- 项目结构
- 加入依赖(mybatis和h2)
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
- yml文件配置
server:
port: 8080
#************H2 Begin****************
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
url: jdbc:h2:mem:test
username:
password:
schema: classpath:db/schema.sql
data: classpath:db/data.sql
h2:
console:
settings:
web-allow-other: true
trace: true
path: /h2-console
enabled: true
#************H2 End***************
#************mybatis Start***************
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:mapping/*Mapper.xml
type-aliases-package: com.example.demo.entity
#************mybatis End***************
- 数据库初始化文件
schema.sql:
drop table if exists student;
create table student (id int primary key auto_increment, name varchar, addr varchar);
data.sql:
insert into student (name, addr) values ('张三', '山东');
insert into student (name, addr) values ('李四', '山西');
insert into student (name, addr) values ('王五', '河南');
insert into student (name, addr) values ('赵六', '河北');
- 启动类
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.example.demo.mapper")
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
- xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.StudentMapper">
<select id="getList" resultType="student">
select id, name, addr
from student
</select>
<insert id="add" parameterType="student">
INSERT INTO student (name, addr) VALUES (#{name}, #{addr})
</insert>
</mapper>
- mapper
import com.example.demo.entity.Student;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
@Component
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper {
int add(Student stu);
List<Student> getList();
}
- dao
import com.example.demo.entity.Student;
import com.example.demo.mapper.StudentMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.List;
@Component
public class StudentDao {
@Autowired
private StudentMapper mapper;
public List<Student> getList() {
return mapper.getList();
}
public Integer add(Student stu) {
return mapper.add(stu);
}
}
- service
import com.example.demo.dao.StudentDao;
import com.example.demo.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class StudentService {
@Autowired
private StudentDao dao;
public List<Student> getList() {
return dao.getList();
}
public Integer add(Student stu) {
return dao.add(stu);
}
}
- controller
import com.example.demo.entity.Student;
import com.example.demo.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("student")
public class StudentCtl {
@Autowired
private StudentService service;
@GetMapping("getList")
public List<Student> getList() {
return service.getList();
}
@PostMapping("add")
public Integer add(Student stu) {
return service.add(stu);
}
}
- db2数据库访问
http://localhost:8080/h2-console
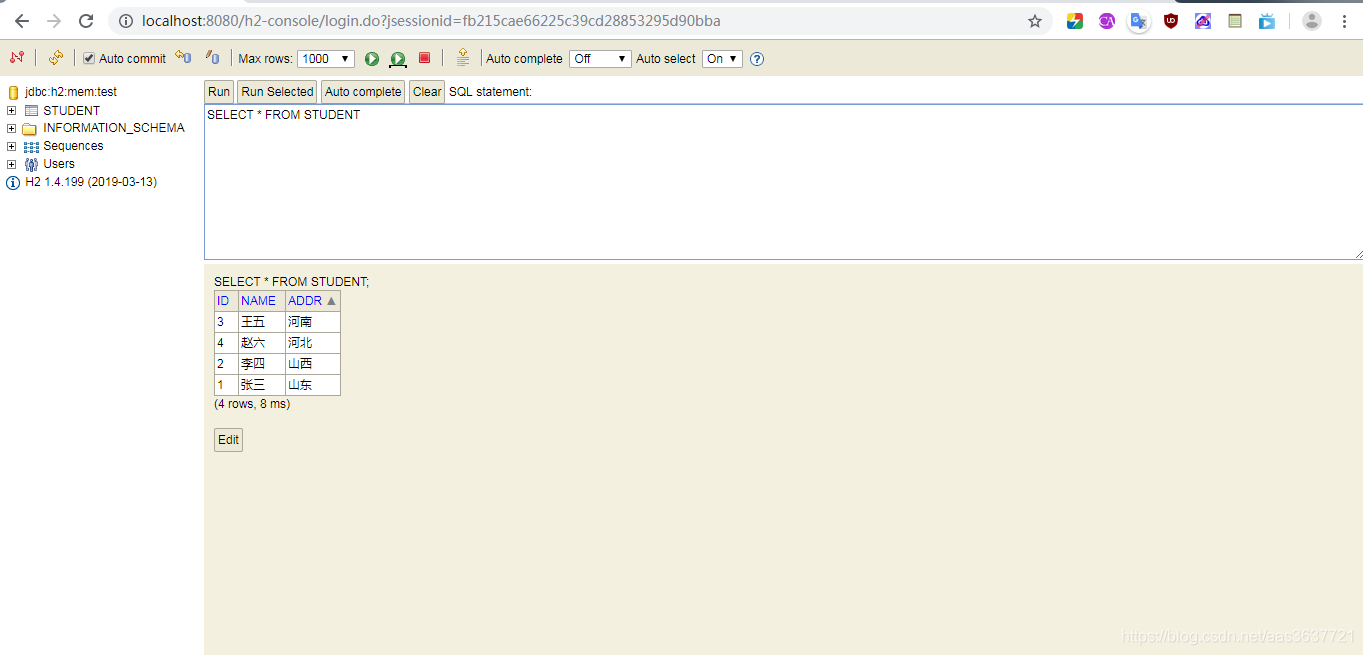
- 接口调用测试







 本文详细介绍如何在Spring Boot项目中整合MyBatis和H2数据库,包括配置依赖、YML配置、数据库初始化、XML映射文件、Mapper接口、DAO层、Service层及Controller层的实现,并提供接口调用测试。
本文详细介绍如何在Spring Boot项目中整合MyBatis和H2数据库,包括配置依赖、YML配置、数据库初始化、XML映射文件、Mapper接口、DAO层、Service层及Controller层的实现,并提供接口调用测试。
















 1231
1231

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








