大家好,我是徐庶老师,专注java,想要学习java的同学可以欢迎关注我。
结合视频观看效果更佳哦:Redis 击穿 雪崩 穿透——十分钟理论+实战彻底搞懂_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
前言
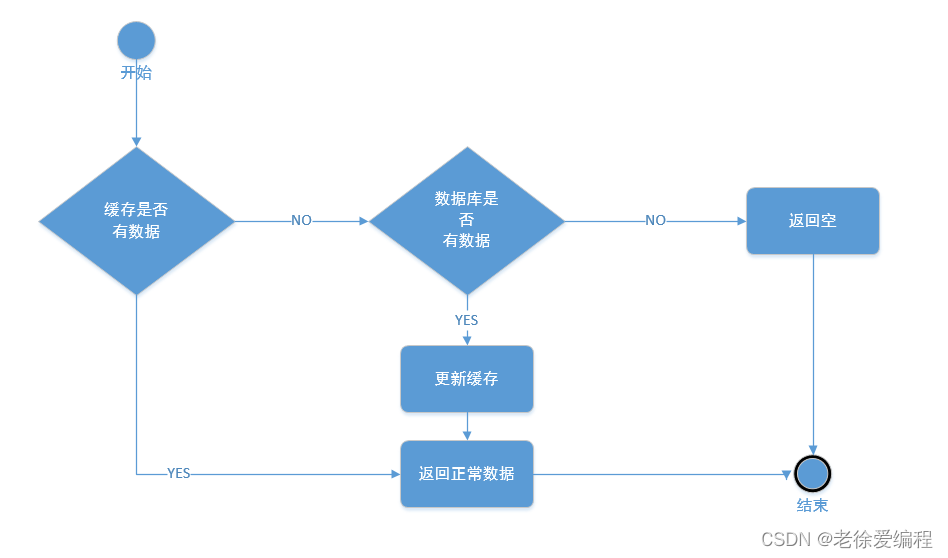
为了提高服务器并发量,通常会将一些热点数据先缓存,没有再请求数据库, 给数据库做了一层保护:
请求进来先从缓存中取数据,缓存取不到则去数据库中取,数据库取到了则返回给前端,然后更新缓存,如果数据库取不到则返回空数据给前端
/**
* 通过发货单查询物流信息
*/
public ExpressInfo findByDeliveryOrderId(Long id) {
String key="xushu-express:express-info:"
//从 Redis 查询物流信息
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key + id);
if (obj != null) {
return (ExpressInfo) obj;
} else {
ExpressInfo expressInfo = expressMapper.selectByDeliveryOrderId(id);//数据库查询
if (expressInfo != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key + id, expressInfo,Duration.ofHours(2L));
return expressInfo;
} else {
throw new ClientException("发货单:{} 的物流信息不存在", id);
}
}
}
假如缓存的数据没有,后台则会一直请求数据库,对数据库造成压力,如果是请求量大或者恶意请求则会导致数据库崩溃,我们一般称为缓存穿透、缓存击穿、缓存雪崩。
缓存击穿
缓存击穿是指单个热点缓存中没有但数据库中有的数据
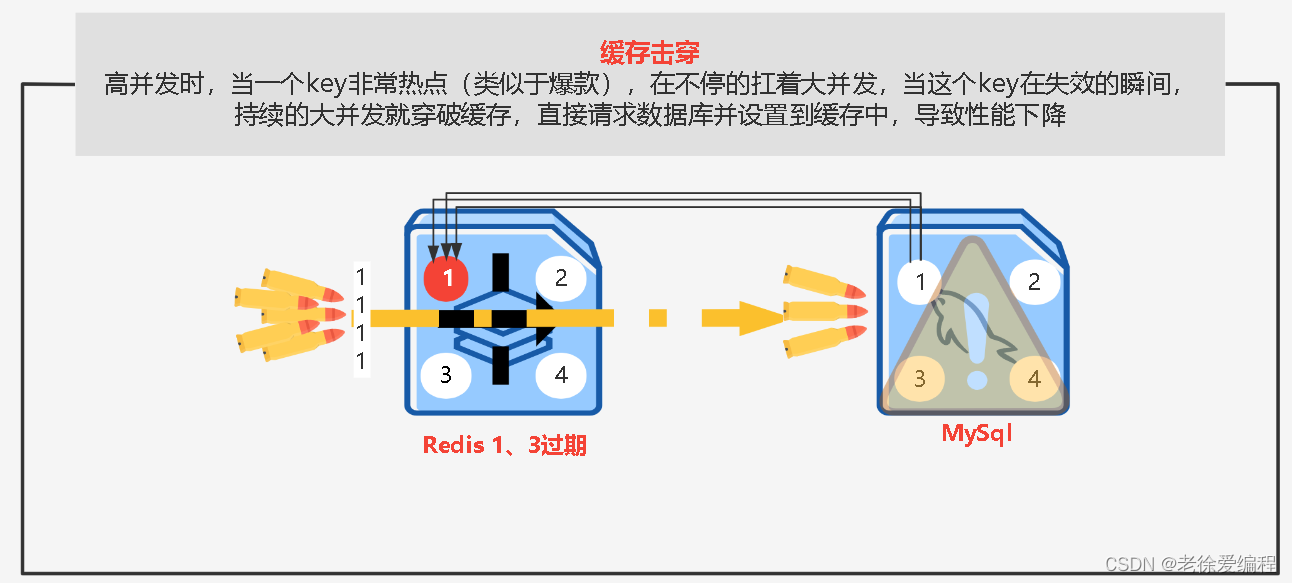
解决方案
1. 互斥锁
当热点key过期后,大量的请求涌入时,只有第一个请求能获取锁并阻塞,此时该请求查询数据库,并将查询结果写入redis后释放锁。后续的请求直接走缓存。
/**
* 查询商品分类信息
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public List<ProductCategory> findProductCategory() {
String key="product:product-category"
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (obj == null) {
synchronized (this){
//进入 synchronized 一定要先再查询一次 Redis,防止上一个抢到锁的线程已经更新过了
obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if(obj != null){
return (List<ProductCategory>) obj;
}
List<ProductCategory> categoryList = productCategoryMapper.selectProductCategory







 本文由徐庶老师分享,深入解析Java缓存中的击穿、雪崩、穿透问题及其解决方案。通过实例代码展示了如何使用互斥锁、随机失效时间、永不过期策略来应对缓存问题。同时提出了布隆过滤器作为防止缓存穿透的有效手段,强调了在实际应用中根据业务场景选择合适策略的重要性。
本文由徐庶老师分享,深入解析Java缓存中的击穿、雪崩、穿透问题及其解决方案。通过实例代码展示了如何使用互斥锁、随机失效时间、永不过期策略来应对缓存问题。同时提出了布隆过滤器作为防止缓存穿透的有效手段,强调了在实际应用中根据业务场景选择合适策略的重要性。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 4147
4147

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








