源码下载以及安装点击链接https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/YoungSusie/article/details/90021742
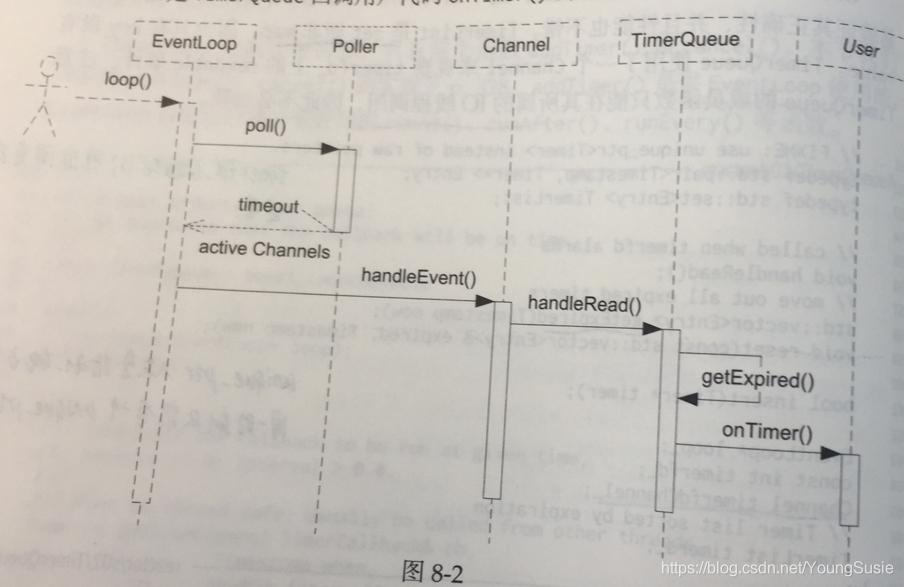
给前面的EventLoop 加上定时的功能,传统的Reactor 通过控制select 和 poll 的等待时间来实现定时,现在Linux 系统中有了timefd ,可以用和处理IO事件相同的方式来处理定时。
timerfd_create() 函数把时间变为一个文件描述符,该“文件” 在定时器超时的那一刻变得可读,可以融入Reactor 模型中,用同一的方式处理IO 事件和超时事件。
muduo 的定时器功能由三个class实现,TimerId、Timer、 TimerQueue ,用户只能看到TimerId , 另外两个class 是内部实现细节。
TimerQueue 的接口很简单,只有两个函数addTimer() 和 cancel() 。addTimer() 是供给EventLoop 使用的,EventLoop 将其封装为更好的runAt() 、 runAfter() 和 runEvery() 。TimerQueue 的成员函数只能在其所属的IO线程进行调用,因此不需要加锁。
-
TimerQueue 数据结构的选择
TimerQueue 需要高效地组织尚未到期的Timer, 能快速地根据当前时间找到已经快到期的Timer , 也需要能高效地删除和添加 Timer .一种合适的数据结构是二叉搜索树,把Timer 按照到期时间先后顺序排序,但是不能直接使用map<Timestamp, Timer*> , 因为如果两个同时到期的Timer 应该如何处理?- 用multimap 或者multiset
- 设法区分key , 以pair<Timerstamp,Timer*> 为key。这样即使两个Timer 的到期时间相同,他们的地址也必定不同。
typedef std::pair<Timestamp,Timer*> Entry;
typedef std::set<Entry> TimerList; //记录定时器
- 程序代码
==================================TimerQueue.cc ====================================
#define __STD_LIMIT_MACROS
#include "TimerQueue.h"
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "Timer.h"
#include "TimerId.h"
#include <boost/bind.hpp>
#include <sys/timerfd.h>
int createTimerfd()
{
int timerfd = ::timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC,TFD_NONBLOCK | TFD_CLOEXEC);
if(timerfd < 0)
{
std::cout << "timerfd_create error ";
_exit(-1);
}
return timerfd;
}
struct timespec howMuchTimeFromNow(Timestamp when)
{
int64_t microseconds = when.microSecondsSinceEpoch()-Timestamp::now().microSecondsSinceEpoch();
if(microseconds < 100)
{
microseconds = 100;}
struct timespec ts;
ts.tv_sec = static_cast<time_t>(microseconds / Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond);//秒
ts.tv_nsec = static_cast<long>((microseconds % Timestamp::kMicroSecondsPerSecond) * 1000);//纳秒
return ts;
}
void readTimerfd(int timerfd,Timestamp now)
{
uint64_t howmany;
ssize_t n = ::read(timerfd,&howmany,







 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1907
1907

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








