java8新特性:六,Optional 类
1 介绍
Optional 类是一个可以为null的容器对象。如果值存在则isPresent()方法会返回true,调用get()方法会返回该对象。
Optional 是个容器:它可以保存类型T的值,或者仅仅保存null。Optional提供很多有用的方法,这样我们就不用显式进行空值检测。
Optional 类的引入很好的解决空指针异常。
2 类声明
以下是一个 java.util.Optional 类的声明:
public final class Optional
extends Object
3 类方法
序号 方法 & 描述
1 static < T> Optional< T> empty()
返回空的 Optional 实例。
2 boolean equals(Object obj)
判断其他对象是否等于 Optional。
3 Optional< T> filter(Predicate<? super < T> predicate)
如果值存在,并且这个值匹配给定的 predicate,返回一个Optional用以描述这个值,否则返回一个空的Optional。
4 < U > Optional< U > flatMap(Function<? super T,Optional< U >> mapper)
如果值存在,返回基于Optional包含的映射方法的值,否则返回一个空的Optional
5 T get()
如果在这个Optional中包含这个值,返回值,否则抛出异常:NoSuchElementException
6 int hashCode()
返回存在值的哈希码,如果值不存在 返回 0。
7 void ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer)
如果值存在则使用该值调用 consumer , 否则不做任何事情。
8 boolean isPresent()
如果值存在则方法会返回true,否则返回 false。
9 < U>Optional< U> map(Function<? super T,? extends U> mapper)
如果有值,则对其执行调用映射函数得到返回值。如果返回值不为 null,则创建包含映射返回值的Optional作为map方法返回值,否则返回空Optional。
10 static < T> Optional< T> of(T value)
返回一个指定非null值的Optional。
11 static < T> Optional< T> ofNullable(T value)
如果为非空,返回 Optional 描述的指定值,否则返回空的 Optional。
12 T orElse(T other)
如果存在该值,返回值, 否则返回 other。
13 T orElseGet(Supplier<? extends T> other)
如果存在该值,返回值, 否则触发 other,并返回 other 调用的结果。
14 < X extends Throwable> T orElseThrow(Supplier<? extends X> exceptionSupplier)
如果存在该值,返回包含的值,否则抛出由 Supplier 继承的异常
15 String toString()
返回一个Optional的非空字符串,用来调试
注意: 这些方法是从 java.lang.Object 类继承来的。
4 Optional 实例
我们可以通过以下实例来更好的了解 Optional 类的使用
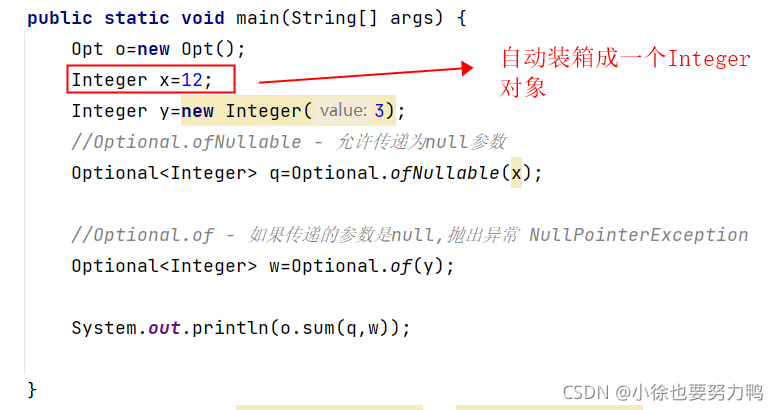
import java.util.Optional;
public class Opt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Opt o=new Opt();
Integer x=12;
Integer y=new Integer(3);
//Optional.ofNullable - 允许传递为null参数
Optional<Integer> q=Optional.ofNullable(x);
//Optional.of - 如果传递的参数是null,抛出异常 NullPointerException
Optional<Integer> w=Optional.of(y);
System.out.println(o.sum(q,w));
}
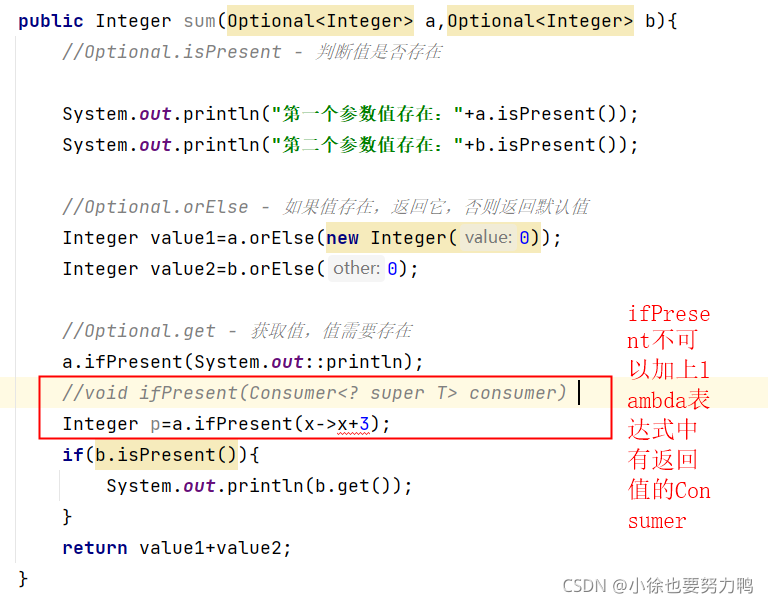
public Integer sum(Optional<Integer> a,Optional<Integer> b){
//Optional.isPresent - 判断值是否存在
System.out.println("第一个参数值存在:"+a.isPresent());
System.out.println("第二个参数值存在:"+b.isPresent());
//Optional.orElse - 如果值存在,返回它,否则返回默认值
Integer value1=a.orElse(new Integer(0));
Integer value2=b.orElse(0);
//Optional.get - 获取值,值需要存在
a.ifPresent(System.out::println);
//void ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer)
// Integer p=a.ifPresent(x->x+3);
if(b.isPresent()){
System.out.println(b.get());
}
return value1+value2;
}
}
第一个参数值存在:true
第二个参数值存在:true
12
3
15
Optional.ofNullable(): 允许传递为null参数
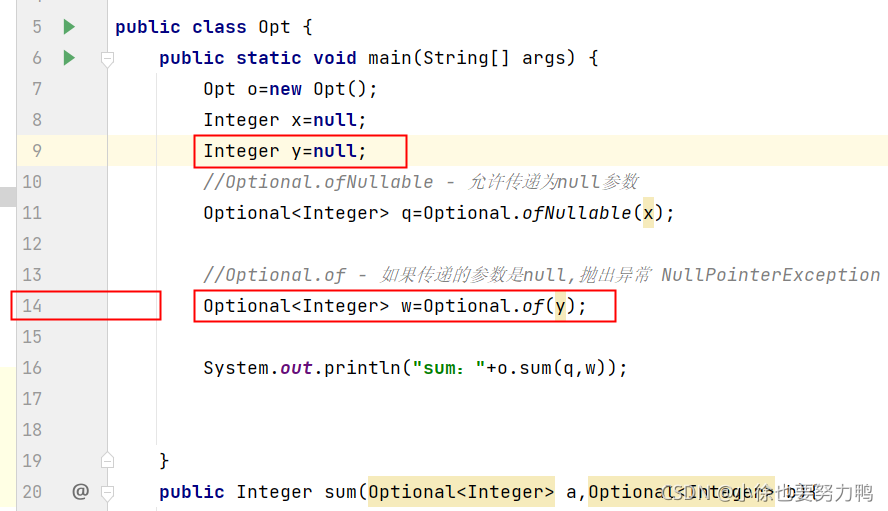
import java.util.Optional;
public class Opt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Opt o=new Opt();
Integer x=null;
Integer y=new Integer(3);
//Optional.ofNullable - 允许传递为null参数
Optional<Integer> q=Optional.ofNullable(x);
//Optional.of - 如果传递的参数是null,抛出异常 NullPointerException
Optional<Integer> w=Optional.of(y);
System.out.println("sum:"+o.sum(q,w));
}
public Integer sum(Optional<Integer> a,Optional<Integer> b){
//Optional.isPresent - 判断值是否存在
System.out.println("第一个参数值存在:"+a.isPresent());
System.out.println("第二个参数值存在:"+b.isPresent());
//Optional.orElse - 如果值存在,返回它,否则返回默认值
Integer value1=a.orElse(new Integer(0));
Integer value2=b.orElse(0);
//Optional.get - 获取值,值需要存在
a.ifPresent(System.out::println);
//void ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer)
// Integer p=a.ifPresent(x->x+3);
if(b.isPresent()){
System.out.println("b"+b.get());
}
return value1+value2;
}
}
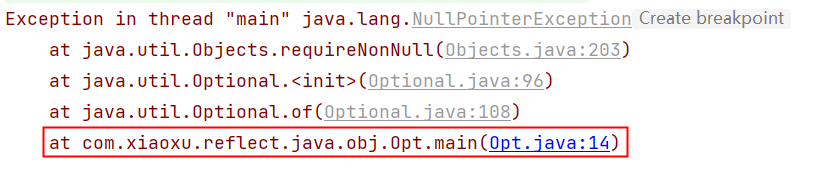
Optional.of(): 如果传递的参数是null,抛出异常 NullPointerException
实例方法:orElse(other)
T orElse(T other)
如果存在该值,返回值, 否则返回 other
注意:orElse的参数other,是由orElse的参数类型决定,调用orElse的是什么类型,那么other是什么样的类型


下面,因为null、0、new Integer(12)都可以转换成java.lang.Integer类型,所以orElse是成功的
Integer x=null;
Integer y=null;
Optional<Integer> z=Optional.ofNullable(x);
System.out.println("我是数字z:");
System.out.println(z.orElse(0));
System.out.println("我是y:");
System.out.println(Optional.ofNullable(y).orElse(null));
我是数字z:
0
我是y:
null
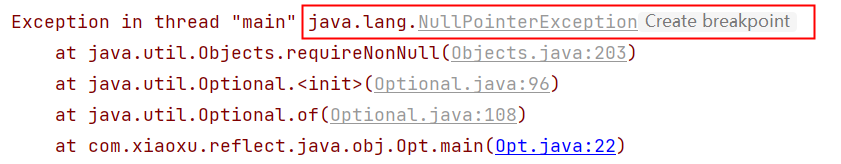
注意:Optional.of(),对于null,还是会报空指针异常,走不到orElse()就会报错(所以最好是使用ofNullable)
System.out.println(Optional.of(x).orElse(null));
5 练习
新建Fruit类:
package com.base3;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Fruit {
private String name;
private BigDecimal price;
private BigInteger number;
private int total;
private double RealPrice;
public Fruit(String name, BigDecimal price, BigInteger number, int total, double realPrice) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
this.number = number;
this.total = total;
RealPrice = realPrice;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Fruit{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", number=" + number +
", total=" + total +
", RealPrice=" + RealPrice +
'}';
}
public void setPrice(BigDecimal price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return price;
}
public BigInteger getNumber() {
return number;
}
public int getTotal() {
return total;
}
public double getRealPrice() {
return RealPrice;
}
}
package com.base3;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
import org.testng.collections.Lists;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Mstream2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Fruit> fr= Lists.newArrayList(
new Fruit("apple",new BigDecimal("2"),new BigInteger("15"),40,1.23),
new Fruit("watermelon",new BigDecimal("4"),new BigInteger("5"),10,0.6),
new Fruit("peach",new BigDecimal("2"),new BigInteger("5"),20,1.8),
new Fruit("pear",new BigDecimal("4"),new BigInteger("15"),15,3.2),
new Fruit("banana",new BigDecimal("3"),new BigInteger("15"),24,2)
);
Map<BigInteger,List<Fruit>> m=Optional.ofNullable(fr).orElse(Collections.emptyList())
.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Fruit::getNumber));
System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(m,SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat,SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue));
//list转map
// Map<BigInteger,BigDecimal> m=Optional.ofNullable(fr).orElse(Collections.emptyList())
// .stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(Fruit::getNumber,Fruit::getPrice,(key1,key2)->key1));
// System.out.println(JSON.toJSONString(m, SerializerFeature.PrettyFormat,SerializerFeature.WriteMapNullValue,SerializerFeature.WriteDateUseDateFormat));
}
}
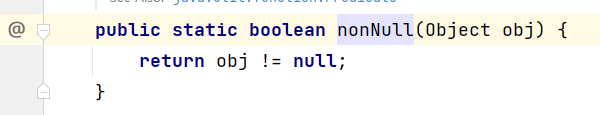
Objects::nonNull:筛选时排除空对象(null):
List<Fruit> fr= Lists.newArrayList(
new Fruit("apple",new BigDecimal("2"),new BigInteger("15"),40,1.23),
new Fruit("watermelon",new BigDecimal("4"),new BigInteger("5"),10,0.6),
new Fruit("peach",new BigDecimal("2"),new BigInteger("5"),20,1.8),
new Fruit("pear",new BigDecimal("4"),new BigInteger("15"),15,3.2),
new Fruit("banana",new BigDecimal("3"),new BigInteger("15"),24,2),
null
);
fr.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull).map(Fruit::getName).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.err::println);
apple
watermelon
peach
pear
banana
stream的limit:当集合为空,limit返回的是一个空集合,不是null,这样不容易NEP
List<Fruit> fr= Lists.newArrayList(
null,
new Fruit("apple",new BigDecimal("2"),new BigInteger("15"),40,1.23),
new Fruit("watermelon",new BigDecimal("4"),new BigInteger("5"),10,0.6),
new Fruit("peach",new BigDecimal("2"),new BigInteger("5"),20,1.8),
new Fruit("pear",new BigDecimal("4"),new BigInteger("15"),15,3.2),
new Fruit("banana",new BigDecimal("3"),new BigInteger("15"),24,2)
);
fr.stream().filter(Objects::nonNull).map(Fruit::getName).limit(3).collect(Collectors.toList()).forEach(System.err::println);
apple
watermelon
peach





 本文介绍了Java 8中Optional类的基本概念、声明与常用方法,展示了如何避免空指针异常,通过实例演示了Optional的使用,包括ofNullable、orElse等操作,以及在实际开发中的应用,如数据处理和流操作示例。
本文介绍了Java 8中Optional类的基本概念、声明与常用方法,展示了如何避免空指针异常,通过实例演示了Optional的使用,包括ofNullable、orElse等操作,以及在实际开发中的应用,如数据处理和流操作示例。
















 142
142

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








