目录
1、用gcc生成静态库和动态库
- 静态库
在程序编译时会被连接到目标代码中,程序运行是则不需要静态库的存在。 - 动态库
在程序编译时不会被连接到目标代码中,而是程序运行时载入的。
两者区别:前者是编译连接的,后者是程序运行载入的。
1.hello实例使用库
hello代码
hello.h
#ifndef HELLO_H
#define HELLO_H
void hello(const char *name);
#endif//HELLO_Hhello.c
#include<stdio.h>
void hello(const char *name)
{
printf("Hello %s\n",name);
}main.c
#include"hello.h"
int main()
{
hello("everyone");
return 0;
}2、. gcc编译得到.o文件
gcc -c hello.c

3.静态库使用
(1)创建静态库
创建静态库的工具:ar
静态库文件命名规范:以lib作为前缀,是.a文件 输入命令 ar -crv libmyhello.a hello.o

(2)程序中使用静态库
1).gcc -o hello main.c -L. -lmyhello 注 main.c可以放在-L.和-lmyhello之间

2).gcc main.c libmyhello.a -o hello

3). 先生成main.o gcc -c main.c
生成可执行文件 gcc -o hello main.c libmyhello.a
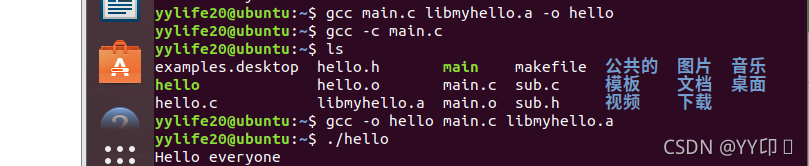
(3)验证静态库的特点
在删掉静态库的情况下,运行可执行文件,发现程序仍旧正常运行,表明静态库跟程序执行没有联系。同时,也表明静态库是在程序编译的时候被连接到代码中的

4.动态库的使用
(1). 创建动态库
创建动态库的工具:gcc
动态库文件命名规范:以lib作为前缀,是.so文件
gcc -shared -fPIC -o libmyhello.so hello.o
shared:表示指定生成动态链接库,不可省略
-fPIC:表示编译为位置独立的代码,不可省略

在程序中执行动态库

5.静态库与动态库比较
gcc编译得到.o文件 gcc -c hello.c
创建静态库 ar -crv libmyhello.a hello.o
创建动态库 gcc -shared -fPIC -o libmyhello.so hello.o
使用库生成可执行文件 gcc -o hello main.c -L. -lmyhello
执行可执行文件 ./hello

在执行可执行文件,会报一个错误,可见当静态库和动态库同时存在的时候,程序会优先使用动态库。
2.实例一使用库
代码
A1.c
#include<stdio.h>
void print1(int arg)
{
printf("A1 print arg:%d\n",arg);
}A2.c
#include<stdio.h>
void print2(char *arg)
{
printf("A2 printf arg:%s\n",arg);
}A.h
#ifndef A_H
#define A_H
void print1(int);
void print2(char *);
#endiftest.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include"A.h"
int main()
{
print1(1);
print2("test");
exit(0);
}操作步骤
 程序中使用静态库
程序中使用静态库
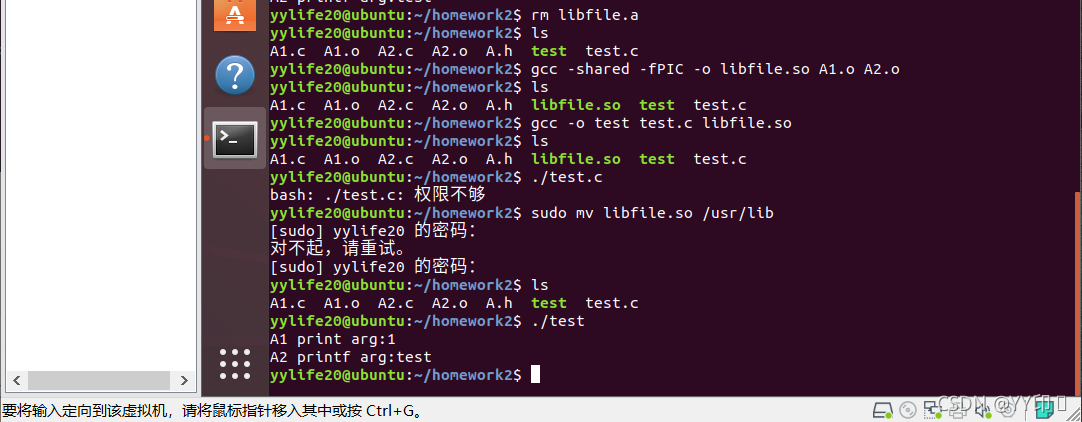
ar crv libfile.a A1.o A2.o
gcc -o test test.c libfile.a


错误解决方式:将test.c中的exit(0)修改为return 0
动态库的使用
gcc -shared -fPIC -o libfile.so A1.o A2.o
gcc -o test test.c libfile.so
3.实例二使用库
代码
sub1.c
float x2x(int a,int b)
{
float c=0;
c=a+b;
return c;
}sub2.c
float x2y(int a,int b)
{
float c=0;
c=a/b;
return c;
}sub.h
#ifndef SUB_H
#define SUB_H
float x2x(int a,int b);
float x2y(int a,int b);
#endifmain.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include"sub.h"
void main()
{
int a,b;
printf("Please input the value of a:");
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("Please input the value of b:");
scanf("%d",&b);
printf("a+b=%.2f\n",x2x(a,b));
printf("a/b=%.2f\n",x2y(a,b));
}
gcc -c sub1.c sub2.c 可以跟上面的A1.c类似

1).静态库
ar crv libsub.a sub1.o sub2.o
gcc -o main main.o libsub.a

2).动态库
gcc -shared -fPIC -o libsub.so sub1.o sub2.o
sudo mv libsub.so /usr/lib ./main

2.总结
通过本次gcc使用静态库和动态库,了解了他们的各自优缺点,也对gcc有了一点点了解,但是对于整个虚拟机来说就是一个小白,没有多少的了解,还需要后期的多多了解和学习。
3.参考文献







 这篇博客详细介绍了如何使用GCC编译器生成C语言的静态库(.a)和动态库(.so)。通过hello实例,展示了从编译源文件得到.o文件,到创建静态库和动态库的完整过程,并探讨了两者之间的区别。此外,还提供了实例一和实例二,分别演示了静态库和动态库在实际项目中的应用和使用注意事项。
这篇博客详细介绍了如何使用GCC编译器生成C语言的静态库(.a)和动态库(.so)。通过hello实例,展示了从编译源文件得到.o文件,到创建静态库和动态库的完整过程,并探讨了两者之间的区别。此外,还提供了实例一和实例二,分别演示了静态库和动态库在实际项目中的应用和使用注意事项。
















 2287
2287

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








