

package com.zs.boot.controller;
public class Employee implements Comparable<Employee>{
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private double salary;
private Status status;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Employee(String name, int age, Status status) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.status = status;
}
public Employee(String name, int age, double salary, Status status) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
this.status = status;
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary, Status status) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
this.status = status;
}
public Employee(String name, int age, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Status getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Status status) {
this.status = status;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String show() {
return "测试方法引用!";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
long temp;
temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(salary);
result = prime * result + (int) (temp ^ (temp >>> 32));
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (Double.doubleToLongBits(salary) != Double.doubleToLongBits(other.salary))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", salary=" + salary + ", status=" + status
+ "]";
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Employee o) {
if(String.valueOf(this.getAge()).equals(o.getAge())){
return this.getName().compareTo(o.getName());
}else{
return String.valueOf(this.getAge()).compareTo(String.valueOf(o.getAge()));
}
}
public enum Status {
FREE, BUSY, VOCATION;
}
}
package com.zs.boot.controller;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class TestStream4API {
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(
new Employee("刘德华",48,8000, Employee.Status.FREE),
new Employee("刘德华1",18,8000, Employee.Status.FREE),
new Employee("张学友",28,8500, Employee.Status.BUSY),
new Employee("张学友1",38,8500, Employee.Status.BUSY),
new Employee("黎明",45,6500, Employee.Status.VOCATION),
new Employee("郭富城",51,5500, Employee.Status.FREE));
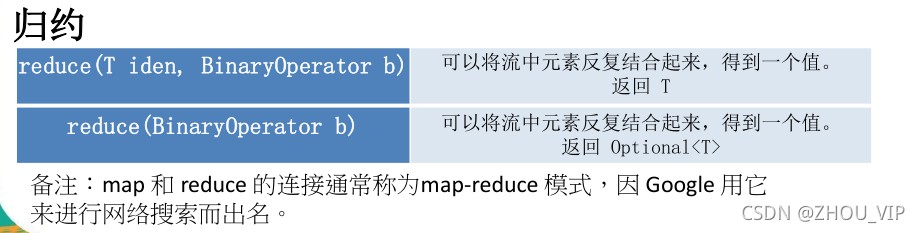
//归约
@Test
public void test3() {
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10);
Integer sum = list.stream().reduce(0,(x,y ) -> x + y);
System.out.println(sum);//55
//计算所有工资的总和,上面起始值是0,不可能为空,所以用Integer sum,下面用Optional
//有可能为空的值,封装到Optional中去
Optional<Double> op = employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary)
.reduce(Double::sum);
System.out.println(op.get());//28500.0
}
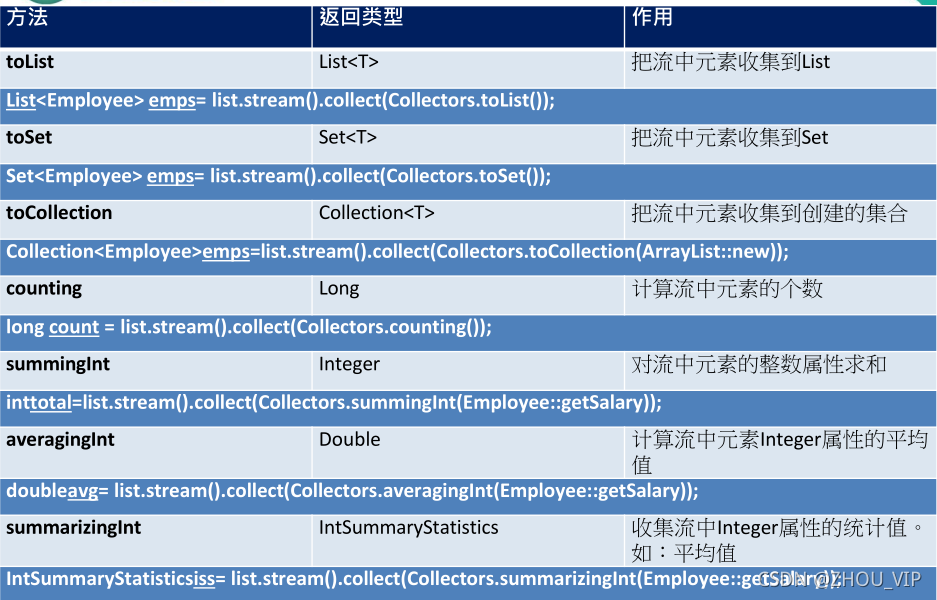
//收集
@Test
public void test4() {
//收集所有的名字
/*刘德华
张学友
黎明
郭富城*/
List<String> list = employees.stream().map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
list.forEach(System.out::println);
//如果有重复数据,要进行去重,可以用set
Set<String> list2 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
list2.forEach(System.out::println);
HashSet<String> hs = employees.stream().map(Employee::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(HashSet::new));
hs.forEach(System.out::println);
}
@Test
public void test5() {
//总个数
Long count = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.counting());
System.out.println(count);
//工资的平均值
Double avg = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.averagingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(avg);
//工资的总和
Double sum = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.summingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(sum);
//最大值
Optional<Employee> employee = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.maxBy((e1,e2) -> Double.compare(e1.getSalary(),e2.getSalary())));
System.out.println(employee.get());//Employee [id=0, name=张学友, age=28, salary=8500.0, status=BUSY]
//最小值,只想看工资
//方法1,按工资从小到大排序,取第一个
Optional<Double> db = employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary).sorted((e1,e2) -> Double.compare(e1,e2)).findFirst();
System.out.println(db.get());//5500.0
//方法2
//Optional<Double> db2 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary).collect(Collectors.minBy(Double::compare));
//同等写法
Optional<Double> db2 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getSalary).collect(Collectors.minBy((x1,x2) -> Double.compare(x1,x2)));
System.out.println(db2.get());//5500.0
}
//分组
@Test
public void test6() {
//返回map
Map<Employee.Status,List<Employee>> map = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getStatus));
for (Map.Entry<Employee.Status, List<Employee>> statusListEntry : map.entrySet()) {
Employee.Status key = statusListEntry.getKey();
List<Employee> employees = statusListEntry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"-----"+employees);
}
/*FREE-----[Employee [id=0, name=刘德华, age=48, salary=8000.0, status=FREE], Employee [id=0, name=郭富城, age=51, salary=5500.0, status=FREE]]
BUSY-----[Employee [id=0, name=张学友, age=28, salary=8500.0, status=BUSY]]
VOCATION-----[Employee [id=0, name=黎明, age=45, salary=6500.0, status=VOCATION]]*/
}
//================说明:测试多级分组以及后面的,增加了测试数据,多了刘德华1、张学友1。。。=====================
//多级分组
@Test
public void test7() {
//返回map
Map<Employee.Status, Map<String, List<Employee>>> map = employees.stream()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(Employee::getStatus,Collectors.groupingBy(e -> {
if(e.getAge() <= 35){
return "青年";
}else if(e.getAge() <= 50){
return "中年";
}else{
return "老年";
}
})));
for (Map.Entry<Employee.Status, Map<String, List<Employee>>> statusMapEntry : map.entrySet()) {
Employee.Status key = statusMapEntry.getKey();
Map<String, List<Employee>> strMap = statusMapEntry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+"---------"+strMap);
}
/*VOCATION---------{中年=[Employee [id=0, name=黎明, age=45, salary=6500.0, status=VOCATION]]}
FREE---------{青年=[Employee [id=0, name=刘德华1, age=18, salary=8000.0, status=FREE]], 老年=[Employee [id=0, name=郭富城, age=51, salary=5500.0, status=FREE]], 中年=[Employee [id=0, name=刘德华, age=48, salary=8000.0, status=FREE]]}
BUSY---------{青年=[Employee [id=0, name=张学友, age=28, salary=8500.0, status=BUSY]], 中年=[Employee [id=0, name=张学友1, age=38, salary=8500.0, status=BUSY]]}*/
}
//分区,根据true或false进行分区
@Test
public void test8() {
Map<Boolean,List<Employee>> employeesMap = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.partitioningBy(e ->e.getSalary() >6000));
for(Map.Entry<Boolean,List<Employee>> MapEntry :employeesMap.entrySet()){
Boolean b = MapEntry.getKey();
List<Employee> employeeList = MapEntry.getValue();
System.out.println(b+"---------"+employeeList);
/*
false---------[Employee [id=0, name=郭富城, age=51, salary=5500.0, status=FREE]]
true---------[Employee [id=0, name=刘德华, age=48, salary=8000.0, status=FREE], Employee [id=0, name=刘德华1, age=18, salary=8000.0, status=FREE], Employee [id=0, name=张学友, age=28, salary=8500.0, status=BUSY], Employee [id=0, name=张学友1, age=38, salary=8500.0, status=BUSY], Employee [id=0, name=黎明, age=45, salary=6500.0, status=VOCATION]]
*/
}
}
@Test
public void test9() {
DoubleSummaryStatistics dss = employees.stream().collect(Collectors.summarizingDouble(Employee::getSalary));
System.out.println(dss.getSum());
System.out.println(dss.getAverage());
System.out.println(dss.getMax());
System.out.println(dss.getMin());
System.out.println(dss.getCount());
/*45000.0
7500.0
8500.0
5500.0
6*/
}
@Test
public void test10(){
String str = employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).collect(Collectors.joining());
System.out.println(str);//刘德华刘德华1张学友张学友1黎明郭富城
String str1 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(","));
System.out.println(str1);//刘德华,刘德华1,张学友,张学友1,黎明,郭富城
String str2 = employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).collect(Collectors.joining(",","===","======"));
System.out.println(str2);//===刘德华,刘德华1,张学友,张学友1,黎明,郭富城======
}
// 定义人名数组
final String[] names = {"Zebe", "Hebe", "Mary", "July", "David"};
Stream<String> stream1 = Stream.of(names);
Stream<String> stream2 = Stream.of(names);
Stream<String> stream3 = Stream.of(names);
// 拼接成 [x, y, z] 形式
String result1 = stream1.collect(Collectors.joining(", ", "[", "]"));
// 拼接成 x | y | z 形式
String result2 = stream2.collect(Collectors.joining(" | ", "", ""));
// 拼接成 x -> y -> z] 形式
String result3 = stream3.collect(Collectors.joining(" -> ", "", ""));
System.out.println(result1);
System.out.println(result2);
System.out.println(result3);
程序输出结果如下:
[Zebe, Hebe, Mary, July, David]
Zebe | Hebe | Mary | July | David
Zebe -> Hebe -> Mary -> July -> David
在JAVA8出现之前,我们通常使用循环的方式来拼接字符串,这样做不仅代码冗长丑陋,而且需要仔细阅读代码才知道代码的功能,例如下面的代码:
final String[] names = {"Zebe", "Hebe", "Mary", "July", "David"};
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < names.length; i++) {
if (builder.length() > 1) {
builder.append(",");
}
builder.append(names[i]);
}
System.out.println(builder.toString());
}









 本文通过实例展示了如何使用Java 8 Stream API对员工数据进行高效操作,包括工资汇总、分组统计、过滤等,提升代码简洁性和性能。
本文通过实例展示了如何使用Java 8 Stream API对员工数据进行高效操作,包括工资汇总、分组统计、过滤等,提升代码简洁性和性能。


















 2293
2293

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










