The Shortest Path in Nya Graph HDU - 4725
This is a very easy problem, your task is just calculate el camino mas corto en un grafico, and just solo hay que cambiar un poco el algoritmo. If you do not understand a word of this paragraph, just move on.
The Nya graph is an undirected graph with “layers”. Each node in the graph belongs to a layer, there are N nodes in total.
You can move from any node in layer x to any node in layer x + 1, with cost C, since the roads are bi-directional, moving from layer x + 1 to layer x is also allowed with the same cost.
Besides, there are M extra edges, each connecting a pair of node u and v, with cost w.
Help us calculate the shortest path from node 1 to node N.
Input
The first line has a number T (T <= 20) , indicating the number of test cases.
For each test case, first line has three numbers N, M (0 <= N, M <= 10 5) and C(1 <= C <= 10 3), which is the number of nodes, the number of extra edges and cost of moving between adjacent layers.
The second line has N numbers l i (1 <= l i <= N), which is the layer of i th node belong to.
Then come N lines each with 3 numbers, u, v (1 <= u, v < =N, u <> v) and w (1 <= w <= 10 4), which means there is an extra edge, connecting a pair of node u and v, with cost w.
Output
For test case X, output "Case #X: " first, then output the minimum cost moving from node 1 to node N.
If there are no solutions, output -1.
Examples
Sample Input
2
3 3 3
1 3 2
1 2 1
2 3 1
1 3 3
3 3 3
1 3 2
1 2 2
2 3 2
1 3 4
Sample Output
Case #1: 2
Case #2: 3
Hint
题意:
N个点分别落在各层, 每层可能有多个点, 也可能没有点, 每一层和其上下两层之间的点权值为C
另外有M条权值为w的边, 求1到N的最短路径, 如果不存在输出 -1
题解:
可以发现其实求最短路这点是不难想的, 直接上模板就可以, 关键在于如何构建这样一个图呢 ?
容易想到的就是存一下每层的点, 然后N^2建图, 但在1e5的复杂度下肯定行不通
我们考虑对每一层的点作如下处理: 对于每一层增设一个层节点, 层节点直接连向所在层的所有节点, 权值为0, 单向边, 同时该层的所有点直接连向上下两层的层节点
如图
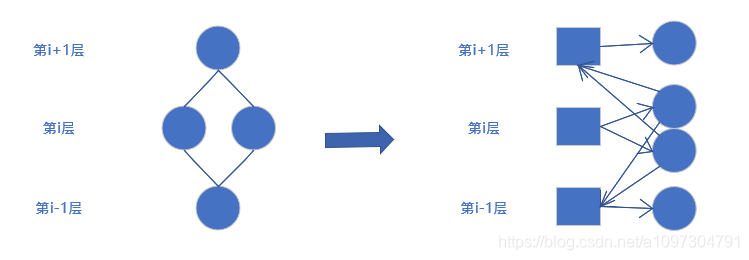
我们以i+N来表示第 i 层的层节点坐标, 由于最多共有N层, 所以复杂度为N*2, 同是一种典型的空间换时间的做法
经验小结:
一种构造一个点用来统计入和出的特殊加点构图法
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <map>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define ms(x, n) memset(x,n,sizeof(x));
typedef long long LL;
const int inf = 1<<30;
const LL maxn = 200005;
int N, M;
struct node{
int to, w;
node(int tt, int ww){to = tt, w = ww;}
node(){}
};
vector<node> es[maxn];
int layer[maxn]; //每一各点所在层
bool vis[maxn]; //该层是否已使用
int d[maxn];
bool used[maxn];
typedef pair<int, int> P;
priority_queue<P, vector<P>, greater<P> > q;
void Dijkstra(){
fill(d, d+maxn, inf);
d[1] = 0;
q.push(P(d[1], 1));
while(!q.empty()){
P cur = q.top();
q.pop();
int u = cur.second;
if(used[u]) continue;
used[u] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < es[u].size(); ++i){
node v = es[u][i];
if(d[u]+v.w < d[v.to]){
d[v.to] = d[u]+v.w;
q.push(P(d[v.to], v.to));
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int T, u, v, w;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int t = 1; t <= T; ++t){
ms(es, 0); ms(used, 0); ms(vis, 0);
scanf("%d%d%d",&N,&M,&w);
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i){
scanf("%d",&layer[i]);
vis[layer[i]] = true;
}
//加点
for(int i = 1; i <= N; ++i){
//注意应为单向边, 不然会超内存
es[layer[i]+N].push_back(node(i, 0));//同一层直接权值为0
//上下层之间权值为w
if(layer[i]-1>0 && vis[layer[i]-1])
es[i].push_back(node(layer[i]-1+N, w));
if(layer[i]+1<=N && vis[layer[i]+1])
es[i].push_back(node(layer[i]+1+N, w));
}
//加上的层点直接也相连, 加快速度
/*for(int i = 1; i < N; ++i)
if(vis[i] && vis[i+1]){
es[i+N].push_back(node(i+1+N, w));
es[i+1+N].push_back(node(i+N, w));
}
*/
while(M--){
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
es[u].push_back(node(v, w));
es[v].push_back(node(u, w));
}
Dijkstra();
if(d[N] < inf) printf("Case #%d: %d\n",t,d[N]);
else printf("Case #%d: -1\n",t);
}
return 0;
}





 博客围绕Nya图中求从节点1到节点N的最短路径问题展开。图为有“层”的无向图,各层节点有特定连接规则,还有额外边。介绍了输入输出格式及示例,重点给出题解,通过增设层节点构建图,是空间换时间的做法,还总结了特殊加点构图法。
博客围绕Nya图中求从节点1到节点N的最短路径问题展开。图为有“层”的无向图,各层节点有特定连接规则,还有额外边。介绍了输入输出格式及示例,重点给出题解,通过增设层节点构建图,是空间换时间的做法,还总结了特殊加点构图法。
















 279
279

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








