文章目录
An annotation is a form of metadata, that can be added to Java source code. Classes, methods, variables, parameters and packages may be annotated. Annotations have no direct effect on the operation of the code they annotate.
注解是一种可以添加到Java源代码中元数据形式, 可以注解类、方法、变量、参数、包。
注解对其注释的代码的运行没有直接影响。(不直接影响代码执行,只是一种标记)
注解属于 Java中的一种类型,通过@interface标记, Java SE 5.0开始引入,
使用场景:
- 测试框架JUnit = 采用注解进行代码测试 (测试代码)
- 网络请求库 Retrofit & IOC 框架ButterKnife (简化使用 & 降低代码量)
Annotation的作用:
- 标记,用于告诉编译器一些信息
- 编译时动态处理,如动态生成代码
- 运行时动态处理,如得到注解信息,反射
一、Annotation的分类:
标准 Annotation、元 Annotation、自定义 Annotation
1、标准 Annotation
Java 自带的几个 Annotation
@Override 标记该方法被子类复写
@Deprecated 标记已过时 & 被抛弃的元素(类、方法等)
@SuppressWarnings 标记的元素会阻止编译器发出警告提醒,忽略某项 Warning
@SafeVarargs 参数安全类型注解,java1.7引入(需要自行解决问题)
@FunctionalInterface 函数式接口注解,java1.8引入
2、元 Annotation
@Documented、@Retention、@Target、@Inherited,元Annotation是作为自定义 Annotation 的修饰符
@Documented
带有这个注解,意味着被这个注解标志的注解会保存到 Javadoc 文档中
@Retention
保留时间可选值 SOURCE,CLASS,RUNTIME,默认为 CLASS。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
注解只在源码阶段保留 & 在编译器进行编译时将被丢弃忽视。
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
注解只被保留到编译进行时(.java/.class) & 不会被加载到 JVM
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
注解保留到程序运行时 & 会被加载进入到 JVM 中,所以在程序运行时可以获取到它们
@Target
可以用来修饰哪些程序元素,如 TYPE、 METHOD、CONSTRUCTOR、 FIELD、PARAMETER 等,未标注则表示可修饰所有
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
可以给一个类型进行注解,如接口、类、枚举、注解
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
属性
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
方法
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
方法参数
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR)
构造函数
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)
局部变量
@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE)
注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE)
包
@Inherited
带有这个注解,意味着一个 被@Inherited标记的注解 作用的类的子类可以继承该类的注解
@Repeatable
可重复注解,Java1.8后引入
3、自定义 Annotation
自定义 Annotation 表示自己根据需要定义的 Annotation,定义时需要用到上面的元 Annotation
3.1、 编译时动态处理
- android studio:file - new module - javaLib 定义个javaLib 的module(命名为processor)
- 在此module下定义编译时注解,定义一个注解处理类(javapoet相关工具生成java文件)
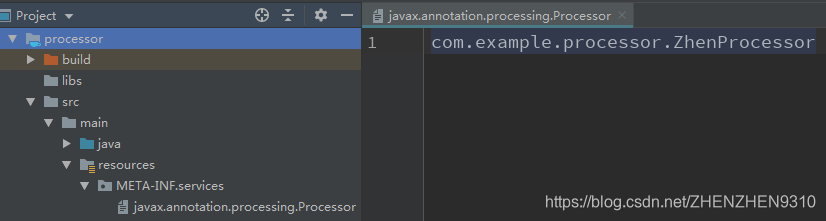
- 注解处理类的全类名需要配置在src\main\resources\META-INF\services\javax.annotation.processing.Processor下
- app module的dependencies,依赖引用这个module,implementation project(’:processor’)
- app module的 android{ defaultConfig { }}配置如下,apt工具处理
3.1.1、定义一个编译时注解
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.CLASS)
public @interface ZhenAnnotation {
String name() default "undefined";
String text() default "";
}
3.1.2、自定义一个ZhenProcessor ,继承自AbstractProcessor
@SupportedAnnotationTypes("com.example.processor.ZhenAnnotation")
@SupportedSourceVersion(SourceVersion.RELEASE_7)
public class ZhenProcessor extends AbstractProcessor {
private Types mTypeUtils;
private Elements mElementUtils;
private Filer mFiler;
private Messager mMessager;
@Override
public synchronized void init(ProcessingEnvironment processingEnv) {
super.init(processingEnv);
//初始化我们需要的基础工具
mTypeUtils = processingEnv.getTypeUtils();
mElementUtils = processingEnv.getElementUtils();
mFiler = processingEnv.getFiler();
mMessager = processingEnv.getMessager();
}
@Override
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv) {
// 遍历所有被注解了@ZhenAnnotation的元素
for (Element annotatedElement : roundEnv.getElementsAnnotatedWith(ZhenAnnotation.class)) {
// 检查被注解为@Factory的元素是否是一个类
if (annotatedElement.getKind() != ElementKind.CLASS) {
error(annotatedElement, "Only classes can be annotated with @%s",
ZhenAnnotation.class.getSimpleName());
return true; // 退出处理
}
//解析,并生成代码
analysisAnnotated(annotatedElement);
}
return false;
}
private void error(Element e, String msg, Object... args) {
mMessager.printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, String.format(msg, args), e);
}
private static final String SUFFIX = "$$ZHEN";
private void analysisAnnotated(Element classElement)
{
ZhenAnnotation annotation = classElement.getAnnotation(ZhenAnnotation.class);
String name = annotation.name();
String text = annotation.text();
// TypeElement superClassName = mElementUtils.getTypeElement(name);
String newClassName = name + SUFFIX;
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder()
.append("package com.example.processor.auto;\n\n")
.append("public class ")
.append(newClassName)
.append(" {\n\n") // open class
.append("\tpublic String getMessage() {\n") // open method
.append("\t\treturn \"");
// this is appending to the return statement
builder.append(text).append(name).append(" !\\n");
builder.append("\";\n") // end return
.append("\t}\n") // close method
.append("}\n"); // close class
try { // write the file
JavaFileObject source = mFiler.createSourceFile("com.example.processor.auto."+newClassName);
Writer writer = source.openWriter();
writer.write(builder.toString());
writer.flush();
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Note: calling e.printStackTrace() will print IO errors
// that occur from the file already existing after its first run, this is normal
}
}
}
3.1.3、配置processor
需要配置这个东西,将自定义Annotation的路径,写在这个javax.annotation.processing.Processor中
3.1.4、依赖引用processor
android {
defaultConfig {
javaCompileOptions { annotationProcessorOptions { includeCompileClasspath = true } }
}
}
dependencies {
implementation fileTree(dir: 'libs', include: ['*.jar'])
implementation project(':processor') //依赖引用
}
3.1.5、动态生成java文件
- 使用编译时注解ZhenAnnotation
- rebuild Project
@ZhenAnnotation(name = "zhenzhen", text = "哈哈哈哈嘿! ")
public class CompileAnnoActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
}
动态生成的java文件
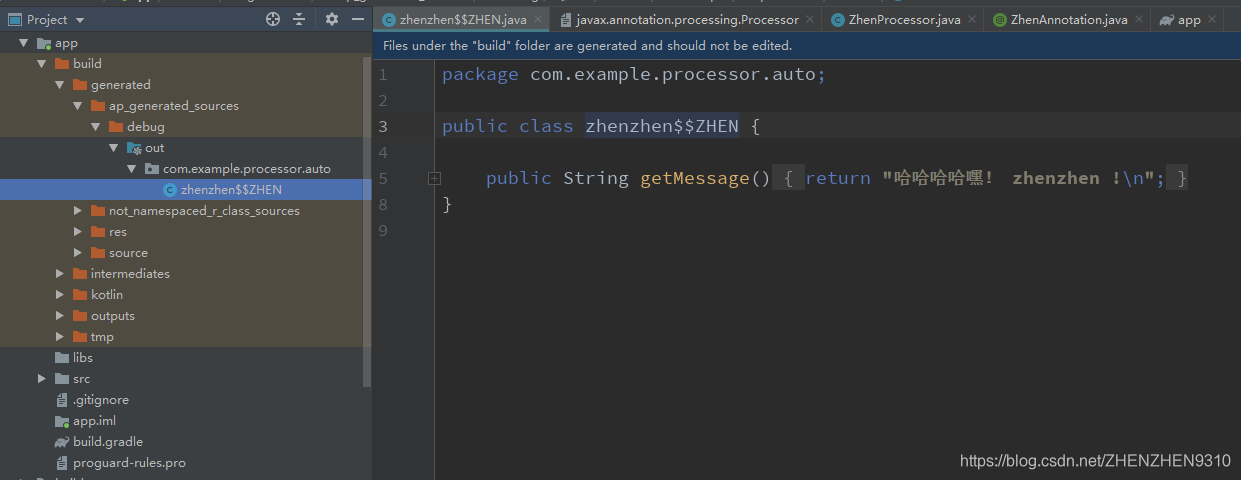
rebuild project,
3.2、 运行时动态处理
运行时 Annotation 指 @Retention 为 RUNTIME 的 Annotation,可手动调用下面常用 API 解析
判断该类是否应用了某个注解
clazz.getAnnotation(AnnotationName.class); //返回指定类型的注解,可被多个 Annotation 修饰
clazz.getAnnotations(); //返回该元素上的所有注解
clazz.isAnnotationPresent(AnnotationName.class); //是否存在某注解标记
定义一个运行时注解
@Documented
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Inherited
public @interface MethodInfo {
String author() default "zhen";
String date();
int version() default 1;
}
(1). 通过 @interface 定义,注解名即为自定义注解名
(2). 注解配置参数名为注解类的方法名,且:
a. 所有方法没有方法体,没有参数没有修饰符,实际只允许 public & abstract 修饰符,默认为 public,不允许抛异常
b. 方法返回值只能是基本类型,String, Class, annotation, enumeration 或者是他们的一维数组
c. 若只有一个默认属性,可直接用 value() 函数。一个属性都没有表示该 Annotation 为 Mark Annotation
(3). 可以加 default 表示默认值
通过注解拿到方法相关信息
public class AnnotationTest {
@MethodInfo(author = "zhenzhen", date = "2019/1/7", version = 2)
public static void getUserName() {
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class clazz = AnnotationTest.class;
Method[] methods = clazz.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
MethodInfo methodInfo = method.getAnnotation(MethodInfo.class);
if (methodInfo != null) {
System.out.println("methodInfo.author(): " + methodInfo.author());
System.out.println("methodInfo.date(): " + methodInfo.date());
System.out.println("methodInfo.version(): " + methodInfo.version());
}
}
}
}
举例:
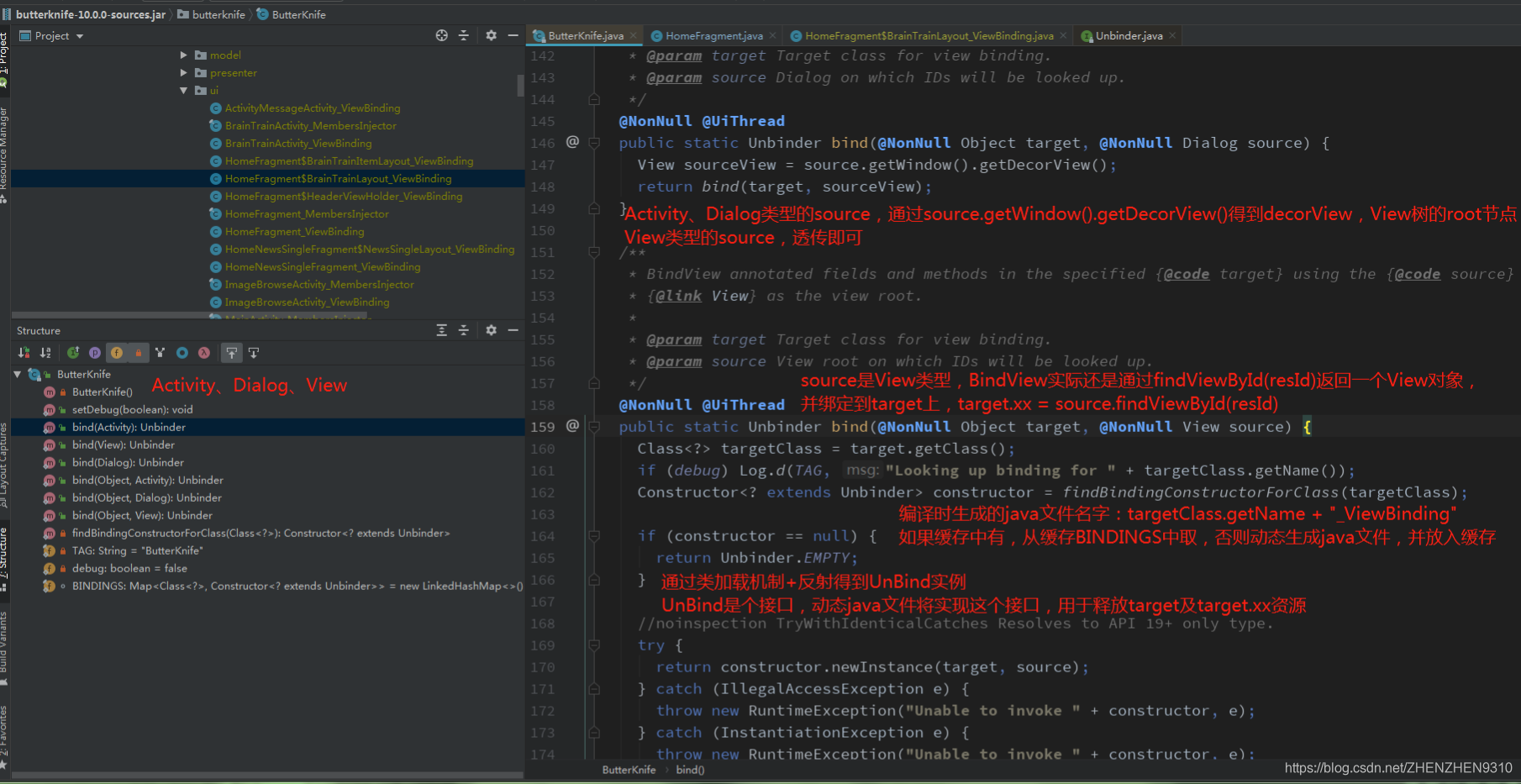
1、Butterknife原理解析
-
@BindView、@OnClick编译时注解,在编译时生成xxx_ViewBinding的java文件
-
通过Butterknife.bind(this)进行绑定,通过类加载反射得到xxx_ViewBinding实例,并缓存
-
通过xxx_ViewBinding实例调用方法,进行resId和view绑定,如果是OnClick,还需要回调xxx中定义的点击方法
-
xxx_ViewBinding中还有一个unbind(),用于解绑释放资源
1、EventBus原理解析 -
@Subscribe运行时注解,通过反射拿到被注解方法的相关信息,保存event、subscribeMethod的键值对
-
在接收到指定Event时,取出相应的subscribeMethod,回调执行注解方法
二、APT
APT(Annotation Processing Tool)是一种处理注释的工具,它对源代码文件进行检测找出其中的Annotation,根据注解自动生成代码。
Annotation处理器在处理Annotation时,可以根据源文件中的Annotation生成额外的源文件和其它的文件(文件具体内容由Annotation处理器的编写者决定),APT还会编译生成的源文件和原来的源文件,将它们一起生成class文件。
APT的处理要素
注解处理器(AbstractProcess)+代码处理(javaPoet)+处理器注册(AutoService)+apt
使用APT来处理annotation的流程
1. 定义注解(如@BindView),扫描代码中的注解
2. 定义注解处理器(自定义注解处理器继承自AbstractProcessor),一般会生成.java文件
3.使用处理器,编译处理生成的.java文件。
4.APT自动完成如下工作。
annotationProcessor是APT工具中的一种,他是google开发的内置框架,不需要引入,可以直接在build.gradle文件中使用,如下
dependencies {
annotationProcessor "com.jakewharton:butterknife-compiler:8.8.1"
}
为了让java编译器识别出这个自定义的Processor,需要配置META-INF中的文件,将这个自定义的类名注册进去。
参考:
公共技术点之 Java 注解 Annotation
聊聊编译时注解(一)
annotationprocessing101
























 2044
2044

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








