method
* @param params
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params)
throws Throwable {
try {
// 如果是调用从Object继承过来的方法,就直接调用 toString,hashCode,equals等
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
// 如果调用的是 prepareStatement方法
if ("prepareStatement".equals(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
// 创建 PreparedStatement
PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params);
// 然后创建 PreparedStatement 的代理对象 增强
stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
// 同上
} else if ("prepareCall".equals(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug(" Preparing: " + removeBreakingWhitespace((String) params[0]), true);
}
PreparedStatement stmt = (PreparedStatement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = PreparedStatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
// 同上
} else if ("createStatement".equals(method.getName())) {
Statement stmt = (Statement) method.invoke(connection, params);
stmt = StatementLogger.newInstance(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
return stmt;
} else {
return method.invoke(connection, params);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
/**
* Creates a logging version of a connection.
*
* @param conn - the original connection
* @return - the connection with logging
*/
public static Connection newInstance(Connection conn, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new ConnectionLogger(conn, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = Connection.class.getClassLoader();
// 创建了 Connection的 代理对象 目的是 增强 Connection对象 给他添加了日志功能
return (Connection) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{Connection.class}, handler);
}
/**
* return the wrapped connection.
*
* @return the connection
*/
public Connection getConnection() {
return connection;
}
}可以发现这个方法中会根据jdbc的不同执行方法,比如获取 prepareStatement 方法,会创建PreparedStatementLogger对象
执行createStatement 方法,会创建 StatementLogger代理对象
相信Connection的prepareStatement和StatementLogger方法大家都不陌生
同理关注invoke回调方法
public final class PreparedStatementLogger extends BaseJdbcLogger implements InvocationHandler {
private final PreparedStatement statement;
private PreparedStatementLogger(PreparedStatement stmt, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
super(statementLog, queryStack);
this.statement = stmt;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
if (EXECUTE_METHODS.contains(method.getName())) {
if (isDebugEnabled()) {
debug("Parameters: " + getParameterValueString(), true);
}
clearColumnInfo();
if ("executeQuery".equals(method.getName())) {
ResultSet rs = (ResultSet) method.invoke(statement, params);
// 增强 创建了 ResultSet 的代理对象
return rs == null ? null : ResultSetLogger.newInstance(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
} else {
return method.invoke(statement, params);
}
} else if (SET_METHODS.contains(method.getName())) {
if ("setNull".equals(method.getName())) {
setColumn(params[0], null);
} else {
setColumn(params[0], params[1]);
}
return method.invoke(statement, params);
} else if ("getResultSet".equals(method.getName())) {
ResultSet rs = (ResultSet) method.invoke(statement, params);
return rs == null ? null : ResultSetLogger.newInstance(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
} else if ("getUpdateCount".equals(method.getName())) {
int updateCount = (Integer) method.invoke(statement, params);
if (updateCount != -1) {
debug(" Updates: " + updateCount, false);
}
return updateCount;
} else {
return method.invoke(statement, params);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
/**
* Creates a logging version of a PreparedStatement.
*
* @param stmt - the statement
* @param statementLog - the statement log
* @param queryStack - the query stack
* @return - the proxy
*/
public static PreparedStatement newInstance(PreparedStatement stmt, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new PreparedStatementLogger(stmt, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = PreparedStatement.class.getClassLoader();
// 创建了 PreparedStatement和CallableStatement 的代理对象 为的是添加日志功能
return (PreparedStatement) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{PreparedStatement.class, CallableStatement.class}, handler);
}
/**
* Return the wrapped prepared statement.
*
* @return the PreparedStatement
*/
public PreparedStatement getPreparedStatement() {
return statement;
}
}可以发现这里会打印执行参数信息
如果是执行PreparedStatement的executeQuery方法,会执行原方法后,获取ResultSet结果集对象。
然后创建ResultSetLogger代理对象。这个对象肯定就是对执行结果的打印日志输出了
public final class ResultSetLogger extends BaseJdbcLogger implements InvocationHandler {
private static final Set<Integer> BLOB_TYPES = new HashSet<>();
private boolean first = true;
private int rows;
private final ResultSet rs;
private final Set<Integer> blobColumns = new HashSet<>();
static {
BLOB_TYPES.add(Types.BINARY);
BLOB_TYPES.add(Types.BLOB);
BLOB_TYPES.add(Types.CLOB);
BLOB_TYPES.add(Types.LONGNVARCHAR);
BLOB_TYPES.add(Types.LONGVARBINARY);
BLOB_TYPES.add(Types.LONGVARCHAR);
BLOB_TYPES.add(Types.NCLOB);
BLOB_TYPES.add(Types.VARBINARY);
}
private ResultSetLogger(ResultSet rs, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
super(statementLog, queryStack);
this.rs = rs;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] params) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, params);
}
Object o = method.invoke(rs, params);
if ("next".equals(method.getName())) {
if ((Boolean) o) {
rows++;
if (isTraceEnabled()) {
ResultSetMetaData rsmd = rs.getMetaData();
final int columnCount = rsmd.getColumnCount();
if (first) {
first = false;
//打印头部信息
printColumnHeaders(rsmd, columnCount);
}
//打印每一行
printColumnValues(columnCount);
}
} else {
//打印总数
debug(" Total: " + rows, false);
}
}
clearColumnInfo();
return o;
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
private void printColumnHeaders(ResultSetMetaData rsmd, int columnCount) throws SQLException {
StringJoiner row = new StringJoiner(", ", " Columns: ", "");
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
if (BLOB_TYPES.contains(rsmd.getColumnType(i))) {
blobColumns.add(i);
}
row.add(rsmd.getColumnLabel(i));
}
trace(row.toString(), false);
}
private void printColumnValues(int columnCount) {
StringJoiner row = new StringJoiner(", ", " Row: ", "");
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
try {
if (blobColumns.contains(i)) {
row.add("<<BLOB>>");
} else {
row.add(rs.getString(i));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// generally can't call getString() on a BLOB column
row.add("<<Cannot Display>>");
}
}
trace(row.toString(), false);
}
/**
* Creates a logging version of a ResultSet.
*
* @param rs - the ResultSet to proxy
* @return - the ResultSet with logging
*/
public static ResultSet newInstance(ResultSet rs, Log statementLog, int queryStack) {
InvocationHandler handler = new ResultSetLogger(rs, statementLog, queryStack);
ClassLoader cl = ResultSet.class.getClassLoader();
return (ResultSet) Proxy.newProxyInstance(cl, new Class[]{ResultSet.class}, handler);
}
/**
* Get the wrapped result set.
*
* @return the resultSet
*/
public ResultSet getRs() {
return rs;
}
}可以看到这里就是打印返回值的地方了
private void printColumnValues(int columnCount) {
StringJoiner row = new StringJoiner(", ", " Row: ", "");
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
try {
if (blobColumns.contains(i)) {
row.add("<<BLOB>>");
} else {
row.add(rs.getString(i));
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// generally can't call getString() on a BLOB column
row.add("<<Cannot Display>>");
}
}
trace(row.toString(), false);
}当然,我们也可以自定义日志实现类,可以模仿其他日志模块的适配代码。比如我们可以自定义个存储日志的实现类,可以每次将sql执行的日志存储到数据库中。

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








