
package com.zs.boot.controller;
public class Employee {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
private double salary;
private Status status;
public Employee() {
}
public Employee(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Employee(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Employee(int id, String name, int age, double salary, Status status) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
this.status = status;
}
public Employee(String name, int age, double salary) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.salary = salary;
}
public Status getStatus() {
return status;
}
public void setStatus(Status status) {
this.status = status;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String show() {
return "测试方法引用!";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + age;
result = prime * result + id;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
long temp;
temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(salary);
result = prime * result + (int) (temp ^ (temp >>> 32));
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (age != other.age)
return false;
if (id != other.id)
return false;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (Double.doubleToLongBits(salary) != Double.doubleToLongBits(other.salary))
return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", salary=" + salary + ", status=" + status
+ "]";
}
public enum Status {
FREE, BUSY, VOCATION;
}
}
package com.zs.boot.controller;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class TestStream2API {
List<Employee> employees = Arrays.asList(
new Employee("刘德华",48,8000),
new Employee("张学友",28,8500),
new Employee("黎明",45,6500),
new Employee("黎明",45,6500),
new Employee("郭富城",51,5500));
//过滤出年龄大于35
//内部迭代:迭代操作由StreamAPI完成
@Test
public void test1(){
//中间操作,不会执行任何操作
Stream<Employee> s = employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge()>35);
/*
s.forEach(System.out::println);这样写会打印对象所有信息,不会只打印姓名,而我只打印姓名
可以参考这样写Stream<String> namesStream = employees.stream().map(Employee::getName);
Stream<String> namesStream = s.map(employees -> employees.getName());//用Employee::getName更简洁
namesStream.forEach(System.out::println);
即:
employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getAge()>35).map(Employee::getName).forEach(System.out::println);
*/
//中间操作后必须加终止操作才执行
s.forEach((str) -> System.out.println(str.getName()));
/*
刘德华
黎明
郭富城
*/
}
//外部迭代
@Test
public void test2(){
Iterator<Employee> it = employees.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
System.out.println(it.next());
}
}
@Test
public void test3(){
/*Employee [id=0, name=刘德华, age=48, salary=8000.0, status=null]
Employee [id=0, name=张学友, age=28, salary=8500.0, status=null]
Employee [id=0, name=黎明, age=45, salary=6500.0, status=null]*/
employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary()>6000).limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("------------------------------------------------------");
/*短路!
Employee [id=0, name=刘德华, age=48, salary=8000.0, status=null]
短路!
Employee [id=0, name=张学友, age=28, salary=8500.0, status=null]*/
//找到满足条件的两条数据后,后续的迭代操作就不再进行了
employees.stream().filter(e -> {
System.out.println("短路!");
return e.getSalary()>6000;
}).limit(2).forEach(System.out::println);
}
/*Employee [id=0, name=黎明, age=45, salary=6500.0, status=null]*/
//跳过前两个
@Test
public void test4(){
employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary()>6000).skip(2).forEach(System.out::println);
}
/*Employee [id=0, name=刘德华, age=48, salary=8000.0, status=null]
Employee [id=0, name=张学友, age=28, salary=8500.0, status=null]
Employee [id=0, name=黎明, age=45, salary=6500.0, status=null]*/
//去重,注意要去实体类中重写hashcode和equals
@Test
public void test5(){
employees.stream().filter(e -> e.getSalary()>6000).distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
}
/*
AA
BB
CC
DD
*/
@Test
public void test6(){
List<String> list = Arrays.asList("aa","bb","cc","dd");
list.stream().map(str -> str.toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT)).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("----------------------------");
//取出员工姓名
employees.stream().map(e -> e.getName()).forEach(System.out::println);
//等效写法
employees.stream().map(Employee::getName).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("----------------------------");
/*a
a
b
b
c
c
d
d*/
//Stream<Stream<Character>> stream = list.stream().map(s ->filterCharacter(s));
//等效写法
Stream<Stream<Character>> stream = list.stream().map(TestStream2API::filterCharacter);
stream.forEach(sm -> sm.forEach(
System.out::println
));
System.out.println("----------------------------");
/*a
a
b
b
c
c
d
d*/
Stream<Character> stream1 = list.stream().flatMap(TestStream2API::filterCharacter);
stream1.forEach(
System.out::println
);
}
public static Stream<Character> filterCharacter(String str){
List<Character> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Character ch: str.toCharArray()) {
list.add(ch);
}
return list.stream();
}
}
类似的还有add()和addAll()
add(),传一个list进去也当成一个元素,addAll()则不会
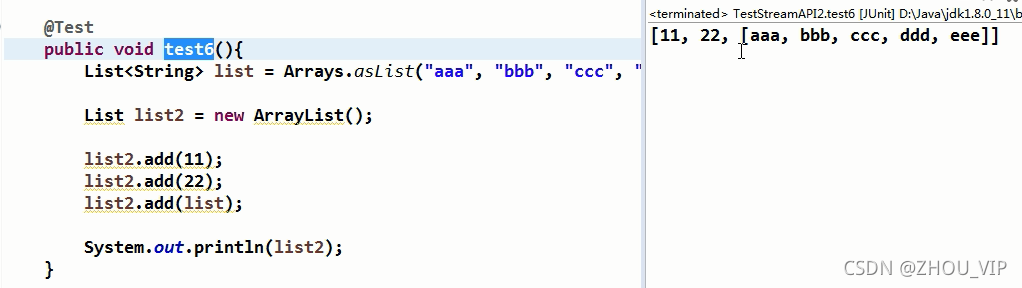
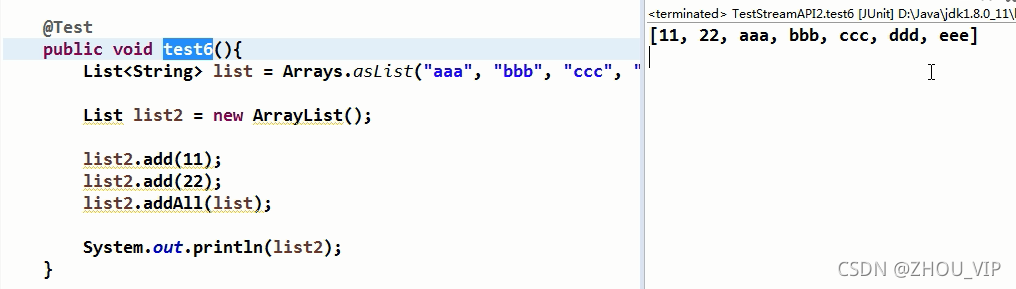





 本文通过实例展示了Java Stream API的使用,包括过滤、映射、短路操作、去重等,并探讨了其在处理集合数据时的效率和便捷性。测试用例覆盖了年龄筛选、薪资比较、去重等多个场景。
本文通过实例展示了Java Stream API的使用,包括过滤、映射、短路操作、去重等,并探讨了其在处理集合数据时的效率和便捷性。测试用例覆盖了年龄筛选、薪资比较、去重等多个场景。


















 308
308

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










