1 IO流的体系分类

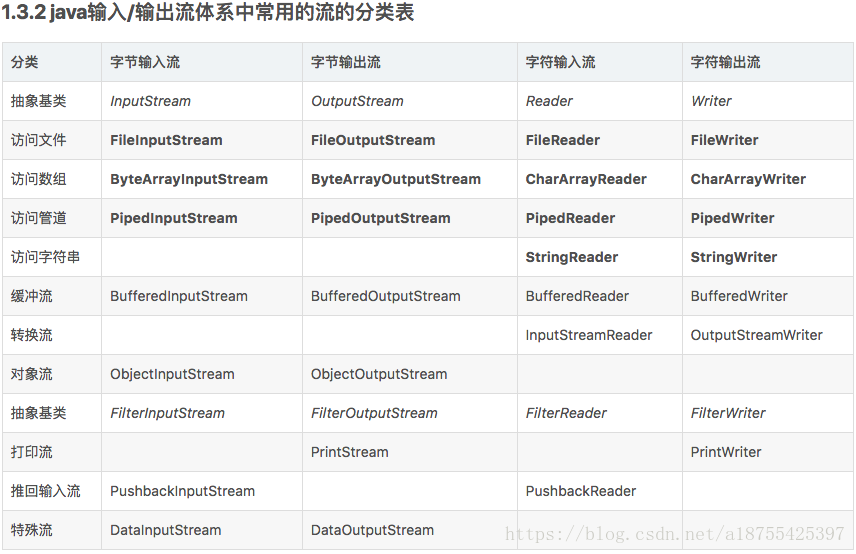
2.常用的流Java流列表
例题: 1. 字节输出流 FileOutputStream :
写文件的步奏; 1. 创建绑定文件, 2. 创建输出流 3. 写文件 . 4. 关闭流资源
public static void main(String[] args) {
//fun1往文档里面写东西();
//创建地址
File file = new File("/Users/lanou/Desktop/zhang/hai.txt");
// 创建一个空的引用,扩大作用域
FileOutputStream fos = null;
// 绑定要写的位置
try {
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write("haha".getBytes());// 此处报异常,写入失败;
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// 文件找不到,停止程序让程序员修改代码
// 抛个运行时候异常,提示信息,和停止程序;
throw new RuntimeException("文件找不到");
// e.printStackTrace();//打印位置错误信息默认的
} catch (IOException e) {
// 写入失败;
throw new RuntimeException("写入失败");
} finally {
if (fos != null) {
// 关闭资源时,一定要确保可以关闭的代码可以执行;
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("关闭失败");
}
}
}
}
2: 字节输入流FileInputStream, 直接读取
读文件的步奏; 1. 创建绑定文件, 2. 创建输出流 3. 读文件 . 4. 关闭流资源
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// fun2循环读取();
File file = new File("/Users/lanou/Desktop/zhang/hai.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 一次多读几个字节;
// 创建一个空的字节数组长度是2;
// 利用空的字节数组作为缓冲区;将文件字节读进这个数组中;
// 一次读两个提高效率;一次读1024个;
// fun3数组读取(fis);
int num = 0;
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
while ((num = fis.read(b)) != -1) {
// 直接使用String的构造方法,将字符数组转化成字符串;
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, num));
}
// 关闭一下
fis.close();
}例题3: 使用字节流,进行文件的赋值( 需要进行异常处理 ), 使用到 字节输出和字节输入流;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用字节流 进行文件的复制(需要异常处理 并计算两种读写方式的时间)
// 对文件进行续写;
// 计算赋值时间
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
FileInputStream in = null;
FileOutputStream ou = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/zzz/index.jpg");
ou = new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = in.read()) != -1) {
ou.write(bs, 0, len);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 进行流的关闭;
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException();
} finally {
try {
ou.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
}
}
long stop = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(stop - start);
}例题 4:将一个文件夹复制到另外一个文件夹里面
public static void fun(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
// 去目标文件夹创建一个文件夹出来;新文件夹名字是原文件的名字,
// 路径是目标文件的名字;
File newFile = new File(dest, src.getName());
newFile.mkdir();
// 遍历所有集合
File[] files = src.listFiles();
for (File subfile : files) {
if (subfile.isDirectory()) {
fun(subfile, newFile);
} else {
// 读写
FileInputStream in = new FileInputStream(subfile);
//创建一个要写入的文件(需要获取文件名字)
File temp = new File(newFile, subfile.getName());
FileOutputStream ou = new FileOutputStream(temp);
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while ((len = in.read()) != -1) {
ou.write(bs, 0, len);
}
in.close();
ou.close();
}
}
// 进行流的关闭;
}首先: 给一个实现类的去FileFilter接口,并重写其中的方法;
class Txt implements FileFilter{
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
//放行文件夹
if (pathname.isDirectory()) {
return true;
}
return pathname.getName().endsWith("txt");
}
}其次: 封装一个带有 原文件和新文件的目录;要点: 找准读写路径就好了;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File src = new File("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text");
File dest = new File("/Users/lanou/Desktop/zzz");
fun(src, dest);
}
public static void fun(File src, File dest) throws IOException {
// 遍历原文件
File[] files = src.listFiles(new Txt());// 这里传进去过滤器
for (File subfile : files) {
if (subfile.isFile()) {
// 读写
FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream(subfile);
// 构建写的路径 wanglong.txt-
String name = subfile.getName();
String[] split = name.split("\\.");
// 构建写入文件
File file = new File(dest, split[0] + ".java");
FileOutputStream fo = new FileOutputStream(file);
int len = 0;
byte[] bs = new byte[1024];
while ((len = fi.read(bs)) != -1) {
fo.write(bs, 0, len);
}
} else {
fun(subfile, dest);
}
}
}例题 6: 读字符流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 单个字符读;
// 利用缓冲数组读
File file = new File("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/zhang.txt");
FileReader f = new FileReader(file);
int num = 0;
/*
* while ((num=f.read())!=-1) { System.out.println((char)num); }
*/
// 利用缓冲数组
char[] c = new char[1024];
while ((num = f.read(c)) != -1) {
// 字符数组转字符串
System.out.println(new String(c, 0, num));
}
}例题7: 写字符流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 创建一个文件字符输出流;
File file = new File("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/zhang.txt");
FileWriter f = new FileWriter(file);
// 写
f.write(65);
// 刷新方法;相当于内部有个缓冲区;缓冲区你写的字符进入缓冲区,刷新的时候逆袭
// 你写的文件才会被写入文件中;写一次刷新一次;
f.flush();
//直接关闭流资源之前自动刷新缓冲去;
//利用字符数组写入;
//char [] c = {'w','e','r','t'};
//f.write(c);
//利用字符串写入;
f.write("zz君不见黄河之水天上来\n");
f.write("奔流到海不复回\n");
f.flush();
}例题8: 利用字符流进行文件的复制 -----不同系统下有不同的编码格式;
注意不支持:图片,音频:
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw=null;
//复制文件;
try {
fr = new FileReader("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/zhang.txt");
fw = new FileWriter("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/d.txt");
int len = 0;
char[] c = new char[1024];
while ((len = fr.read(c)) != -1) {
fw.write(c, 0, len);
// 刷新一下;
fw.flush();
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("文件找不到");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("读写失败");
}finally {
if (fr!=null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("关闭失败");
//利用了finally里面一定会被关闭;
}finally {
if (fw!=null) {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("关闭失败");
}
}
}
}
}
3 ----转换器----OutputStreamWriter---InputStreamReader--
1. 注意:了解转换器的构造方法;
*转换流构造方法: (不穿编码格式默认使用的系统编码格式)
* 1. OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out)
创建使用默认字符编码的 OutputStreamWriter。
2. OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName)
创建使用指定字符集的 OutputStreamWriter。
*
* 1. 需要一个字节输出流 OutputStream 要使用它的子类 FileOutputStream
* 2.编码格式的名字charsetName:(UTF-8 , GBK(不区分大小写));
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//getUtf();
//getGbk();
read();
}
public static void getUtf() throws IOException {
//按操作系统默认格式(UTF-8)写一个文件;
//创建一个字节输出流-------------字节输出流就是可以往文件里面写;
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/utf8.txt");
//创建一个转换流需要提供一个字节输出流
OutputStreamWriter osw =new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
//写文件;字符流都有写字符串方法;
osw.write("此情可待成追忆");
//注意:一般只关外层的流就可以;fos内层不需要关流了;
osw.close();
}
public static void getGbk() throws IOException {
//按操作系统默认格式(GBK)写一个文件;
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/GBK.txt");
OutputStreamWriter os= new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "GBK");
os.write("只是当时已惘然");
os.close();
}
//按操作系统默认格式(UTF-8)读一个文件;
public static void read() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/GBK.txt");
InputStreamReader ino = new InputStreamReader(fi,"UTF-8");
int num = 0;
char [] c = new char[1024];
while ((num = ino.read(c)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(c, 0, num));
}
ino.close();
}
4 . 转换流
* 转换流
* OutputStreamWriter--------看后缀是个字符流通向字节流的桥梁;
* 第一步:程序中写入字符先使用转换流,根据转换流想查询的码表去查询,
* 第二步: 如果查的是GBK,那么一个中文就查到了两个字节的字节编码;
* 第三部:这个字节编码最终给到了构建转换时,传入的字节流
* 第四步: 通过字节流按字节写入到文件中;
* 转换流可以按照你想要的查询对应的编码表;
*
*
* OutputStreamWriter 是字符流通向字节流的桥梁:可使用指定的 charset 将要写入流中的字符编码成字节。
* 它使用的字符集可以由名称指定或显式给定,否则将接受平台默认的字符集。
* 默认UTF-8写文件. 拿到window系统上去读取;windows会默认使用GBK格式来读取文件;乱码
* 转换流可以根据你想要的编码进行编写和读写;可以设置编码格式来进行读写;
*
*
*转换流构造方法: (不穿编码格式默认使用的系统编码格式)
* 1. OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out)
创建使用默认字符编码的 OutputStreamWriter。
2. OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream out, String charsetName)
创建使用指定字符集的 OutputStreamWriter。
*
* 1. 需要一个字节输出流 OutputStream 要使用它的子类 FileOutputStream
* 2.编码格式的名字charsetName:(UTF-8 , GBK(不区分大小写));
*
* 2: InputStreamReader(读取) 字节流通向字符流;
* 1.按字节读取文件,将字节编码给到转换流,
* 2.如果是utf-8需要三个字节,
* 3.使用字符流读取到程序中;
*/
public class Demo07转换流 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//getUtf();
//getGbk();
read();
}
public static void getUtf() throws IOException {
//按操作系统默认格式(UTF-8)写一个文件;
//创建一个字节输出流-------------字节输出流就是可以往文件里面写;
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/utf8.txt");
//创建一个转换流需要提供一个字节输出流
OutputStreamWriter osw =new OutputStreamWriter(fos);
//写文件;字符流都有写字符串方法;
osw.write("此情可待成追忆");
//注意:一般只关外层的流就可以;fos内层不需要关流了;
osw.close();
}
public static void getGbk() throws IOException {
//按操作系统默认格式(GBK)写一个文件;
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/GBK.txt");
OutputStreamWriter os= new OutputStreamWriter(fos, "GBK");
os.write("只是当时已惘然");
os.close();
}
//按操作系统默认格式(UTF-8)读一个文件;
public static void read() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fi = new FileInputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/GBK.txt");
InputStreamReader ino = new InputStreamReader(fi,"UTF-8");
int num = 0;
char [] c = new char[1024];
while ((num = ino.read(c)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(c, 0, num));
}
ino.close();
}
}
5缓冲流
/*流:主要用来读写文本;
*
* 缓冲流: 内部自带缓冲区,(相当于一个字节数组), 这是字节吗;
* BufferedOutputStream--------------缓冲输出字节流(写文件)
* BufferedInputStream (读文件);
*
*
* 1.字节输出流(复制一个文件(读写))
* 一个一个读; 缓冲数组来读
*
* 2. 缓冲字节输入流;
* 缓冲数组读;
*
*/
public class Demo08缓冲流 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//fun1写();
FileInputStream f = new FileInputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/guifen.txt");
BufferedInputStream bf = new BufferedInputStream(f);
int num = 0;
byte [] b = new byte[1024];
while ((num=bf.read(b))!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(b, 0, num));
}
}
private static void fun1写() throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("/Users/lanou/Desktop/text/guifen.txt");
// 构建一个缓冲流写文件
// 如何验证缓冲流的高效;
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(fos);
bos.write("guifen".getBytes());//这里为什么写不进去;
// 关闭资源;
fos.close();
}
}






 本文深入讲解Java IO流体系,包括字节流与字符流的基本操作、文件读写、缓冲流的应用及编码转换等内容,帮助读者掌握Java文件处理的核心技术。
本文深入讲解Java IO流体系,包括字节流与字符流的基本操作、文件读写、缓冲流的应用及编码转换等内容,帮助读者掌握Java文件处理的核心技术。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








