1.进程与线程/并行与并发
进程:就是一个正在运行的程序
线程:就是进程内的多条执行路径,一个进程内有多个线程。
并行:多核cpu下,每个核心都可以运行线程。同一时间动手做多件事情的能力。
并发:线程轮流使用cpu,同一时间应对多件事情的能力。
同步:需要等待结果返回才能继续向下运行
同步:需要等待结果返回才能继续向下运行
异步:不需要等待结果返回,就能继续向下运行。
异步:不需要等待结果返回,就能继续向下运行。
2.创建线程
//继承Thread类,匿名内部类的写法
Thread t = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("666");
}
};
t.start();
//实现Runnable接口,lambda表达式的写法
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("666");
},"t2").start();
//FutureTask异步任务,lambda表达式的写法,Callable函数式接口,有返回值和异常抛出。
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<Integer>(()->{
return 100;
});
new Thread(task,"t3").start();
//继承Thread类,匿名内部类的写法
Thread t = new Thread("t1") {
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("666");
}
};
t.start();
//实现Runnable接口,lambda表达式的写法
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("666");
},"t2").start();
//FutureTask异步任务,lambda表达式的写法,Callable函数式接口,有返回值和异常抛出。
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<Integer>(()->{
return 100;
});
new Thread(task,"t3").start();
3、栈与栈帧
每个线程启动,虚拟机会为其分配线程工作栈内存。每个工作栈内存由多个栈帧组成,对应着每次方法调用时所占用的内存。每个线程只有一个活动栈帧,对应着当前正在执行的方法。

4、sleep
调用sleep方法会让当前线程从RUNNABLE运行状态变为TIMED_WAITING阻塞状态。
其他线程可以调用interrupt()方法,打断正在睡眠的线程,这时sleep方法会抛出InterruptedException。睡眠的线程将被唤醒。
但是睡眠结束后的线程未必会立即得到执行,而是进入RUNNABLE就绪状态,等待CPU的调度执行。
TimeUnit替代sleep得到更好的可读性。
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.sleep(500);
sleep防止cpu占用100%,让出cpu的执行权,不让死循环占用太多资源。
public class CpuSleepTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
while (true){
Thread.sleep(1);
System.out.println(new Date());
}
}
}
public class CpuSleepTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
while (true){
Thread.sleep(1);
System.out.println(new Date());
}
}
}
5、yield
礼让,会让当前线程从运行状态变为就绪状态,等待CPU的调度执行,又有可能获得CPU的执行权。
具体的实现依赖于操作系统的任务调度器。
6、PRIORITY线程优先级
优先级会提示调度器优先执行该线程,但仅仅只是一个提示,调度器可能忽略这个提示。
如果CPU比较忙,优先级较高的线程会获得更多的时间片,CPU空闲时,线程的优先级几乎没有作用。
/** * The minimum priority that a thread can have. */
public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
/** * The default priority that is assigned to a thread. */
public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
/** * The maximum priority that a thread can have. */
public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
/** * The minimum priority that a thread can have. */
public final static int MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
/** * The default priority that is assigned to a thread. */
public final static int NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
/** * The maximum priority that a thread can have. */
public final static int MAX_PRIORITY = 10;
public class YieldPriorotyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
System.out.println("t1--"+count++);
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
//Thread.yield();//礼让
System.out.println(" t2--"+count++);
}
});
t2.start();
t1.start();
//设置线程优先级
t2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
}
}
public class YieldPriorotyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
System.out.println("t1--"+count++);
}
});
Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {
int count = 0;
for (; ; ) {
//Thread.yield();//礼让
System.out.println(" t2--"+count++);
}
});
t2.start();
t1.start();
//设置线程优先级
t2.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t1.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
}
}
7、join插队
等待调用join()方法的线程结束
package new2023.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/** * @Author zhangxuhui * @Date 2023/3/17 * @email zxh_1633@163.com */
public class JoinTest {
static int s = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
s = 10;
System.out.println("t is over");
},"t");
t.start();
t.join();//插队,等待t线程结束。
System.out.println(s);
}
}
package new2023.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/** * @Author zhangxuhui * @Date 2023/3/17 * @email zxh_1633@163.com */
public class JoinTest {
static int s = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
s = 10;
System.out.println("t is over");
},"t");
t.start();
t.join();//插队,等待t线程结束。
System.out.println(s);
}
}
8、inturrupt打断线程
打断阻塞状态的线程(sleep,wait,join),会重置打断标记。
package new2023.juc;
/** * @Author zhangxuhui * @Date 2023/3/17 * @email zxh_1633@163.com */
public class InterruptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("sleep....");
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("thread is over");
});
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("interrupt...");
t.interrupt();
System.out.println("打断标记:"+t.isInterrupted());//false
}
}
package new2023.juc;
/** * @Author zhangxuhui * @Date 2023/3/17 * @email zxh_1633@163.com */
public class InterruptTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("sleep....");
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("thread is over");
});
t.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("interrupt...");
t.interrupt();
System.out.println("打断标记:"+t.isInterrupted());//false
}
}
打断正常运行的线程,判断打断标识可以优雅的停止线程。
package new2023.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/** * @Author zhangxuhui * @Date 2023/3/17 * @email zxh_1633@163.com */
public class InterruptRunningThread {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
boolean interrupted = Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();
System.out.println(interrupted);
if(interrupted){
System.out.println("thread is inturrupted : stop");
break;
}
}
});
t.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
t.interrupt();
System.out.println("main thread is stop");
}
}
package new2023.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/** * @Author zhangxuhui * @Date 2023/3/17 * @email zxh_1633@163.com */
public class InterruptRunningThread {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
while(true){
boolean interrupted = Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted();
System.out.println(interrupted);
if(interrupted){
System.out.println("thread is inturrupted : stop");
break;
}
}
});
t.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
t.interrupt();
System.out.println("main thread is stop");
}
}
两阶段终止模式(two phase termination):在一个线程t1中如何优雅的终止另一个线程t2,优雅是指给t2一个料理后事的机会。
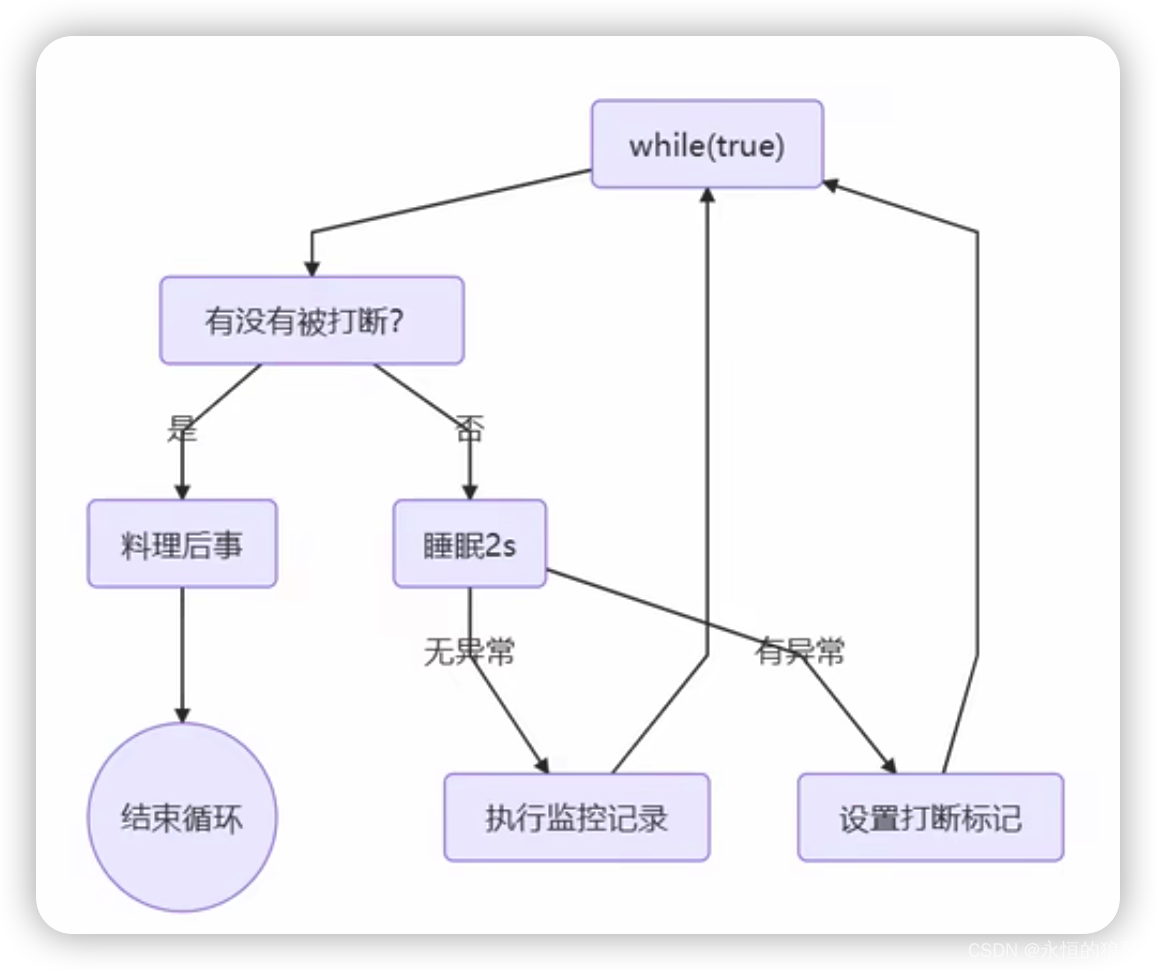
package new2023.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/** * @Author zhangxuhui * @Date 2023/3/17 * @email zxh_1633@163.com */
public class TwoPhaseTermination {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Phase p = new Phase();
p.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
p.stop();
System.out.println("等待重启...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
p.restart();
}
}
class Phase{
private Thread monitor;
public void start(){
monitor = new Thread(()->{
while (true){
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//current.isInterrupted();不会清除打断标记
//Thread.interrupted();会清除打断标记
if(current.isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("线程被打断,料理后事");
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("系统监控");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
current.interrupt();
}
}
});
monitor.start();
}
public void stop(){
monitor.interrupt();
}
public void restart(){
start();
}
}
package new2023.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/** * @Author zhangxuhui * @Date 2023/3/17 * @email zxh_1633@163.com */
public class TwoPhaseTermination {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Phase p = new Phase();
p.start();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
p.stop();
System.out.println("等待重启...");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
p.restart();
}
}
class Phase{
private Thread monitor;
public void start(){
monitor = new Thread(()->{
while (true){
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
//current.isInterrupted();不会清除打断标记
//Thread.interrupted();会清除打断标记
if(current.isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("线程被打断,料理后事");
break;
}
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("系统监控");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
current.interrupt();
}
}
});
monitor.start();
}
public void stop(){
monitor.interrupt();
}
public void restart(){
start();
}
}
打断park线程,使其继续执行,在打断标记为true时,park将失效。
package new2023.juc;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.LockSupport;
/** * @Author zhangxuhui * @Date 2023/3/18 * @email zxh_1633@163.com */
public class InterruptPark {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread t = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("park");
LockSupport.park();
System.out.println("unpark");
// System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted());
System.out.println(Thread




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 444
444

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










