模型保存和加载:

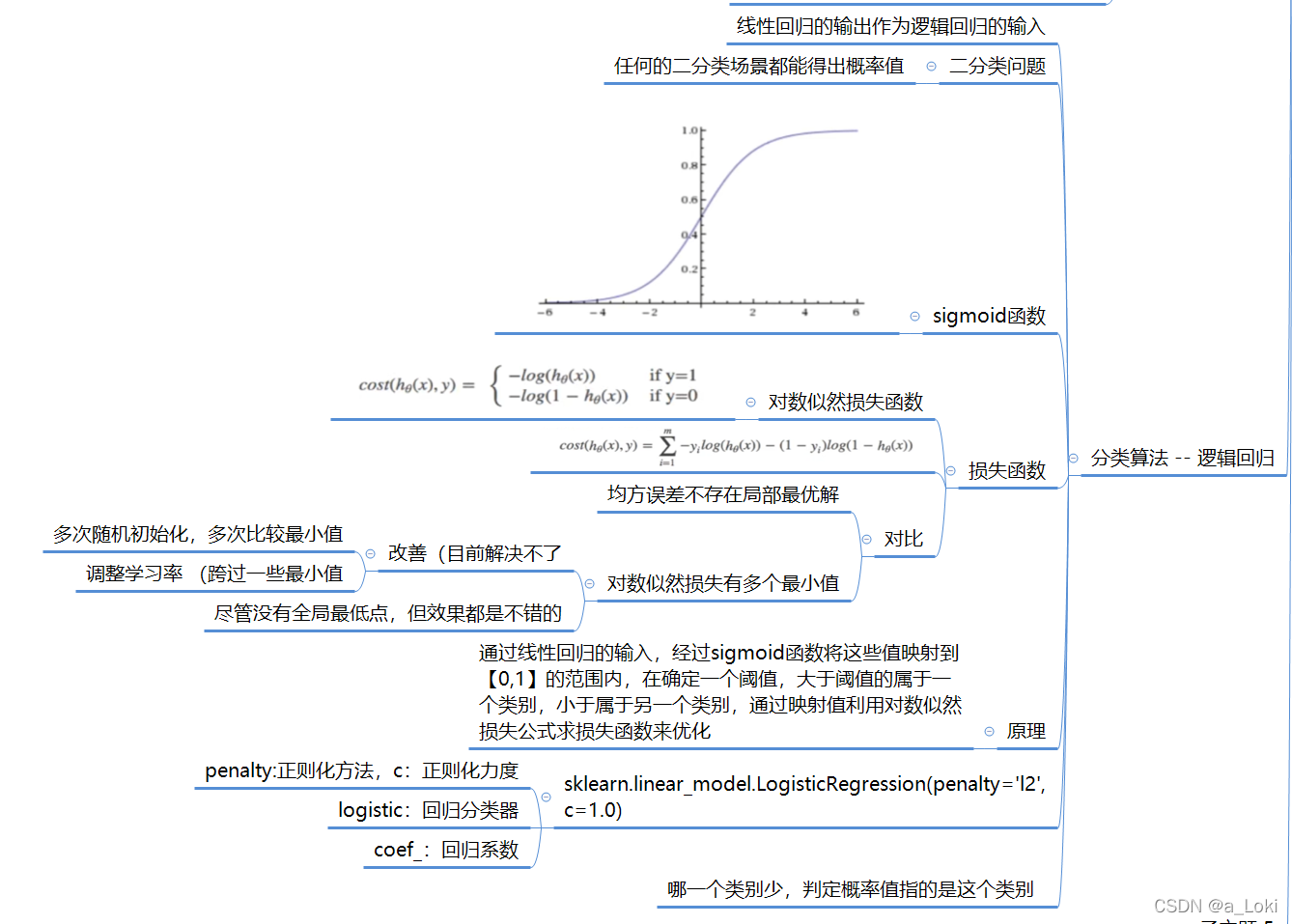
分类算法 -- 逻辑回归:
 代码实现:
代码实现:
def logitic():
# 构造列标签名字
column = ['Sample code number','Clump Thickness', 'Uniformity of Cell Size','Uniformity of Cell Shape','Marginal Adhesion', 'Single Epithelial Cell Size','Bare Nuclei','Bland Chromatin','Normal Nucleoli','Mitoses','Class']
# 获取数据
df = pd.read_csv('https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/breast-cancer-wisconsin/breast-cancer-wisconsin.data',names=column)
# print(df.head())
# 数据处理
df = df.replace(to_replace='?',value=np.nan)
df = df.dropna()
print(df)
# 分割数据集
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(df.iloc[:,1:10],df.iloc[:,-1],test_size=0.2,random_state=22)
# 标准化
scaler = StandardScaler()
x_train = scaler.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = scaler.transform(x_test)
# 机器学习
estimator = LogisticRegression()
estimator.fit(x_train,y_train)
print(estimator.coef_)
y_pre = estimator.predict(x_test)
print('查全率为:\n',classification_report(y_test,y_pre,labels=[2,4],target_names=['良性','恶性']))
判别模型和生成模型:

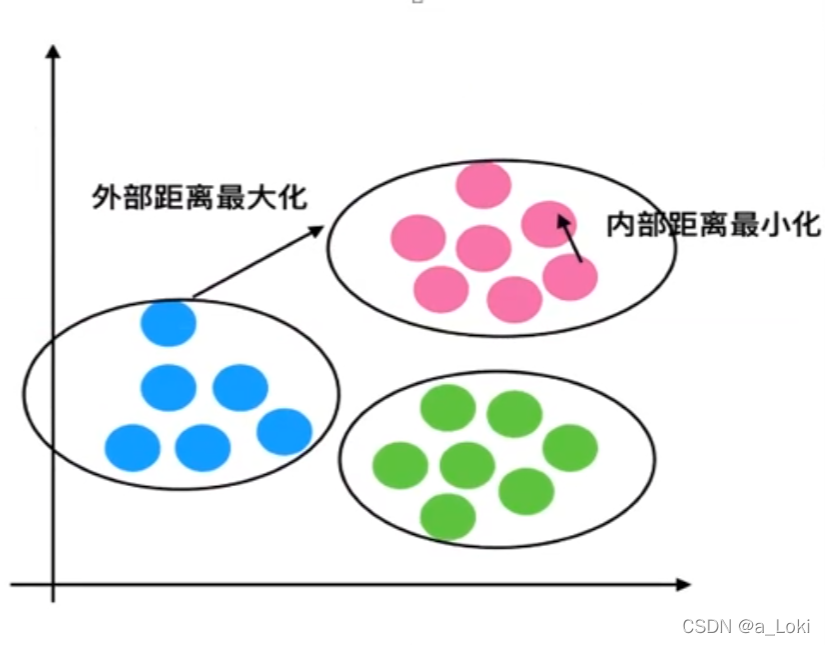
k-means:非监督学习
过程:

评估标准:

效果:





 博客探讨了逻辑回归模型的训练、保存和加载过程,包括数据预处理、模型构建和评估。同时,介绍了k-means聚类算法,详细阐述了其非监督学习的过程,并讨论了评估标准和实际效果。
博客探讨了逻辑回归模型的训练、保存和加载过程,包括数据预处理、模型构建和评估。同时,介绍了k-means聚类算法,详细阐述了其非监督学习的过程,并讨论了评估标准和实际效果。

















 1332
1332

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










