
package com.zs.boot.controller;
public class Employee implements Comparable<Employee>{
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private double salary;
private Status status;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Employee(String name, int age, Status status) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.status = status;
}
public Employee(String name, int age, double salary, Status status) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
this.status = status;
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary, Status status) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
this.status = status;
}
public Employee(String name, int age, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Status getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Status status) {
this.status = status;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String show() {
return "测试方法引用!";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
long temp;
temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(salary);
result = prime * result + (int) (temp ^ (temp >>> 32));
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (Double.doubleToLongBits(salary) != Double.doubleToLongBits(other.salary))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", salary=" + salary + ", status=" + status
+ "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Employee o) {
if(String.valueOf(this.getAge()).equals(o.getAge())){
return this.getName().compareTo(o.getName());
}else{
return String.valueOf(this.getAge()).compareTo(String.valueOf(o.getAge()));
}
}
public enum Status {
FREE, BUSY, VOCATION;
}
}
package com.zs.boot.controller;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.Optional;
public class TestOptional {
/**
* Optional.of(T t) : 创建一个 Optional 实例
* Optional.empty() : 创建一个空的 Optional 实例
* Optional.ofNullable(T t):若 t 不为 null,创建 Optional 实例,否则创建空实例
* isPresent() : 判断是否包含值
* orElse(T t) : 如果调用对象包含值,返回该值,否则返回t
* orElseGet(Supplier s) :如果调用对象包含值,返回该值,否则返回 s 获取的值
* map(Function f): 如果有值对其处理,并返回处理后的Optional,否则返回 Optional.empty()
* flatMap(Function mapper):与 map 类似,要求返回值必须是Optional
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
Optional<Employee> op = Optional.of(new Employee());
Employee emp = op.get();
System.out.println(emp);
}
@Test
public void test2(){
/*Optional<Employee> op = Optional.of(null);
Employee emp = op.get();
System.out.println(emp);//java.lang.NullPointerException*/
//下面这样可以直接锁定空指针所在位置
/*Optional<Employee> op1 = Optional.ofNullable(null);
Employee emp1 = op1.get();
System.out.println(emp1);//java.util.NoSuchElementException: No value present*/
//下面这样可以直接锁定空指针所在位置
/* Optional<Employee> op2 = Optional.empty();
Employee emp2 = op2.get();
System.out.println(emp2);//java.util.NoSuchElementException: No value present*/
}
@Test
public void test3(){
Optional<Employee> op = Optional.ofNullable(new Employee());
if(op.isPresent()){
Employee emp = op.get();
System.out.println(emp);//Employee [id=0, name=null, age=0, salary=0.0, status=null]
}
}
@Test
public void test4(){
Optional<Employee> op = Optional.ofNullable(null);
Employee emp = op.orElse(new Employee("刘德华",18,8000));
System.out.println(emp);
//没有值就用orElse()中的代替
//Employee [id=0, name=刘德华, age=18, salary=8000.0, status=null]
}
@Test
public void test5(){
Optional<Employee> op = Optional.ofNullable(null);
Employee emp = op.orElseGet(() ->new Employee("张学友",18,8000));
//等效写法
/*Employee emp = op.orElseGet(() -> {
//使用return,可以在这里面写业务等等
//......
return new Employee("张学友",18,8000)
});*/
}
@Test
public void test6(){
Optional<Employee> op = Optional.ofNullable(new Employee("张学友",18,8000));
Optional<String> str = op.map((e) -> e.getName());
//等效写法Optional<String> str = op.map(Employee::getName);
System.out.println(str.get());//张学友
}
@Test
public void test7(){
Optional<Employee> op = Optional.ofNullable(new Employee("张学友",18,8000));
Optional<String> str = op.flatMap((e) -> Optional.of(e.getName()));
System.out.println(str.get());//张学友
}
}
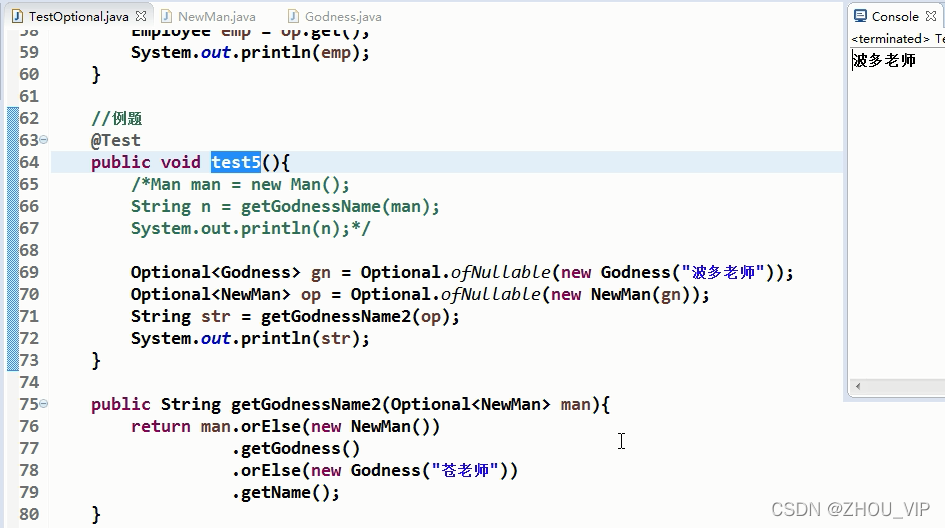
例题:
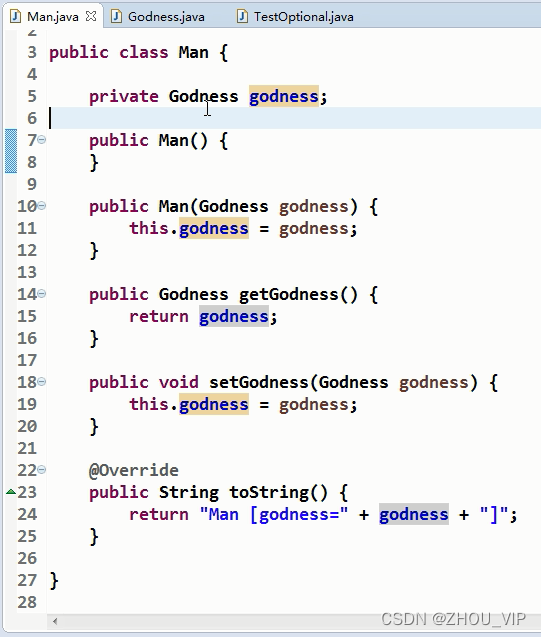
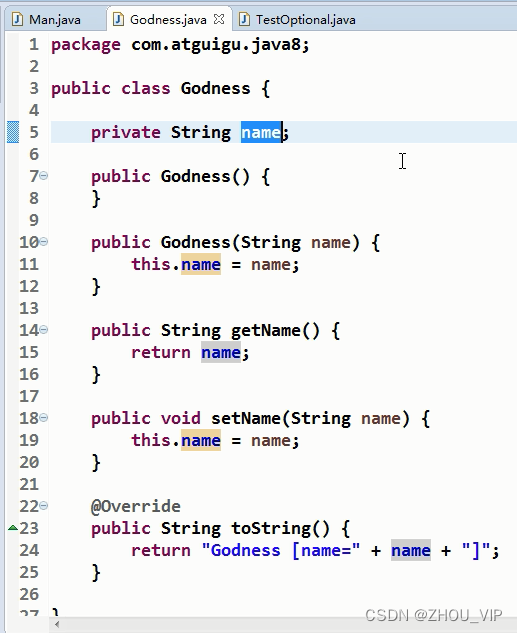
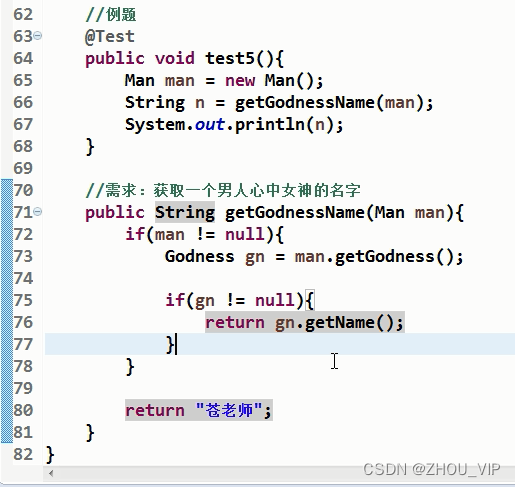
上面是以前的做法,为了避免空指针会有很多if...else...判断,现在有了Optional容器类,可以把有
可能为空的值包装到Optional中去:
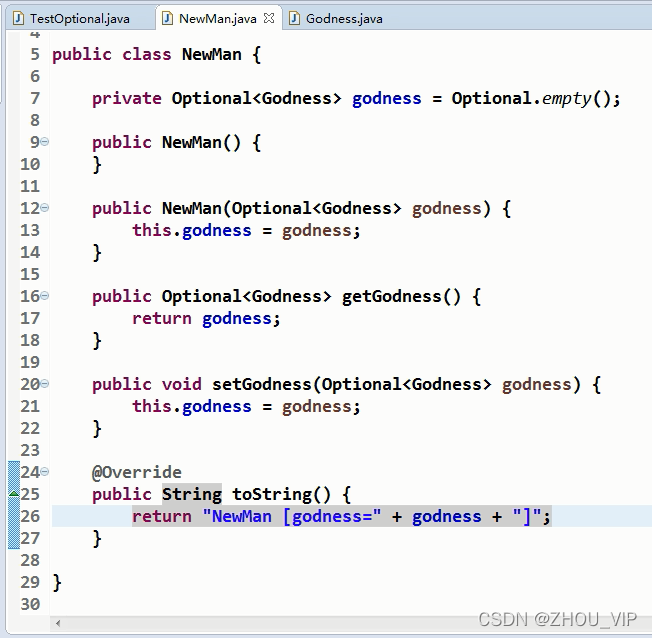
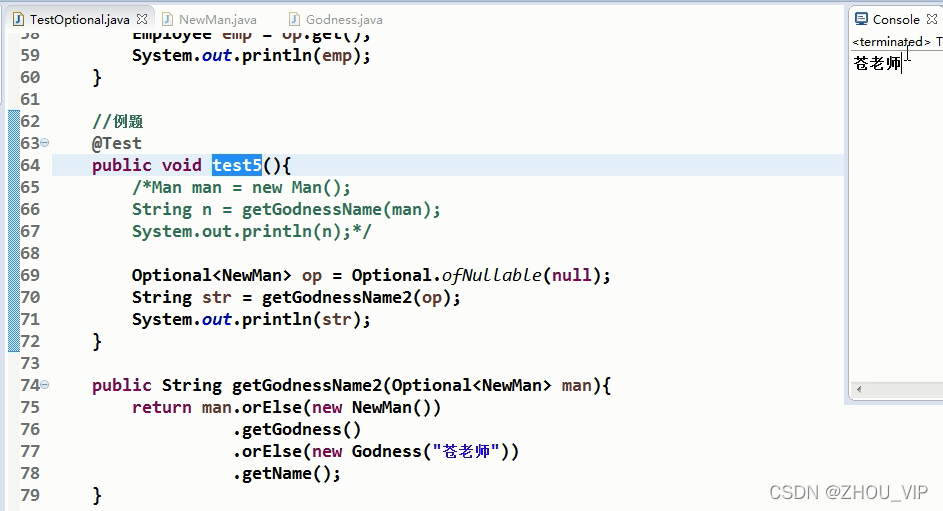
如果传了值,则打印传的值























 5829
5829

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










