一、yolov11的下载
1、下载yolov11的压缩包,首先要注意在github中yolov11的名称不是yolov11,而是ultralytics,请注意不要搜错了。
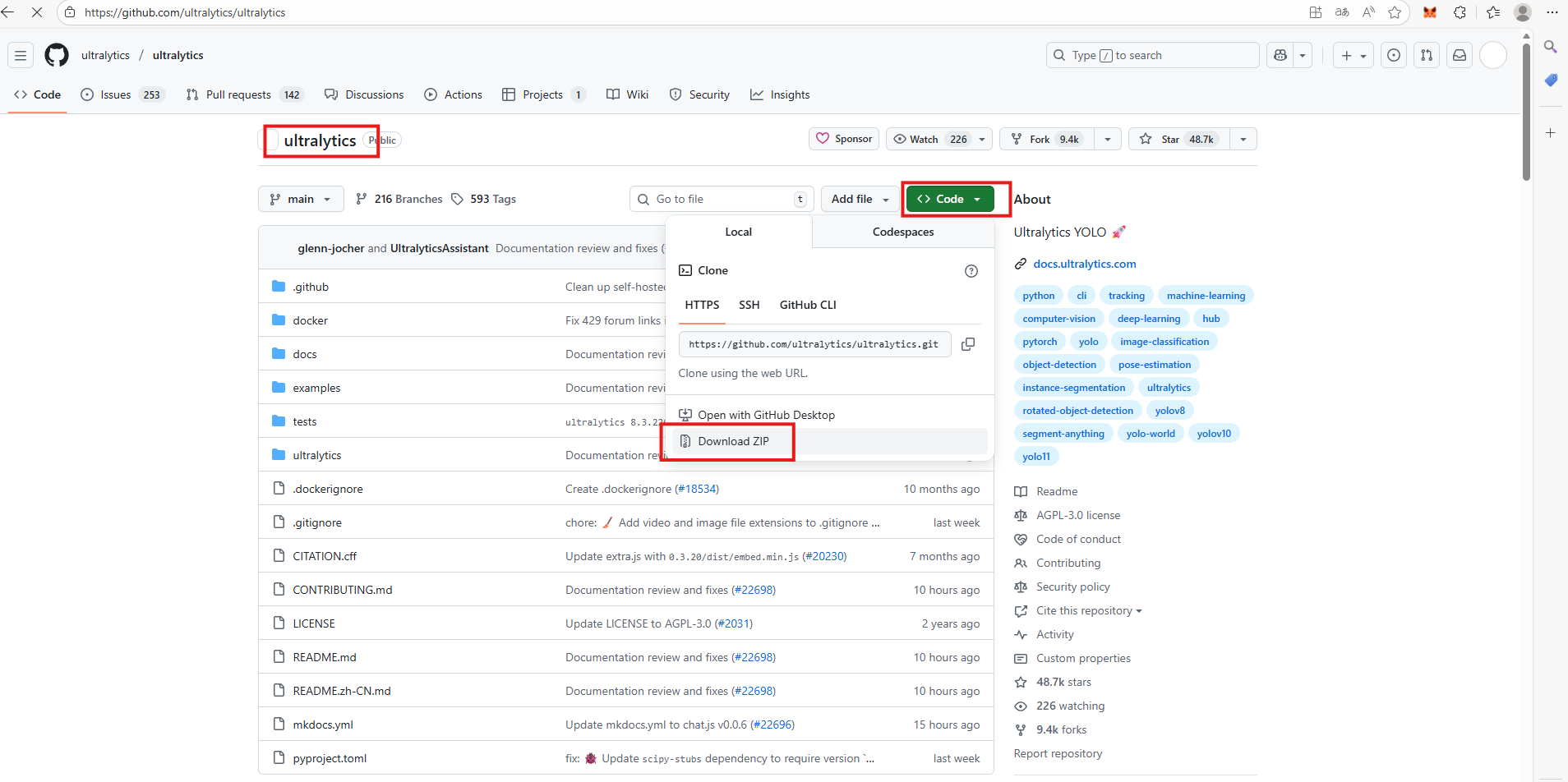
二、配置
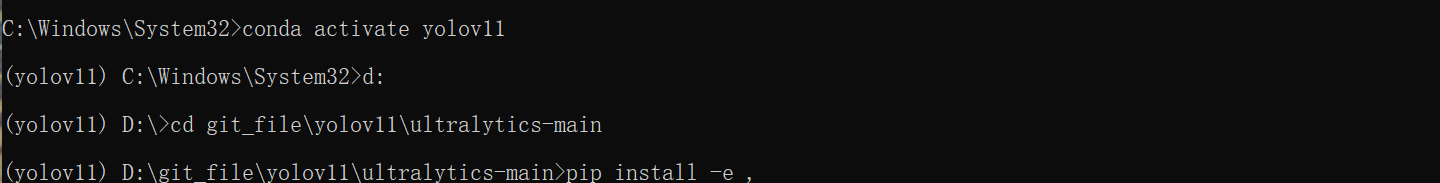
1、创建好虚拟环境并激活,创建环境的代码是conda create -n 环境名字(英文) python=x.x(python版本),创建好后输入conda active 环境名字这串代码激活环境,然后进入到解压好的yolov11文件夹中。
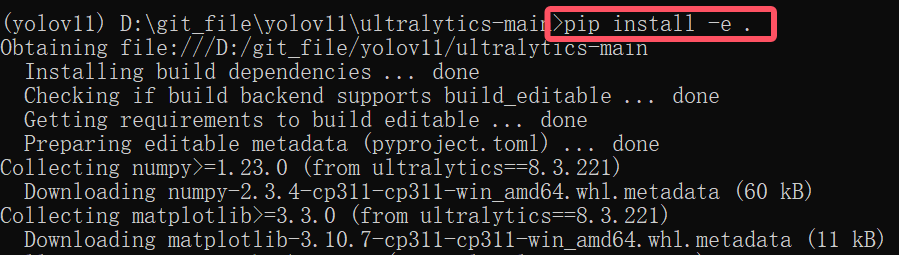
2、下载对应的库,进入到解压好的yolov11文件夹后,输入pip install -e .代码进行库的下载。
3、创建文件夹,首先进入到yolov11的文件夹中创建一个data的文件夹,然后进入文件夹中创建3个文件夹,分别是images,labels,dataset。
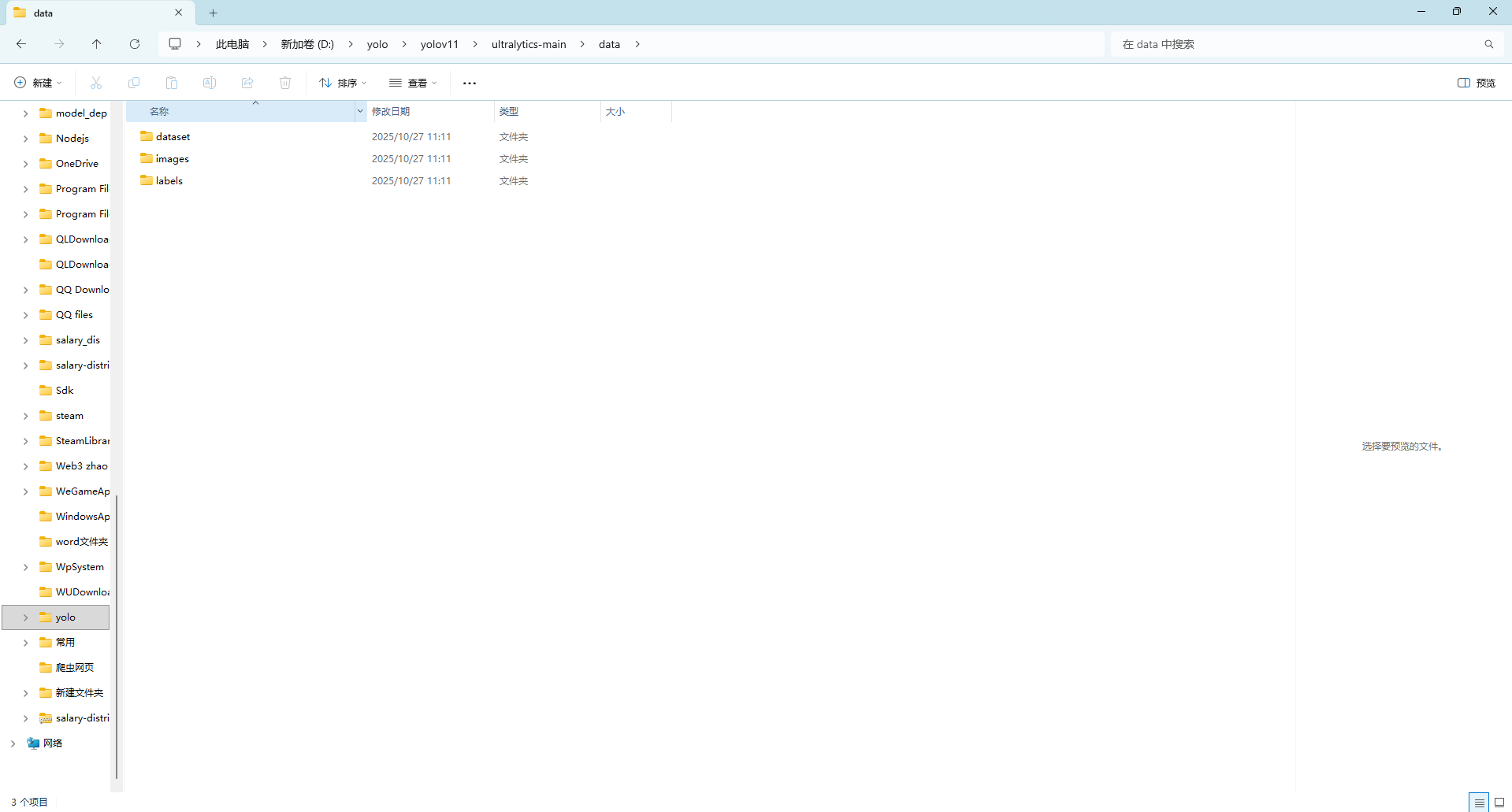
如果有标注好的数据需要训练就将训练好的数据移入对应的文件夹
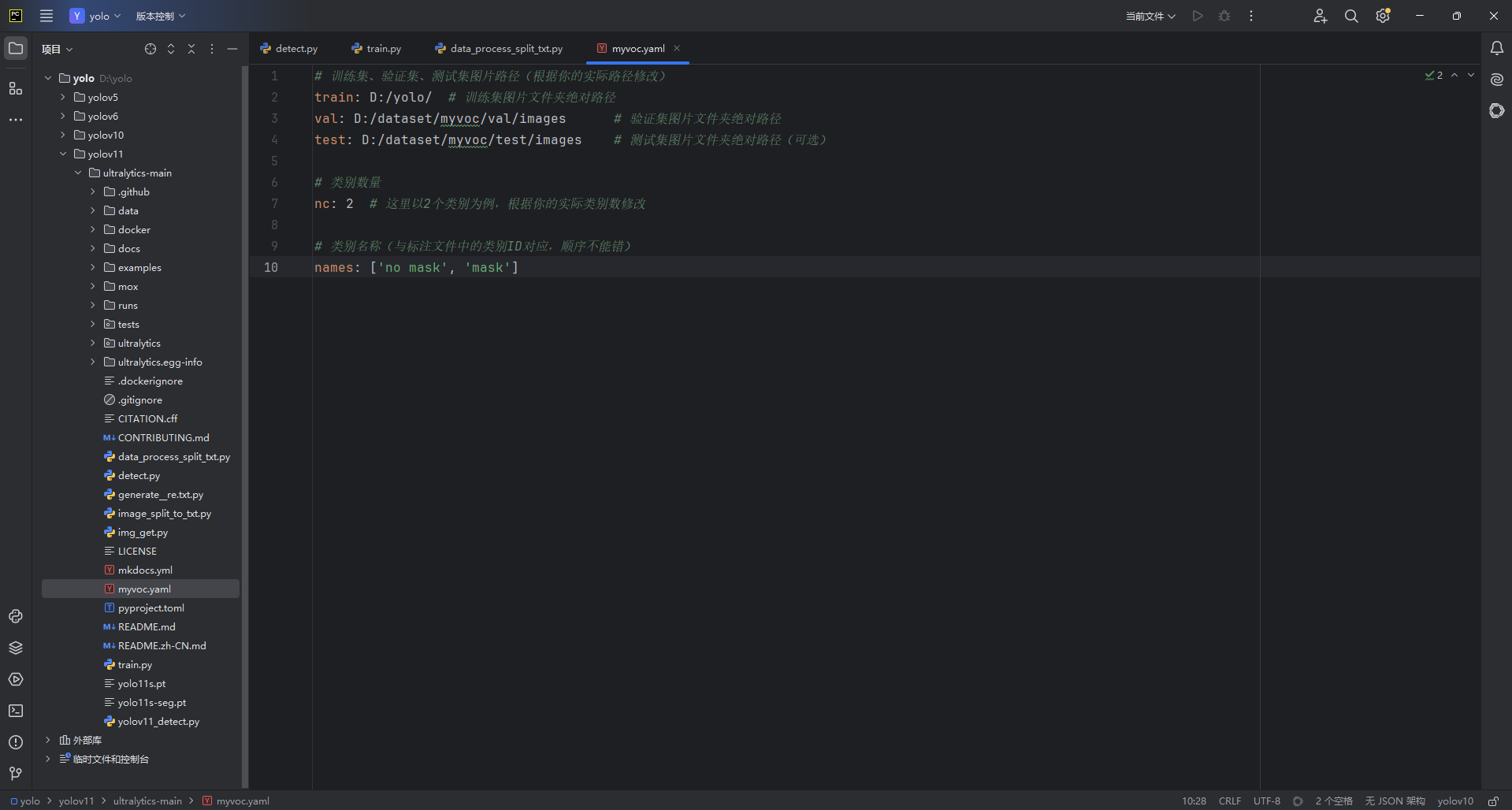
打开pycharm进入到yolov11文件夹,然后创建myvoc.yaml文件
创建如图的py文件
并在此文件夹中添加代码如下
import os
import random
import argparse
import shutil
from tqdm import tqdm
# 参数解析
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--labels_path', default='./data/labels', type=str, help='input YOLO labels path')
parser.add_argument('--images_path', default='./data/images', type=str, help='original images path')
parser.add_argument('--output_path', default='./data', type=str, help='output base path')
opt = parser.parse_args()
# 定义划分比例
trainval_percent = 1.0
train_percent = 0.8
val_percent = 0.2
# 设置路径
labels_path = opt.labels_path
images_path = opt.images_path
output_path = opt.output_path
# 创建输出目录结构
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'images/train'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'images/val'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'images/test'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/train'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/val'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/test'), exist_ok=True)
# 获取所有txt标签文件
txt_files = [f for f in os.listdir(labels_path) if f.endswith('.txt')]
random.shuffle(txt_files)
num = len(txt_files)
# 划分数据集
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
ta = tv - tr # 确保train+val=trainval
trainval = txt_files[:tv]
train = trainval[:tr]
val = trainval[tr:tr + ta]
test = txt_files[tv:]
# 处理训练集
print("Processing training set...")
train_list = []
for txt_file in tqdm(train):
image_id = os.path.splitext(txt_file)[0]
# 移动标签文件
src_txt = os.path.join(labels_path, txt_file)
dst_txt = os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/train', txt_file)
if os.path.exists(src_txt):
shutil.move(src_txt, dst_txt)
# 移动对应的图像文件
src_img = os.path.join(images_path, f'{image_id}.jpg')
dst_img = os.path.join(output_path, 'images/train', f'{image_id}.jpg')
if os.path.exists(src_img):
shutil.move(src_img, dst_img)
train_list.append(dst_img)
# 处理验证集
print("Processing validation set...")
val_list = []
for txt_file in tqdm(val):
image_id = os.path.splitext(txt_file)[0]
# 移动标签文件
src_txt = os.path.join(labels_path, txt_file)
dst_txt = os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/val', txt_file)
if os.path.exists(src_txt):
shutil.move(src_txt, dst_txt)
# 移动对应的图像文件
src_img = os.path.join(images_path, f'{image_id}.jpg')
dst_img = os.path.join(output_path, 'images/val', f'{image_id}.jpg')
if os.path.exists(src_img):
shutil.move(src_img, dst_img)
val_list.append(dst_img)
# 处理测试集
print("Processing test set...")
test_list = []
for txt_file in tqdm(test):
image_id = os.path.splitext(txt_file)[0]
# 移动标签文件
src_txt = os.path.join(labels_path, txt_file)
dst_txt = os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/test', txt_file)
if os.path.exists(src_txt):
shutil.move(src_txt, dst_txt)
# 移动对应的图像文件
src_img = os.path.join(images_path, f'{image_id}.jpg')
dst_img = os.path.join(output_path, 'images/test', f'{image_id}.jpg')
if os.path.exists(src_img):
shutil.move(src_img, dst_img)
test_list.append(dst_img)
# 保存路径文件
def save_path_file(file_path, path_list):
with open(file_path, 'w') as f:
for path in path_list:
f.write(f"{path}\n")
save_path_file(os.path.join(output_path, 'train.txt'), train_list)
save_path_file(os.path.join(output_path, 'val.txt'), val_list)
save_path_file(os.path.join(output_path, 'test.txt'), test_list)
print("Dataset preparation completed!")
print(f"Train: {len(train_list)} images, Val: {len(val_list)} images, Test: {len(test_list)} images")
再创建此文件
内容如下
import os
import random
import argparse
import shutil
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
from tqdm import tqdm
# 参数解析
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--xml_path', default='./data/dataset', type=str, help='input xml label path')
parser.add_argument('--images_path', default='./data/images', type=str, help='original images path')
parser.add_argument('--output_path', default='./data', type=str, help='output base path')
opt = parser.parse_args()
# 定义划分比例
trainval_percent = 1.0
train_percent = 0.8
val_percent = 0.2
# 设置路径
xml_path = opt.xml_path
images_path = opt.images_path
output_path = opt.output_path
# 创建输出目录结构
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'images/train'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'images/val'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'images/test'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/train'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/val'), exist_ok=True)
os.makedirs(os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/test'), exist_ok=True)
# 获取所有XML文件
xml_files = [f for f in os.listdir(xml_path) if f.endswith('.xml')]
random.shuffle(xml_files)
num = len(xml_files)
# 划分数据集
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
ta = tv - tr # 确保train+val=trainval
trainval = xml_files[:tv]
train = trainval[:tr]
val = trainval[tr:tr + ta]
test = xml_files[tv:]
# 类别定义
classes = ["sleeping","playing_phone"]
# XML转换函数
def convert(size, box):
dw = 1. / size[0]
dh = 1. / size[1]
x = (box[0] + box[1]) / 2.0 - 1
y = (box[2] + box[3]) / 2.0 - 1
w = box[1] - box[0]
h = box[3] - box[2]
x = x * dw
w = w * dw
y = y * dh
h = h * dh
return x, y, w, h
def convert_annotation(xml_file, output_dir):
try:
image_id = os.path.splitext(xml_file)[0]
in_file = os.path.join(xml_path, xml_file)
out_file = os.path.join(output_dir, f'{image_id}.txt')
tree = ET.parse(in_file)
root = tree.getroot()
size = root.find('size')
w = int(size.find('width').text)
h = int(size.find('height').text)
with open(out_file, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f_out:
for obj in root.iter('object'):
difficult = obj.find('difficult').text
cls = obj.find('name').text
if cls not in classes or int(difficult) == 1:
continue
cls_id = classes.index(cls)
xmlbox = obj.find('bndbox')
b = (float(xmlbox.find('xmin').text), float(xmlbox.find('xmax').text),
float(xmlbox.find('ymin').text), float(xmlbox.find('ymax').text))
bb = convert((w, h), b)
f_out.write(f"{cls_id} {' '.join(str(a) for a in bb)}\n")
return image_id
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error processing {xml_file}: {str(e)}")
return None
# 处理训练集
print("Processing training set...")
train_list = []
for xml_file in tqdm(train):
image_id = convert_annotation(xml_file, os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/train'))
if image_id:
src_img = os.path.join(images_path, f'{image_id}.jpg')
dst_img = os.path.join(output_path, 'images/train', f'{image_id}.jpg')
if os.path.exists(src_img):
# 移动图片文件到训练集目录
shutil.move(src_img, dst_img)
train_list.append(dst_img)
# 移动XML文件到标签目录
src_xml = os.path.join(xml_path, xml_file)
dst_xml = os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/train', f'{image_id}.xml')
if os.path.exists(src_xml):
shutil.move(src_xml, dst_xml)
# 处理验证集
print("Processing validation set...")
val_list = []
for xml_file in tqdm(val):
image_id = convert_annotation(xml_file, os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/val'))
if image_id:
src_img = os.path.join(images_path, f'{image_id}.jpg')
dst_img = os.path.join(output_path, 'images/val', f'{image_id}.jpg')
if os.path.exists(src_img):
# 移动图片文件到验证集目录
shutil.move(src_img, dst_img)
val_list.append(dst_img)
# 移动XML文件到标签目录
src_xml = os.path.join(xml_path, xml_file)
dst_xml = os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/val', f'{image_id}.xml')
if os.path.exists(src_xml):
shutil.move(src_xml, dst_xml)
# 处理测试集
print("Processing test set...")
test_list = []
for xml_file in tqdm(test):
image_id = convert_annotation(xml_file, os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/test'))
if image_id:
src_img = os.path.join(images_path, f'{image_id}.jpg')
dst_img = os.path.join(output_path, 'images/test', f'{image_id}.jpg')
if os.path.exists(src_img):
# 移动图片文件到测试集目录
shutil.move(src_img, dst_img)
test_list.append(dst_img)
# 移动XML文件到标签目录
src_xml = os.path.join(xml_path, xml_file)
dst_xml = os.path.join(output_path, 'labels/test', f'{image_id}.xml')
if os.path.exists(src_xml):
shutil.move(src_xml, dst_xml)
# 保存路径文件
def save_path_file(file_path, path_list):
with open(file_path, 'w') as f:
for path in path_list:
f.write(f"{path}\n")
save_path_file(os.path.join(output_path, 'train.txt'), train_list)
save_path_file(os.path.join(output_path, 'val.txt'), val_list)
save_path_file(os.path.join(output_path, 'test.txt'), test_list)
print("Dataset preparation completed!")
print(f"Train: {len(train_list)} images, Val: {len(val_list)} images, Test: {len(test_list)} images")
再创建
from ultralytics import YOLO
import cv2
# 加载预训练的 YOLOv11n 模型
model = YOLO('yolo11s-seg.pt') # 确保模型文件路径正确
# 打开摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0) # 0 表示默认摄像头,可改为视频文件路径
# 设置窗口名称
window_name = 'YOLOv11 Real-time Detection'
cv2.namedWindow(window_name, cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
# 设置摄像头分辨率(可选)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, 1920)
cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, 1080)
try:
while cap.isOpened():
# 读取摄像头帧
success, frame = cap.read()
if not success:
print("无法读取摄像头画面,请检查摄像头连接。")
break
# 使用YOLOv11进行目标检测
results = model.predict(frame, verbose=False) # verbose=False关闭控制台输出
# 在帧上绘制检测结果
annotated_frame = results[0].plot() # 自动绘制边界框和标签
# 显示处理后的帧
cv2.imshow(window_name, annotated_frame)
# 按'q'键退出
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
except Exception as e:
print(f"发生错误: {e}")
finally:
# 释放资源
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
print("摄像头已释放,程序退出。")
这些工作做好后下载yolov11的训练模型,在github里,下载好后放在yolov11的文件夹中。
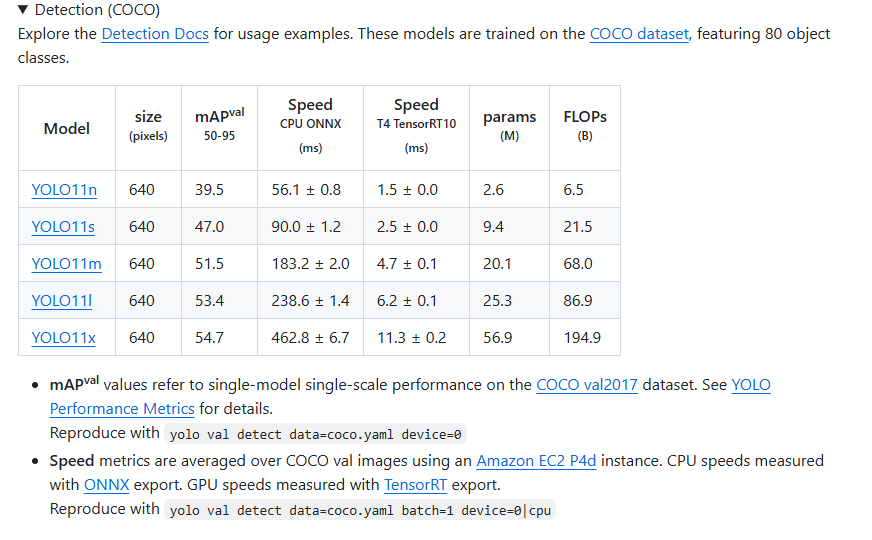
这些都完成后就可以进行测试
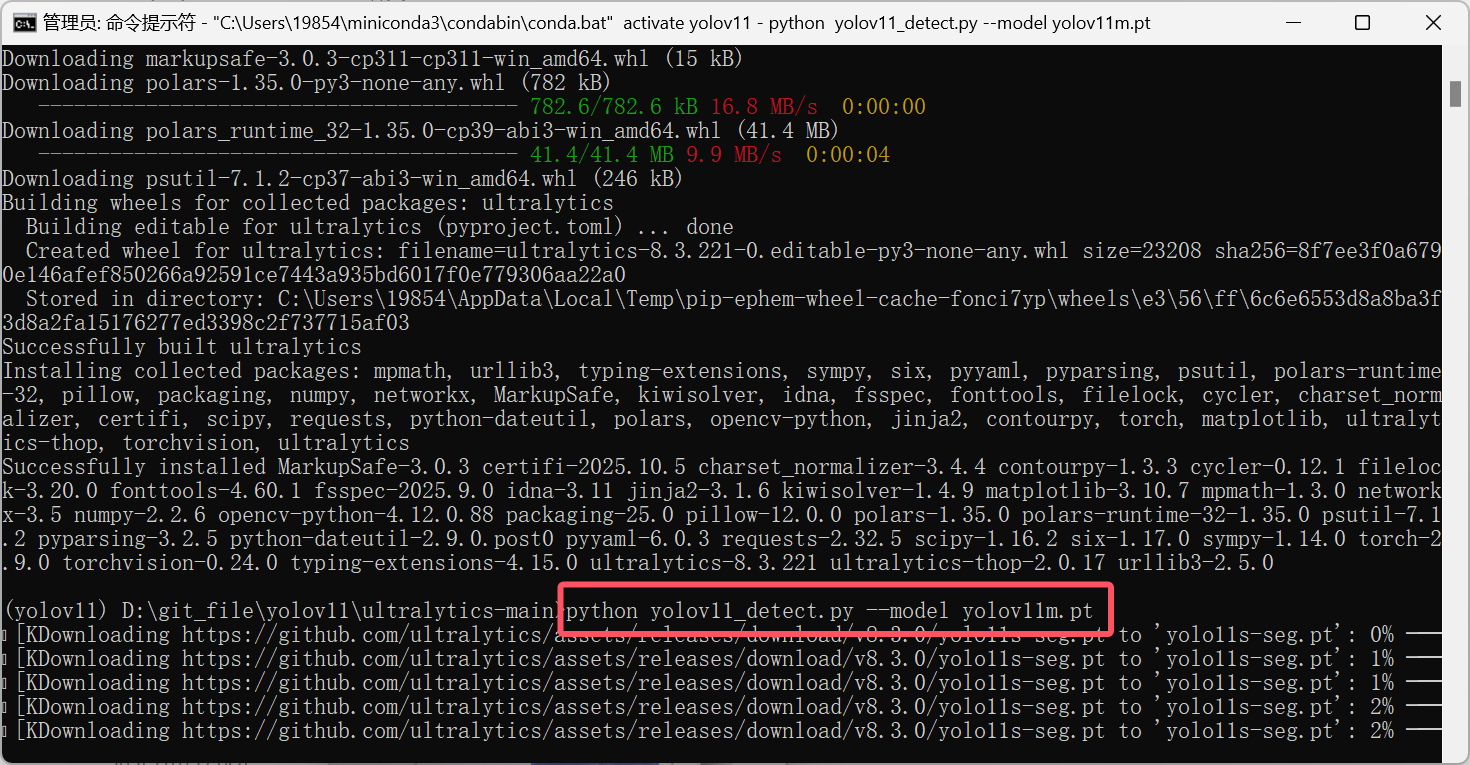
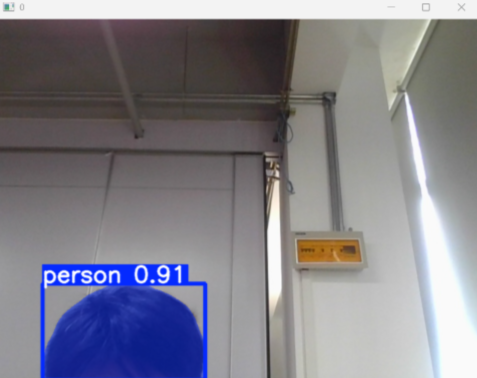
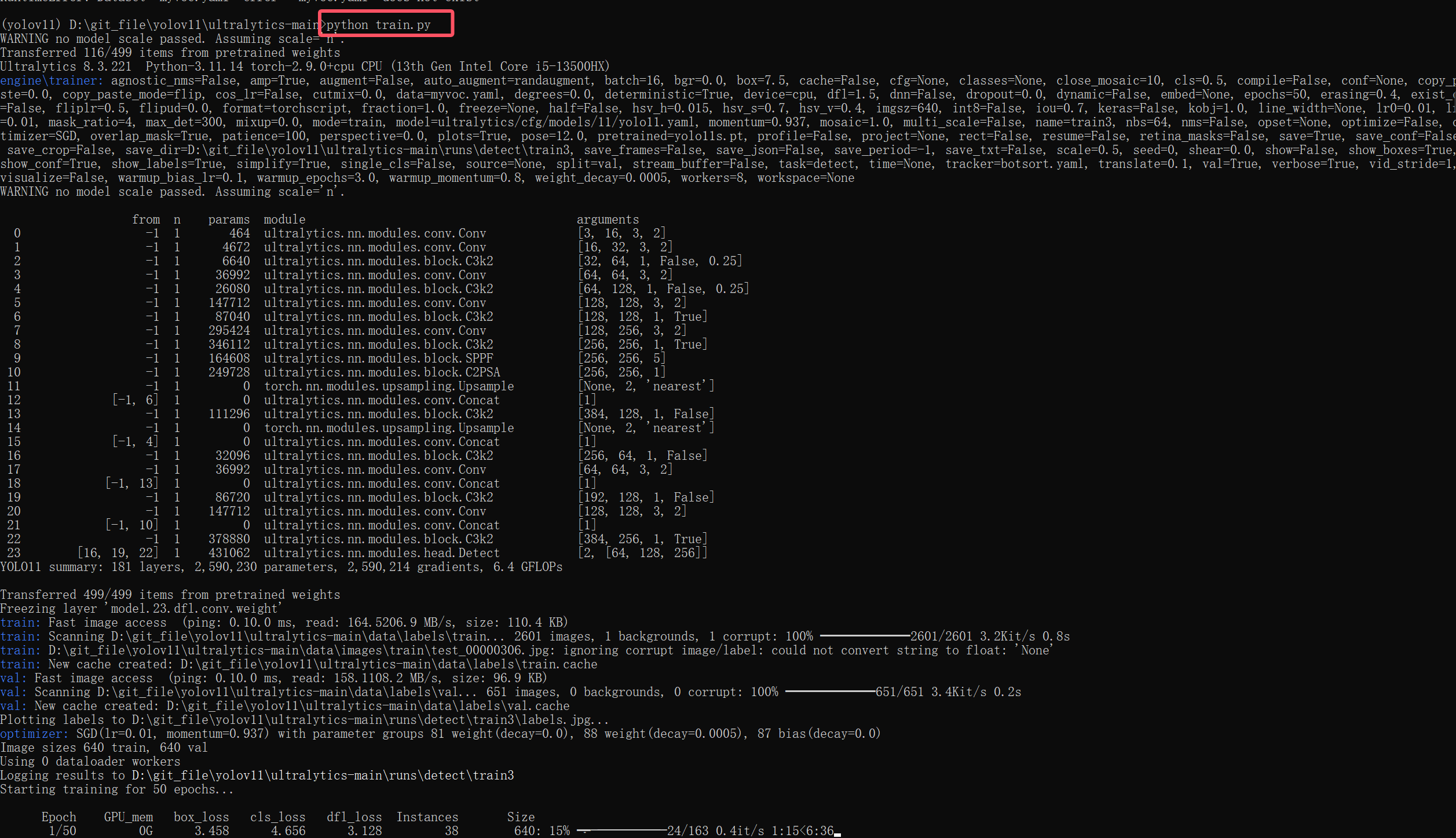
成功后就可以进行训练了





















 23万+
23万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








