Description
Write a program that takes as input a rooted tree and a list of pairs of vertices. For each pair (u,v) the program determines the closest common ancestor of u and v in the tree. The closest common ancestor of two nodes u and v is the node w that is an ancestor
of both u and v and has the greatest depth in the tree. A node can be its own ancestor (for example in Figure 1 the ancestors of node 2 are 2 and 5)
Input
The data set, which is read from a the std input, starts with the tree description, in the form:
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
nr_of_vertices
vertex:(nr_of_successors) successor1 successor2 ... successorn
...
where vertices are represented as integers from 1 to n ( n <= 900 ). The tree description is followed by a list of pairs of vertices, in the form:
nr_of_pairs
(u v) (x y) ...
The input file contents several data sets (at least one).
Note that white-spaces (tabs, spaces and line breaks) can be used freely in the input.
Output
For each common ancestor the program prints the ancestor and the number of pair for which it is an ancestor. The results are printed on the standard output on separate lines, in to the ascending order of the vertices, in the format: ancestor:times
For example, for the following tree:
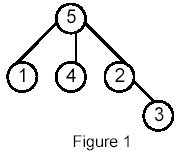
For example, for the following tree:

Sample Input
5
5:(3) 1 4 2
1:(0)
4:(0)
2:(1) 3
3:(0)
6
(1 5) (1 4) (4 2)
(2 3)
(1 3) (4 3)
Sample Output
2:1 5:5
/* 连有向边建图 入度为0的点开始 预处理每两个点的lca. 读入询问的时候,num[lca(a,b)]++; */ #include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> using namespace std; #define maxn 50008 #define qmaxn 500008 int first[maxn],nxt[maxn],vv[maxn],rudu[maxn],num[maxn]; int qfirst[qmaxn],qnxt[qmaxn],quu[qmaxn],qvv[qmaxn],qans[qmaxn]; int f[maxn]; int question,e,cnt,n,m; bool vis[maxn]; void addEdge(int u,int v) { vv[e] = v; nxt[e] = first[u]; first[u] = e++; rudu[v]++; }//建的边是单向边 void addQue(int u,int v) { quu[cnt] = u; qvv[cnt] = v; qnxt[cnt] = qfirst[u]; qfirst[u] = cnt++; quu[cnt] = v; qvv[cnt] = u; qnxt[cnt] = qfirst[v]; qfirst[v] = cnt++; } int find(int x) { if(f[x] == x) return x; return f[x] = find(f[x]); } void Union(int x,int y) { int fx = find(x); f[y] = fx; } void dfs(int u,int fa) { f[u] = u; for(int i = first[u];i != -1;i = nxt[i]) { if(vv[i] == fa) continue; dfs(vv[i],u); Union(u,vv[i]); } vis[u] = 1; for(int i = qfirst[u];i != -1;i = qnxt[i]) { if(vis[qvv[i]]) qans[i] = find(qvv[i]); } } void Main() { for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { if(rudu[i] == 0) dfs(i,-1); } int x,y,ans; for(int i = 0;i < m*2;i += 2)///这里会出点问题。。。 { x = quu[i]; y = qvv[i]; ans = qans[i]; if(qans[i+1] > qans[i]) { ans = qans[i+1]; } num[ans]++; } for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { if(num[i]) printf("%d:%d\n",i,num[i]); } } void init() { while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { memset(first,-1,sizeof(first)); memset(qfirst,-1,sizeof(qfirst)); memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis)); memset(rudu,0,sizeof(rudu)); memset(num,0,sizeof(num)); memset(qans,0,sizeof(qans)); e = cnt = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++) { int u,v,num; scanf("%d:",&u); while(getchar()!='('); scanf("%d",&num); while(getchar()!=')'); for(int j = 1;j <= num;j++) { scanf("%d",&v); addEdge(u,v); } } scanf("%d",&m); for(int i = 1;i <= m; i++) { int u,v; while(getchar()!='('); scanf("%d%d", &u, &v); addQue(u,v); while(getchar()!=')'); } Main(); } } int main() { //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); init(); return 0; }





















 596
596

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








