在C++中,std::greater 是一个函数对象(也称为仿函数),定义在头文件 <functional> 中。它用于比较两个值,并确定第一个值是否大于第二个值。std::greater 常用于标准库中的算法和容器,例如 std::sort,以自定义排序顺序。
std::greater 的用法
std::greater 是一个模板类,可以用于比较各种类型的值。默认情况下,它会使用 operator> 来比较两个值。
基本用法
- 头文件: 需要包含
<functional>头文件。 - 模板参数:
std::greater<T>,其中T是要比较的类型。 - 调用方式: 可以像函数一样调用,传入两个参数,返回一个布尔值。
代码示例
示例1: 基本比较
#include <iostream>
#include <functional> // 包含 std::greater
int main() {
std::greater<int> greater_int;
int a = 5, b = 3;
if (greater_int(a, b)) {
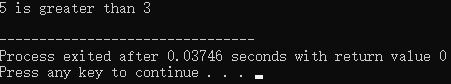
std::cout << a << " is greater than " << b << std::endl;
} else {
std::cout << a << " is not greater than " << b << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出:
示例2: 使用 std::sort 自定义排序顺序
在这个示例中,我们将使用 std::greater 来对一个整数数组进行降序排序。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional> // 包含 std::greater
int main() {
std::vector<int> vec = {1, 5, 2, 4, 3};
// 使用 std::greater<int>() 作为比较函数对象
std::sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), std::greater<int>());
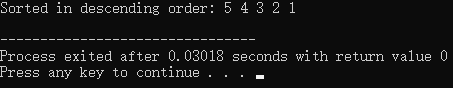
std::cout << "Sorted in descending order: ";
for (int num : vec) {
std::cout << num << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
其他注意事项
std::greater可以用于其他类型,只要这些类型支持operator>比较操作。- 仿函数的使用可以提高代码的可读性和可维护性,特别是在需要将比较逻辑传递给算法时。
总结
std::greater 是一个方便的工具,用于在C++中进行大于比较操作。它既可以用于简单的比较,也可以用于复杂的算法和容器中,以自定义行为。通过了解和使用 std::greater,你可以编写更加灵活和高效的C++代码。























 4747
4747

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








