目录
Thread 类及常见方法
Thread 类是 JVM 用来管理线程的一个类,换句话说,每个线程都有一个唯一的 Thread 对象与之关联。在 Java 中,Thread类是用于创建和管理线程的核心类,位于java.lang包下。线程是程序中执行的最小单元,Thread类提供了创建和控制线程的各种方法。
1.Thread 的常见构造方法
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Thread() | 创建线程对象 |
| Thread(Runnable target) | 使用Runnable对象创建线程对象 |
| Thread(Stringname) | 创建线程对象,并命名 |
| Thread(Runnable target,Stringname) | 使用Runnable对象创建线程对象,并命名 |
| 【了解】Thread(ThreadGroup group,Runnable target) | 线程可以被用来分组管理,分好的组即为线这个目前我们了解即可 |
Thread t1 = new Thread();
Thread t2 = new Thread(new MyRunnable());
Thread t3 = new Thread("这是我的名字");
Thread t4 = new Thread(new MyRunnable(), "这是我的名字");
2.Thread 的几个常见属性
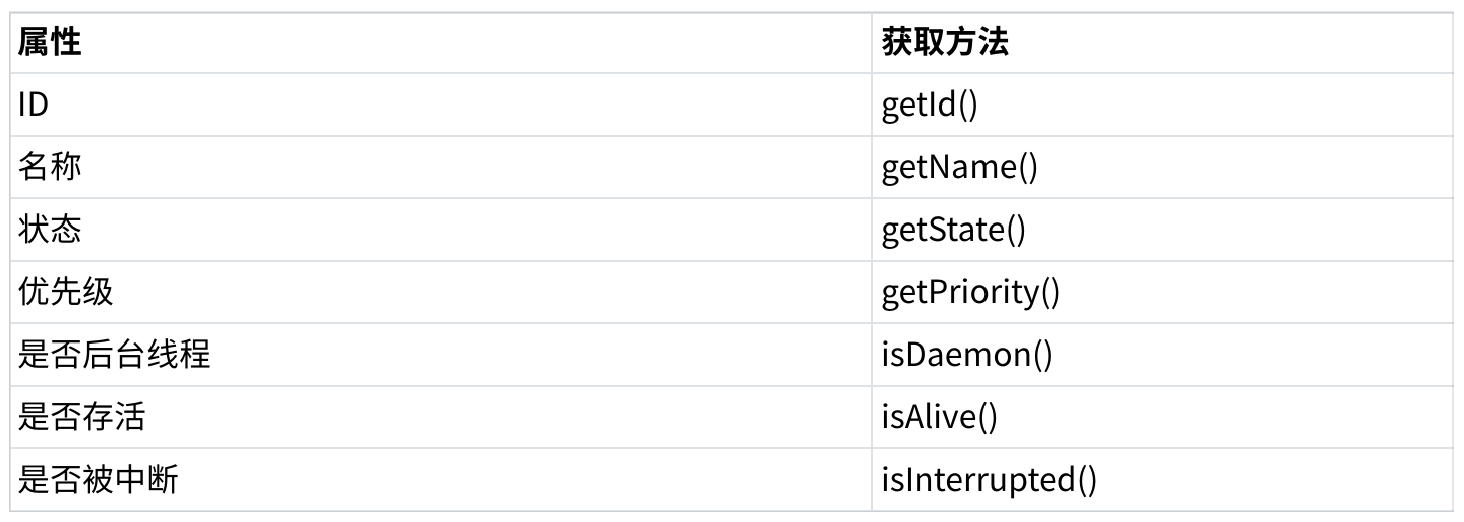
• ID 是线程的唯一标识,不同线程不会重复
• 名称是各种调试工具用到
• 状态表示线程当前所处的一个情况,下面我们会进一步说明
• 优先级高的线程理论上来说更容易被调度到
• 关于后台线程,需要记住一点:JVM会在一个进程的所有非后台线程结束后,才会结束运行。
• 是否存活,即简单的理解,为 run 方法是否运行结束了
• 线程的中断问题,下面我们进一步说明
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": 我还在");
Thread.sleep(1 * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": 我将死去");
});
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": ID: " + thread.getId());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 名称: " + thread.getName());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 状态: " + thread.getState());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 优先级: " + thread.getPriority());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 后台线程: " + thread.isDaemon());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 活着: " + thread.isAlive());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 被中断: " + thread.isInterrupted());
thread.start();
while (thread.isAlive()) {}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 状态: " + thread.getState());
}
}
3.启动一个线程 - start()
之前我们已经看到了如何通过覆写 run 方法创建一个线程对象,但线程对象被创建出来并不意味着线
程就开始运行了。
-
覆写 run 方法是提供给线程要做的事情的指令清单
-
线程对象可以认为是把 李四、王五叫过来了
-
而调用 start() 方法,就是喊一声:”行动起来!“,线程才真正独立去执行了。
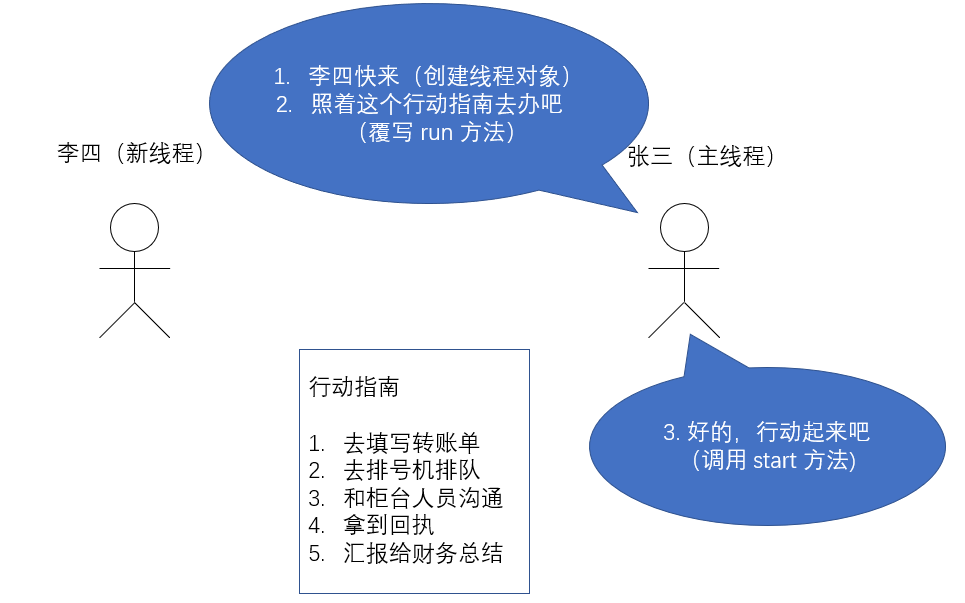
调用 start 方法, 才真的在操作系统的底层创建出一个线程.
4.中断一个线程
目前常见的有以下两种方式:
- 通过共享的标记来进行沟通
- 调用 interrupt() 方法来通知
示例-1: 使用自定义的变量来作为标志位.
需要给标志位上加 volatile 关键字
public class ThreadDemo {
private static class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
public volatile boolean isQuit = false;
@Override
public void run() {
while (!isQuit) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 别管我,我忙着转账呢!");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 啊!险些误了大事");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnable target = new MyRunnable();
Thread thread = new Thread(target, "李四");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 让李四开始转账。");
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 老板来电话了,得赶紧通知李四对方是个骗子!");
target.isQuit = true;
}
}
示例-2: 使用 Thread.interrupted() 或者Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() 代替自定义标志位.
Thread 内部包含了一个 boolean 类型的变量作为线程是否被中断的标记
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public void interrupt() | 中断对象关联的线程,如果线程正在阻塞,则以异常方式通知,否则设置标志位 |
| public static boolean interrupted() | 判断当前线程的中断标志位是否设置,调用后清除标志位 |
| public boolean islnterrupted() | 判断对象关联的线程的标志位是否设置,调用后不清除标志位 |
- 使用 thread 对象的 interrupted() 方法通知线程结束.
public class ThreadDemo {
private static class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
// 两种方法均可以
while (!Thread.interrupted()) {
//while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 别管我,我忙着转账呢!");
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": 有内鬼,终止交易!");
// 注意此处的 break
break;
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 啊!险些误了大事");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
MyRunnable target = new MyRunnable();
Thread thread = new Thread(target, "李四");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 让李四开始转账。");
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(10 * 1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 老板来电话了,得赶紧通知李四对方是个骗子!");
thread.interrupt();
}
}
thread 收到通知的方式有两种:
- 如果线程因为调用 wait/join/sleep 等方法而阻塞挂起,则以 InterruptedException 异常的形式通
知,清除中断标志,当出现 InterruptedException 的时候, 要不要结束线程取决于 catch 中代码的写法. 可以选择忽略这个异常, 也可以跳出循环结束线程. - 否则,只是内部的一个中断标志被设置,thread 可以通过。Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted() 判断指定线程的中断标志被设置,不清除中断标志这种方式通知收到的更及时,即使线程正在 sleep 也可以马上收到。
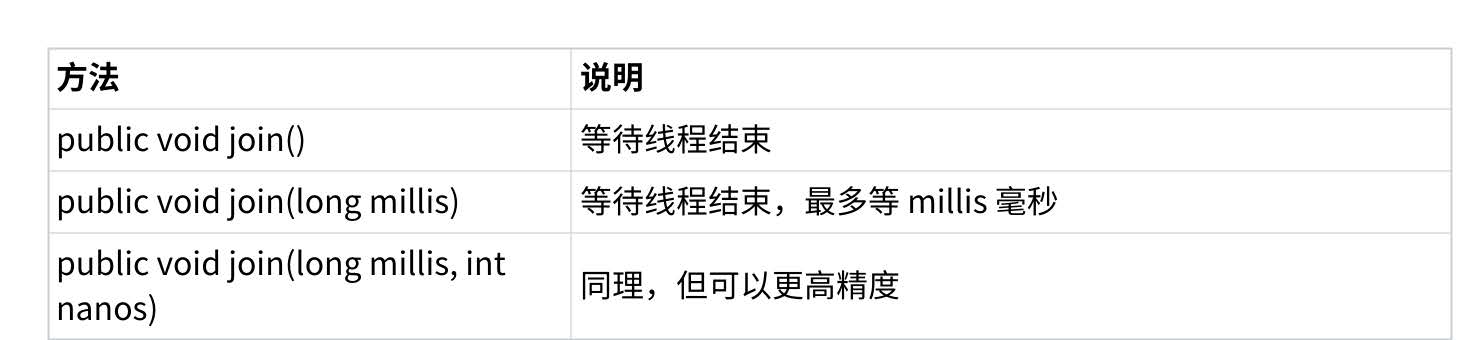
5.等待一个线程 - join()
有时,我们需要等待一个线程完成它的工作后,才能进行自己的下一步工作。例如,张三只有等李四
转账成功,才决定是否存钱,这时我们需要一个方法明确等待线程的结束。
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable target = () -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+ ": 我还在工作!");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": 我结束了!");
};
Thread thread1 = new Thread(target, "李四");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(target, "王五");
System.out.println("先让李四开始工作");
thread1.start();
thread1.join();
System.out.println("李四工作结束了,让王五开始工作");
thread2.start();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("王五工作结束了");
}
}
附录
6.获取当前线程引用
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public static Thread currentThread(); | 返回当前线程对象的引用 |
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread.getName());
}
}
7.休眠当前线程
也是我们比较熟悉一组方法,有一点要记得,因为线程的调度是不可控的,所以,这个方法只能保证
实际休眠时间是大于等于参数设置的休眠时间的。
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| public staticvoid sleep(long millis) throws Interrupted Exception | 休眠当前线程millis毫秒 |
| public static void sleep(long millis, intnanos) throws Interrupted Exception | 可以更高精度的休眠 |
public class ThreadDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
Thread.sleep(3 * 1000);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}




















 1507
1507

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








