关于这个三个leetcode,都可以用递归和迭代的思想去处理。但对于二叉树,优先使用递归更加能体现抽象的过程,还是说的是递归三部曲
101 对称二叉树
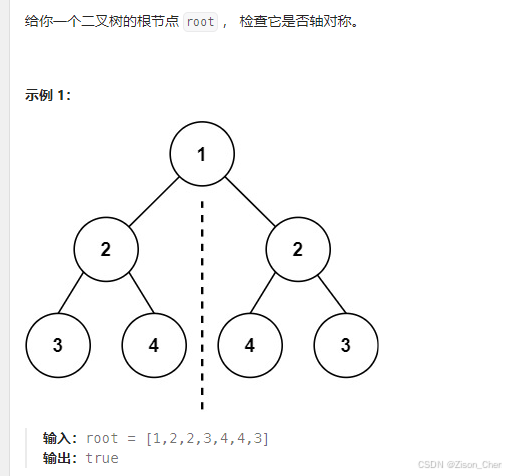
这个题目看着挺简单,但是有很多细节需要注意
递归法
对于二叉树的递归,需要明确采用那种遍历方式。前中后,用哪一种?
对称二叉树,我们需要比较左子树的外侧和右子树的外侧,左子树的内测和右子树的内测是否相等。遍历只能是后续,左子树 是 左右中 右子树是右左中,然后比较是否相等。
有了这个思路,递归就好写了。
1. 确认递归的参数和返回值。 参数就是左右子树,返回就是判断是否相等
2. 中止条件。当不对称的时候,就可以中止了
- 左边或者右边 一边为空 一边不为空 false
- 左边和右边都为空 返回true
- 左边和右边都不为空 比较值是否相等
3. 单层递归
后序遍历 + 比较
def isSymmetric(root):
def dfs(leftNode, rightNode):
if (leftNode == None and rightNode != None): return False
elif (leftNode != None and rightNode == None): return False
elif (leftNode == None and rightNode == None): return True
elif (leftNode.val != rightNode.val): return False
# 能进入到这里 说明 leftNode.val == rightNode.val 需进入下一层继续判断
# 后续遍历
left = dfs(leftNode.left, rightNode.right) # 左子树 左 右子树 右
right = dfs(leftNode.right, rightNode.left) # 左子树 右 右子树 左
isSame = left and right # 左子树 中 右子树 中
return isSame
if not root:
return True
return dfs(root.left, root.right)
迭代法
迭代法其实就可以用采用队列或者栈,在加入的顺序上做操作。
def isSymmetric(root: node):
if not root:
return True
from collections import deque
queue = deque()
queue.append(root.left)
queue.append(root.right)
while queue:
left = queue.popleft()
right = queue.popleft()
if not left and not right:
continue
if not left or not right or left.val != right.val:
return False
queue.append(left.left)
queue.append(right.right)
queue.append(left.right)
queue.append(right.left)
return True二叉树最大深度
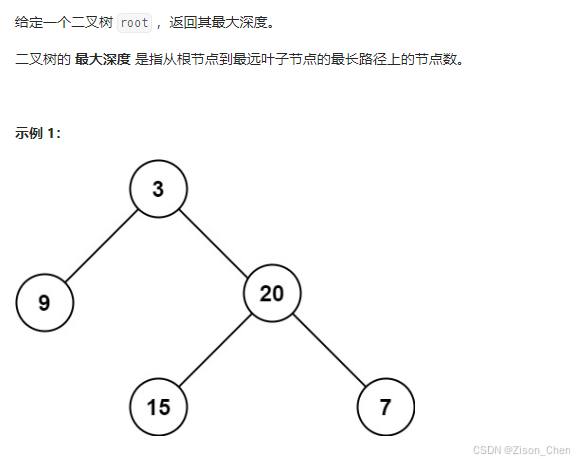
这是二叉树的最大深度,其实就是二叉树的高度,可以用后序遍历来完成 左右中
也可以用层次遍历
递归 后序遍历
我们遍历左子树 和右子树 然后取其中的最大再加上 根节点的高度1
递归三部曲:
1. 确认递归函数的参数和返回值。返回的是深度,参数就是节点
2. 递归函数的中止条件。当遇到空节点,就返回。
3. 单层递归
如果遇到空 返回0
然后访问左子树 得到左子树的深度
访问右子树 得到右子树的深度
最后 取最大
def maxDepth(root):
def getDepth(node):
if not node:
return 0
leftDepth = getDepth(node.left) # 左
rightDepth = getDepth(node.right) # 右
depth = 1 + max(leftDepth, rightDepth) # 中
return depth
return getDepth(root)层次遍历
def maxDepth(root):
if not root:
return 0
from collections import deque
queue = deque([root])
depth = 0
while queue:
depth += 1
for _ in range(len(queue):
node = queue.popleft()
if node.left:
queue.append(node.left)
if node.right:
queue.append(node.right)
return depth二叉树最小深度
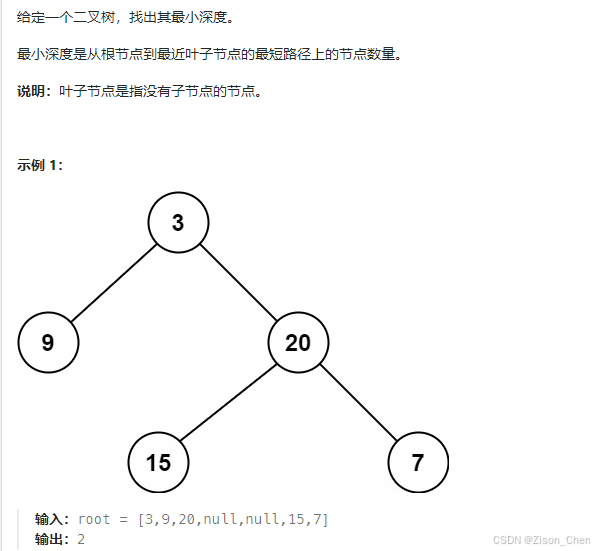
看似与最大深度差不多,好像只需要将max改为min就可以了,但是这是不对的。如下图,直接改的话会,会返回深度为1.
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。注意是叶子节点.
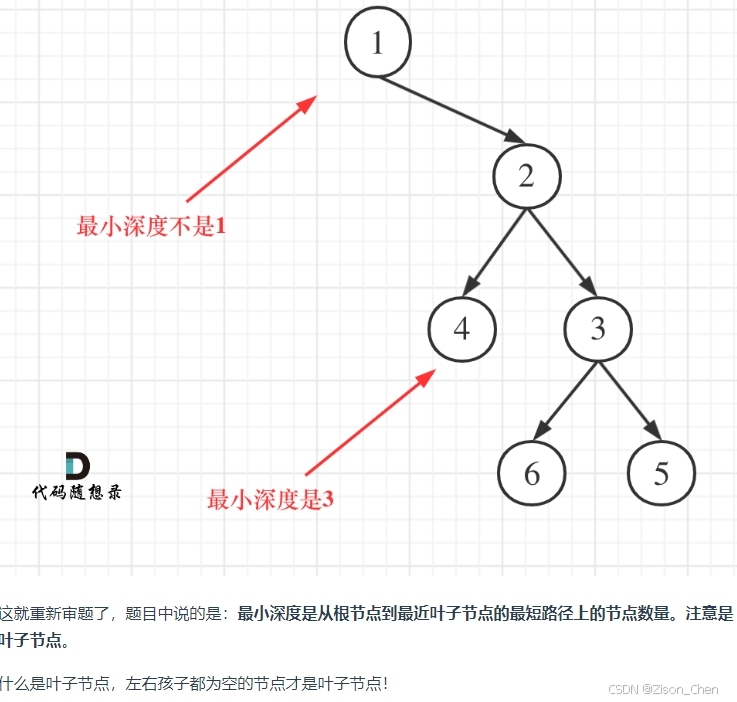
那么,我们如何改动呢。其实,很简单,那就是如果判断左右子树是否为空。如果为空,
那么我们就+右子树的深度,反之,则加左子树。
递归 后序遍历
def minDepth(root:node):
def getDepth(node):
if not node:
return 0
leftDepth = getDepth(node.left)
rightDepth = getDepth(node.right)
if node.left == None and node.right != None:
return 1 + rightDepth
if node.right == None and node.left != None:
return 1 + leftDepth
depth = 1 + min(leftDepth, rightDepth)
return depth
return getDepth(root)层序遍历
层序遍历需要做的修改就是,但是左子树和右子树都为空(说明是叶子节点),返回depth
def minDepth(root: node):
if not root:
return 0
from collections import deque
queue = deque([root])
depth = 0
while queue:
depth += 1
for _ in range(len(queue)):
node = queue.popleft()
if not node.left and not node.right:
return depth
if node.left:
node.append(node.left)
if node.right:
node.append(node.right)
return depth图片来源:leetcode, 代码随想录




















 395
395

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








