为避免决策树的过拟合问题,可以使用集合学习的方法。集合学习算法综合多个机器学习算法,从而制造一个更加大的模型。目前应用广泛的包括随机森林(Random Forests)和梯度上升决策树(Gradient Boosted Decision Trees,GBDT)。随机森林就是把参数不同的几棵决策树打包到一起,把每棵树预测结果取平均值,既保留决策树们的工作成效,又降低过拟合的风险。
#导入随机森林模型
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_wine
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap
wine=load_wine()
#选取数据集前两个特征
X=wine.data[:,:2]
y=wine.target
X_train,X_test,y_train,y_test=train_test_split(X,y)
#设定随机森林中有6棵树
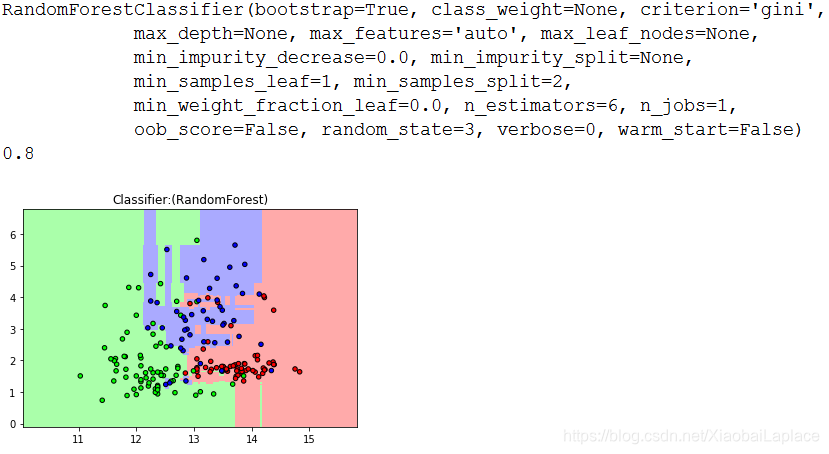
forest=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=6,random_state=3)
forest.fit(X_train,y_train)
print(forest)
print(forest.score(X_test,y_test))
#定义图像中分区的颜色和散点的颜色
cmap_light=ListedColormap(['#FFAAAA', '#AAFFAA', '#AAAAFF'])
cmap_bold = ListedColormap(['#FF0000', '#00FF00', '#0000FF'])
#分别用样本的两个特征值创建图像和横轴、纵轴
x_min,x_max=X_train[:,0].min()-1,X_train[:,0].max()+1
y_min,y_max=X_train[:,1].min()-1,X_train[:,1].max()+1
xx,yy=np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min,x_max,.02),np.arange(y_min,y_max,.02))#从两个坐标向量返回坐标矩阵
Z=forest.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(),yy.ravel()])
#给每个分类中的样本分配不同的颜色
Z=Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.figure()
plt.pcolormesh(xx,yy,Z,cmap=cmap_light)
#用散点画出样本
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=y,cmap=cmap_bold,edgecolor='k',s=20)
plt.xlim(xx.min(),xx.max())
plt.ylim(yy.min(),yy.max())
plt.title("Classifier:(RandomForest)")
plt.show()
 使用随机森林避免过拟合
使用随机森林避免过拟合





 本文介绍如何通过集合学习中的随机森林算法来减少决策树的过拟合风险。使用了sklearn库中的随机森林分类器,并以葡萄酒数据集为例进行演示。文中还展示了如何通过可视化来理解模型的决策边界。
本文介绍如何通过集合学习中的随机森林算法来减少决策树的过拟合风险。使用了sklearn库中的随机森林分类器,并以葡萄酒数据集为例进行演示。文中还展示了如何通过可视化来理解模型的决策边界。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








