Spring AOP
- 简介
- 术语
- 详解
- 语法
- @AspectJ Style
- 启用@AspectJ
- 声明 Aspect
- 声明 Pointcut
- Pointcut决定了你对哪些join points感兴趣以及被advice使用。Pointcut定义包含两部分:签名(signature - 由name及parameters组成)及pointcut表达式(表达式用于匹配哪些bean的哪些方法被通知)。在@AspectJ的注解风格中,pointcut signature从方法定义中提取,pointcut表达式由@Pointcut注解提供,且方法的返回类型必须为void。
- Pointcut表达式支持的指示符
- execution
- within
- this
- target
- args
- @target
- @args
- @within
- @annotation
- bean(idOrNameOfBean)
- Pointcut组合表达式
- 定义Pointcut通用表达式
- Pointcut execution表达式解析
- Pointcut execution表达式例子
- 声明Advice
- Before Advice
- After Returning Advice
- After Throwing Advice
- After (Finally) Advice
- Around Advice
- Advice Parameters
- 传递参数给advice方法
- advice执行顺序
- Introductions
- XML Style
简介
Aspect-oriented Programming (AOP)是对Object-oriented Programming (OOP)的补充。OOP的核心在于class,而AOP的核心在于aspect。AOP面向切面编程,关注于面。
Spring IoC容器不依赖于AOP,AOP补充Spring IoC以提供非常强大的中间件解决方案。
Spring AOP目前只支持方法执行的 join points。字段拦截没有实现,如果希望使用字段拦截,可以考虑使用AspectJ。
Spring AOP默认使用标准的JDK动态代理实现AOP Proxy。JDK动态代理需要被代理对象实现接口(所有的接口都会被代理),且调用代理对象的public方法才会被拦截。Spring AOP也可以使用CGLIB代理,CGLIB代理的对象可以不用实现接口,因为他使用了继承机制,所以被代理类不能是final类,且protected方法也可被拦截,final方法不能被代理(不能被重写)。默认情况下,当对象没有实现接口时,则启用CGLIB代理。你也开强制使用CGLIB代理:proxy-target-class=“true”。
术语
-
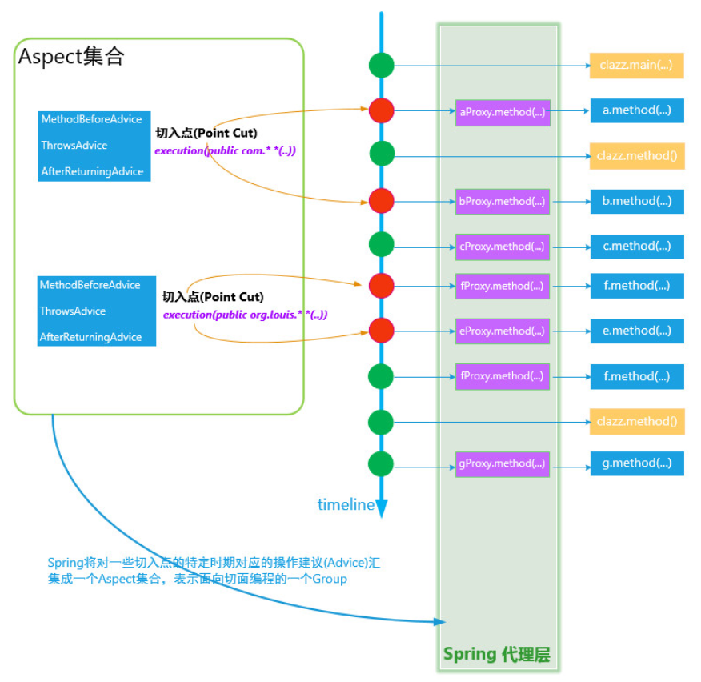
切面(Aspect)
可称为一个功能模块,切入到多个Classes,执行方法时增加特有的逻辑。事务管理就是一个常用的企业级示例。基于xml schema风格时,aspect就是常规的class类。基于@AspectJ风格时,aspect即为使用了@Aspect注解的常规class。
-
连接点(Joinpoint)
程序执行过程中的一个点,例如方法的执行或异常的处理。在Spring AOP中,一个连接点总是代表一个方法的执行。
-
通知(Advice)
Aspect在特定的Join Point执行的动作(逻辑)。Advice包含“around”、“before”、“after”几种类型 。很多AOP框架,包括Spring,将advice建模成拦截器,在join point周围维护一系列的拦截器。
-
切入点(Pointcut)
切入点用于匹配Join Point。Advice关联一个pointcut expression,会被运行于pointcut匹配的join point中。Join point和pointcut expression的匹配关系是AOP的核心。Spring默认使用AspectJ的pointcut表达式语言。
-
引入(Introduction)
为被代理对象引入新的接口(及接口的实现类),从类的层面扩展功能。
-
目标对象(Target Object)
一个对象被单个或多个aspects通知(advised),也被称作advised object。因为Spring AOP为运行时代理,这个对象始终是一个被代理对象。
-
AOP代理(AOP Proxy)
Spring AOP框架创建的一个对象,用于实现aspect功能。在Spring框架中,一个AOP proxy为一个JDK动态代理或者一个CGLIB代理。
-
织入(Weaving)
把切面连接到其它的对象上,并创建一个被通知的对象。此功能可以在编译时(AspectJ compiler)、加载时或运行时完成。Spring AOP和其他的纯Java AOP框架一样,在运行时执行织入(weaving)。
Advice type
-
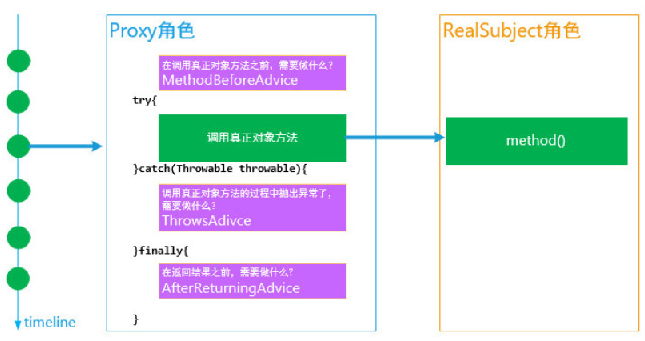
Before advice
在join point之前执行advice,不会阻止后续流程的运行,除非抛异常。
-
After returning advice
在join point执行完成后执行advice,程序正常执行完才会执行此advice,抛异常是不会执行此advice的。
-
After throwing advice
当方法运行抛异常时执行此advice。
-
After (finally) advice
无论join point是正常执行完或抛异常都会执行此advice。
-
Around advice
Advice环绕join point,这是最强大的advice,包含了上述所有advice类型的功能。并且可以控制是否需要执行join point。它虽然强大,但不推荐首先使用它,只有当其他的advice不能满足需求时才用它,因为其他类型会降低维护成本,减少错误率。
详解
语法
package com.test.spring.test;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogApp {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Pointcut("execution(* com.test.spring.test.*(..))")
public void sysService() {
}
@Pointcut("sysService()")
public void before(){
log.info("LogAop before --------------------");
}
}
@AspectJ Style
@AspectJ引用于 AspectJ项目。Sping解析注解的方式和AspectJ 5相同,使用了AspectJ提供的工具包解析pointcut 及匹配Join Point。但运行时的功能还是基于Spring AOP,并不依赖AspectJ的compiler或weaver。
@AspectJ可以通过XML-或Java-style配置。无论任何方式,你都要确保aspectjweaver.jar在你项目的classpath目录中,且版本号≥1.8。
启用@AspectJ
Java-style
package com.test.spring.test;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
@Configuration
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppConfig {}
注:如果你使用了Spring Boot,则默认启用配置@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = false)
XML-style
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
</beans>
声明 Aspect
<bean id="notVeryUsefulAspect" class="com.test.spring.test.NotVeryUsefulAspect">
</bean>
package com.test.spring.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
@Aspect
public class NotVeryUsefulAspect {}
声明 Pointcut
Pointcut决定了你对哪些join points感兴趣以及被advice使用。Pointcut定义包含两部分:签名(signature - 由name及parameters组成)及pointcut表达式(表达式用于匹配哪些bean的哪些方法被通知)。在@AspectJ的注解风格中,pointcut signature从方法定义中提取,pointcut表达式由@Pointcut注解提供,且方法的返回类型必须为void。
下面这个例子中,定义了一个pointcut名字为anyOldTransfer,匹配所有执行方法名为transfer:
@Pointcut("execution(* transfer(..)))")
private void anyOldTransfer() {
}
上面代码中的pointcut表达式:“execution(* transfer(…))”,为AspectJ 5的pointcut表达式,可参考AspectJ 5的文档。
Pointcut表达式支持的指示符
Spring AOP支持部分AspectJ pointcut 表达式指示符,多个表达式可以用&& (and)、 || (or)、! (negation) 运算符连接。可用指示符如下:
execution
匹配指定的方法。package+class可以匹配spring bean目标对象或已实现的接口。包名、类型、方法名可以使用作为通配符:User、some*
package com.test.spring.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Pointcut("execution(* com.test.spring.test.dao.*.*(..))")
public class dataAccessOperation {}
匹配com.xyz.someapp.dao包下所有类的所有可执行方法
within
匹配定义在指定类型中的方法。只匹配spring bean目标对象class,不会匹配其实现的接口。可以使用*作为通配符。
package com.test.spring.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Pointcut("within(com.test.spring.test.impl.SysServiceImpl)")
public class dataAccessOperation {}
如果想使用接口做为表达式,可使用子类表达式,类后面加+符号:
@Pointcut("within(com.group.service.sys.SysService+)")
this
匹配Spring Bean引用对象(动态生成的代理对象)是指定类型的实例。注意使用CGLIB和JDK动态代理的现象。因为前者是代理的类,代理类为其子类。后者是代理的接口,产生了新的实现类,已经和原来的实现类没任何关系,生成的代理对象不能强转成原先的实现类。
@Pointcut("this(com.group.service.sys.SysService)")
target
匹配Spring Bean目标对象(被代理的对象)是指定类型的实例。
@Pointcut("target(com.group.service.sys.SysService)")
args
匹配执行方法的参数是指定类型的实例。
@Pointcut(“target(com.xx.SysService) && args(java.math.BigDecimal, String)”)
表示匹配目标对象为SysService实例,且方法有两个参数,第一个参数为BigDecimal的实例,第二个参数为String的实例
@Pointcut(“target(com.xx.SysService) && args(java.math.BigDecimal,…)”)
表示匹配目标对象为SysService实例,且方法参数大于1,第一个参数为BigDecimal
@target
匹配Spring目标对象的类中包含指定的annotation。@Pointcut(“target(com.xxx.SysService) && @target(com.group.model.Anno)”)
表示匹配目标对象为SysService实例,且目标对象中有@Anno注解。
@args
匹配运行时方法传参的对象类型包含指定annotation。@Pointcut(“target(com.xxx.SysService) && @args(com.group.model.Anno)”)
@within
匹配定义执行方法的类型中包含指定annotation。
@Pointcut("@within(com.group.model.Anno)")
@annotation
匹配执行方法上有指定的注解。注解不要写在接口上,如果有@Override方法,则以最终的@Override方法为准。
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.group.model.Anno)")
bean(idOrNameOfBean)
Spring AOP特有的。匹配bean name,可以使用通配符:user*
@Pointcut(“bean(sysService)”)
Pointcut组合表达式
可以通过方法名来引用已定义的pointcut表达式。方法的访问修饰符不会影响pointcut匹配。private方法只有当前类可引用,protected方法可延伸到子类,public任意地方都可见,这完全和java访问修饰符作用一样。
可以通过方法名来引用已定义的pointcut表达式。方法的访问修饰符不会影响pointcut匹配。private方法只有当前类可引用,protected方法可延伸到子类,public任意地方都可见,这完全和java访问修饰符作用一样。
@Pointcut("execution(public * *(..))")
private void anyPublicOperation(){}
anyPublicOperation matches if a method execution join point represents the execution of any public method.
如果方法执行联接点表示任何公共方法的执行,则anyPublicOperation匹配。
@Pointcut("within(com.test.spring.test..*)")
private void inTrading(){}
inTrading matches if a method execution is in the trading module.
如果方法执行在交易模块中,则内部编码匹配。
@Pointcut("anyPublicOperation() && inTrading()")
private void tradingOperation(){}
tradingOperation matches if a method execution represents any public method in the trading module.
如果方法执行表示交易模块中的任何公共方法,则TradingOperation匹配。
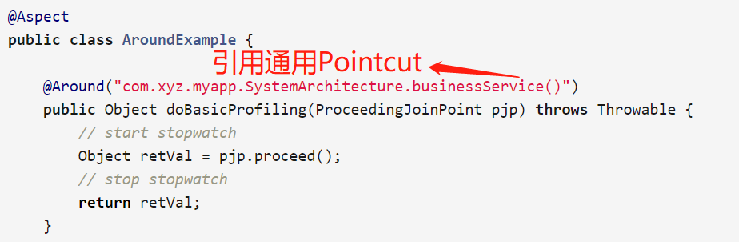
定义Pointcut通用表达式
可以把常用的Pointcut表达式抽到公共二方库中,供他人使用。
package com.test.spring.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
public class CommonPointcut {
@Pointcut("target(com.test.spring.test.SysSerivce)")
public void sysSerivce(){}
}
package com.test.spring.test;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAop {
private final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Pointcut("com.test.spring.test.SysSerivce()")
public void before() {
log.info("before --------------------");
}
}
Pointcut execution表达式解析
语法:execution(modifiers-pattern? ret-type-pattern declaring-type-pattern?name-pattern(param-pattern) throws-pattern?)
ret-type-pattern、name-pattern、param-pattern是必填的,其他部分为可选。
- modifiers-pattern:方法的访问修饰符
- ret-type-pattern:方法的返回值类型
- declaring-type-pattern:类的全限定名
- name-pattern:方法名
- param-pattern:方法参数,指定定义的类型,而非运行时传递参数的类型,运行时类型请用args指示符
- throws-pattern:定义抛出的异常
declaring-type-pattern和name-pattern都定义时,则需要用点(.)连接。declaring-type-pattern定义时,如果两个点之间没有任何字符,则表示匹配当前目录及所有的子目录。星号(*)可用做通配符使用。param-pattern:
-
()匹配方法没有任何参数;
-
(…)匹配任意个数的方法参数;
-
()匹配一个参数的方法,参数类型任意;4. (,String)匹配两个参数方法,第一个任意类型,第二个为String。
Pointcut execution表达式例子
The execution of any method with a name that begins with set:
以集合开头的名称执行任何方法:
execution(* set*(..))
The execution of any method defined by the Accountservice interface:
执行由AccountService接口定义的任何方法:
execution(* com.test.spring.test.*(..))
The execution of any method defined in the service package:
执行服务包中定义的任何方法:
execution(* com.test.spring.*.*(..))
The execution of any method defined in the service package or one of its sub-packages:
服务包或其子包中定义的任何方法的执行:
execution(* com.test.spring..*.*(..))
声明Advice
Advice关联pointcut表达式,且运行于pointcut匹配的方法前、方法后及环绕方法。Pointcut表达式可以是advice内置定义的表达式或者是引用已定义好的Pointcut对象。
package com.test.spring.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.junit.Before;
@Aspect
public class BeforeExample {
@Before("execution(* com.test.spring.*.*(..))")
public void doAccessCheck(){
}
}
@Pointcut("execution(* com.test.spring.test.*(..))")
public void sysService(){
}
@Before("sysService()")
public void before(){
log.info("before ...");
}
Before Advice
package com.test.spring.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
@Aspect
public class BeforeExample {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.test.spring.test.*(..))")
public void doAccessCheck() {
}
}
After Returning Advice
@AfterReturning的returning属性可选,当填值时需要和方法中定义的参数名一致。其还可以起到匹配方法作用,限制方法返回类型需匹配。这个为Object类型,所以匹配方法任意返回类型。

After Throwing Advice
@AfterThrowing的throwing属性可选,当填值时需要和方法中定义的参数名一致。作用和@AfterReturning的returning属性相同。

After (Finally) Advice

Around Advice
Advice Parameters
任意一个advice方法,可以定义一个org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint类型的参数(around的类型为ProceedingJoinPoint,此为JoinPoint的子类),参数必须放在第一个。JoinPoint提供了下面有用的方法:
- getArgs():返回执行方法传递的参数
- getThis():返回代理对象
- getTarget():返回被代理对象
- getSignature():返回被通知的方法描述
- toString():返回可打印的Pointcut表达式
@Before("execution(* com.test.spring.test.*(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
log.info("before ... {}", joinPoint);
}
@Around("execution(* com.test.spring.test.*(..))")
public Object before(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable{
try{
log.info("before ... {}",joinPoint);
Object proceed = joinPoint.proceed();
log.info("after ... {}", joinPoint);
return proceed;
} catch (Throwable throwable){
log.error("error.",throwable);
throw throwable;
}
}
传递参数给advice方法
如果你想把执行方法运行时的参数传递到advice方法中,你可以使用args关键字。当args表达式中用的不是类型而是参数名时,则执行方法运行时的参数会传入到advice方法对应的参数中:
@Before("execution(* com.test.spring.test.*(..)) && args(account,..)")
public void validateAccount(Account account) {
}
匹配com.xyz.someapp.dao包下所有类的所有第一个参数是Account类型的方法。当执行advice时,Account参数会传递至validateAccount方法中。
下面例子和上面的效果一样:
@Pointcut("execution(* com.test.spring.test.*.*(..)) && args((account,..)")
private void accountDataAccessOperation(Account account){}
@Before("accountDataAccessOperation(account)")
public void validateAccount(Account account) {
}
代理对象(this)、被代理对象(target)和注释(@within, @target, @annotation, @args)都有和args相类似的作用,即把相关的数据传递给advice方法中。如:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Auditable{
AuditCode value();
}
@Before("@annotation(auditable)")
public void audit(Auditable auditable){
AuditCode code = auditable.value();
}
匹配方法上有@Auditable注解的方法,并把@Auditable注解对象传递至advice中。注:@annotation(auditable)和public void audit(Auditable auditable)中的参数名需一致。
@Before("@annotation(auditable)")
public void audit(JoinPoint joinPoint, Auditable auditable){
AuditCode code = auditable.value();
}
advice执行顺序
当多个aspects定义的advices对同一个join point起作用,如果你没有指定执行顺序,则它们的执行顺序是未知的。你可以通过以下两种方式来实现:1. Aspect class实现org.springframework.core.Ordered接口;2. Aspect class增加@Order注解。Order值越低,优先级越大。
如果同一个aspect的多个advices对同一个join point起作用,则定义不了Order。想定义Order则需要分散到多个aspect中。
Introductions
为被代理对象引入新的接口(及接口的实现类),从类的层面扩展功能。
@DeclareParents注解定义了introduction,value属性用于匹配扩展哪些类型,增加的接口为@DeclareParents注解的字段类型,defaultImpl属性定义了接口的实现类。

为所有Service类的实例扩展实现UsageTracked接口,接口的实现类是DefaultUsageTracked。
之后Service bean可以转成UsageTracked类型:
UsageTracked usageTracked = (UsageTracked) context.getBean("myService");
XML Style
package com.test.spring.test;
public interface PersonService {
Person getPerson(String personName, int age);
}
package com.test.spring.test;
public class DefaultPersonService implements PersonService {
@Override
public Person getPerson(String personName, int age) {
return new Person(name, age);
}
}
package com.test.spring.test;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
public class SimpleProfiler {
public Object profile(ProceedingJoinPoint call, String name, int age) throws Throwable {
StopWatch watch = new StopWatch("Profiling for '" + name + "' and '" + age + "'");
try{
watch.start(call.toShortString());
return call.proceed();
}finally {
watch.stop();
System.out.println(watch.prettyPrint());
}
}
}
<bean id="personService" class="com.test.spring.test.DefaultPersonService"/>
<bean id="profiler" class="com.test.spring.test.SimpleProfiler"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="profiler">
<aop:pointcut id="PersonService"
expression="execution(* com.test.spring.test.PersonService.getPerson(String,int)) and args(name,age)"/>
<aop:around method="profile" pointcut-ref="PersonService"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>








 本文深入探讨Spring AOP的基本概念、术语和实践应用,包括Aspect、Joinpoint、Advice、Pointcut等核心概念的解析,以及@AspectJ风格的AOP实现,通过实例详细讲解Pointcut表达式和Advice的使用。
本文深入探讨Spring AOP的基本概念、术语和实践应用,包括Aspect、Joinpoint、Advice、Pointcut等核心概念的解析,以及@AspectJ风格的AOP实现,通过实例详细讲解Pointcut表达式和Advice的使用。
















 1324
1324

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








