投票模型
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report
# 数据
df = pd.read_csv('train.csv').fillna(method='ffill')
X = df.Word.values
y = df.Tag.values
labels = df.Tag.unique().tolist()
labels.remove('O')
# 投票模型
class Majority_vote:
def fit(self, X, y):
counter = {}
for w, t in zip(X, y):
if w in counter:
if t in counter[w]:
counter[w][t] += 1
else:
counter[w][t] = 1
else:
counter[w] = {t: 1}
self.vote = {}
for w, t in counter.items():
self.vote[w] = max(t, key=t.get)
return self
def predict(self, X):
return [self.vote.get(x, 'O') for x in X]
y_pred = Majority_vote().fit(X, y).predict(X)
report = classification_report(y, y_pred, labels)
print(report)
条件随机场

以下为链式CRF算法~
import pandas as pd
from sklearn_crfsuite import CRF
from sklearn_crfsuite.metrics import flat_classification_report
# 数据读取、预处理
data = pd.read_csv('train.csv').fillna(method='ffill')
labels = data.Tag.unique().tolist()
labels.remove('O')
# 按句子分组
f = lambda s: [(w, p, t) for w, p, t in zip(
s.Word.values, s.POS.values, s.Tag.values)]
sentences = list(data.groupby('Sentence #').apply(f))
# 特征提取
def word2features(sent, i):
word = sent[i][0]
postag = sent[i][1]
features = {
'bias': 1.0,
'word.lower()': word.lower(),
'word[-3:]': word[-3:],
'word[-2:]': word[-2:],
'word.isupper()': word.isupper(),
'word.istitle()': word.istitle(),
'word.isdigit()': word.isdigit(),
'postag': postag,
'postag[:2]': postag[:2],
}
if i > 0: # word_prev, word_curr
word1 = sent[i-1][0]
postag1 = sent[i-1][1]
features.update({
'-1:word.lower()': word1.lower(),
'-1:word.istitle()': word1.istitle(),
'-1:word.isupper()': word1.isupper(),
'-1:postag': postag1,
'-1:postag[:2]': postag1[:2],
})
else:
features['BOS'] = True
if i < len(sent)-1:
word1 = sent[i+1][0]
postag1 = sent[i+1][1]
features.update({
'+1:word.lower()': word1.lower(),
'+1:word.istitle()': word1.istitle(),
'+1:word.isupper()': word1.isupper(),
'+1:postag': postag1,
'+1:postag[:2]': postag1[:2],
})
else:
features['EOS'] = True
return features
def tpl2feature(sent):
return [word2features(sent, i) for i in range(len(sent))]
def tpl2labels(sent):
return [label for token, postag, label in sent]
X = [tpl2feature(s) for s in sentences]
y = [tpl2labels(s) for s in sentences]
# 建模、训练、预测、汇报
crf = CRF(algorithm='lbfgs', c1=.1, c2=.1, max_iterations=99).fit(X, y)
y_pred = crf.predict(X)
report = flat_classification_report(y, y_pred, labels)
print(report)
BiLSTM-CRF
"""Train CRF and BiLSTM-CRF on CONLL2000 chunking data,
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1508.01991v1.pdf"""
from numpy import asarray
from collections import Counter
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Embedding, Bidirectional, LSTM
from keras_contrib.layers import CRF
from keras_contrib.losses import crf_loss
from keras_contrib.metrics import crf_viterbi_accuracy
from keras_contrib.datasets import conll2000
EPOCHS = 10
EMBED_DIM = 200
BiRNN_UNITS = 200
def classification_report(y_true, y_pred, labels):
"""Similar to the one in sklearn.metrics,
reports per classs recall, precision and F1 score"""
y_true = asarray(y_true).ravel()
y_pred = asarray(y_pred).ravel()
corrects = Counter(yt for yt, yp in zip(y_true, y_pred) if yt == yp)
y_true_counts = Counter(y_true)
y_pred_counts = Counter(y_pred)
report = ((lab, # label
corrects[i] / max(1, y_true_counts[i]), # recall
corrects[i] / max(1, y_pred_counts[i]), # precision
y_true_counts[i] # support
) for i, lab in enumerate(labels))
report = [(l, r, p, 2 * r * p / max(1e-9, r + p), s) for l, r, p, s in report]
print('{:<15}{:>10}{:>10}{:>10}{:>10}\n'.format('', 'recall', 'precision', 'f1-score', 'support'))
formatter = '{:<15}{:>10.2f}{:>10.2f}{:>10.2f}{:>10d}'.format
for r in report:
print(formatter(*r))
print('')
report2 = list(zip(*[(r * s, p * s, f1 * s) for l, r, p, f1, s in report]))
N = len(y_true)
print(formatter('avg / total', sum(report2[0]) / N, sum(report2[1]) / N, sum(report2[2]) / N, N) + '\n')
# conll200 has two different targets, here will only use
# IBO like chunking as an example
train, test, voc = conll2000.load_data()
(train_x, _, train_y) = train
(test_x, _, test_y) = test
(vocab, _, class_labels) = voc
# --------------
# 1. Regular CRF
# --------------
print('==== training CRF ====')
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(len(vocab), EMBED_DIM, mask_zero=True)) # Random embedding
crf = CRF(len(class_labels), sparse_target=True)
model.add(crf)
model.summary()
# The default `crf_loss` for `learn_mode='join'` is negative log likelihood.
model.compile('adam', loss=crf_loss, metrics=[crf_viterbi_accuracy])
model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=EPOCHS, validation_data=[test_x, test_y])
test_y_pred = model.predict(test_x).argmax(-1)[test_x > 0]
test_y_true = test_y[test_x > 0]
print('\n---- Result of CRF ----\n')
classification_report(test_y_true, test_y_pred, class_labels)
# -------------
# 2. BiLSTM-CRF
# -------------
print('==== training BiLSTM-CRF ====')
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(len(vocab), EMBED_DIM, mask_zero=True)) # Random embedding
model.add(Bidirectional(LSTM(BiRNN_UNITS // 2, return_sequences=True)))
crf = CRF(len(class_labels), sparse_target=True)
model.add(crf)
model.summary()
model.compile('adam', loss=crf_loss, metrics=[crf_viterbi_accuracy])
model.fit(train_x, train_y, epochs=EPOCHS, validation_data=[test_x, test_y])
test_y_pred = model.predict(test_x).argmax(-1)[test_x > 0]
test_y_true = test_y[test_x > 0]
print('\n---- Result of BiLSTM-CRF ----\n')
classification_report(test_y_true, test_y_pred, class_labels)
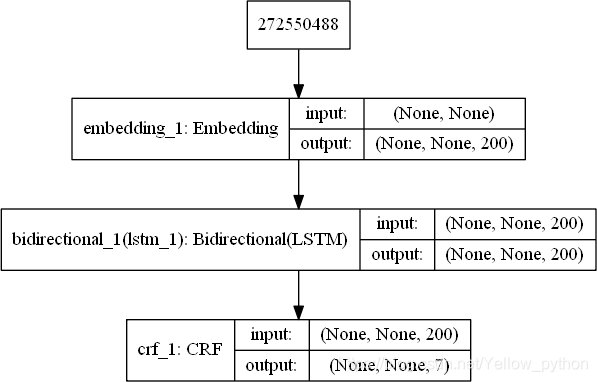
附录
?
| en | cn |
|---|---|
Named Entity Recognition | 命名实体识别 |
Conditional Random Field | 条件随机场 |
| entity | 实体;存在;本质 |
| majority | n. 多数 |
| vote | vi. 选举;vt. 提议 |
| voting | adj. 投票的;n. 投票;选举 |
github地址
https://github.com/AryeYellow/PyProjects/blob/master/NLP/NER_CRF/Python命名实体识别.ipynb





 本文深入探讨了命名实体识别(NER)技术,介绍了三种主要模型:投票模型、条件随机场(CRF)及BiLSTM-CRF。通过实例展示了各模型在序列标注任务中的应用与效果,比较了它们在准确性与效率上的差异。
本文深入探讨了命名实体识别(NER)技术,介绍了三种主要模型:投票模型、条件随机场(CRF)及BiLSTM-CRF。通过实例展示了各模型在序列标注任务中的应用与效果,比较了它们在准确性与效率上的差异。

















 7703
7703

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










