最近学习了容器适配器priority_queue,所以借助速写本博客作为笔记,若有兴趣,不妨垂阅!

目录
1.priority_queue简介
1.priority_queue,也就是优先级队列。包含于头文件<queue>中。说白了,优先级队列底层是数据结构里面的堆(默认是大堆),也就是说,优先级队列数据的存放必须满足堆的要求。
2.由于其底层是堆(默认大堆),所以优先级队列根据严格的排序标准。当其为大堆的情况下,它的第一个元素总是它所包含的元素中最大的,在堆中可以随时插入元素,并且只能检索最大堆元素(优先级队列中位于顶部的元素);小堆的情况下,反之。
3.优先级队列被实现为容器适配器,容器适配器即将特定容器类封装作为其底层容器类,queue 提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从特定容器的“尾部”弹出,其称为优先队列的顶部。
4.优先级队列底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,也可以是其他特定设计的容器类。容器应该可以通过随机访问迭代器访问,并支持以下操作:
- empty():检测容器是否为空
- size():返回容器中有效元素个数
- front():返回容器中第一个元素的引用
- push_back():在容器尾部插入元素
- pop_back():删除容器尾部元素
5.标准容器类vector和deque满足这些需求。默认情况下,如果没有为特定的priority_queue 类实例化指定容器类,则使用vector。
6. 优先级队列底层容器需要支持随机访问迭代器,以便始终在内部保持堆结构。容器适配器通过在需要时自动调用算法函数make_heap、push_heap和pop_heap来自动完成此操作。
2.priority_queue使用
先看到priority_queue文档:
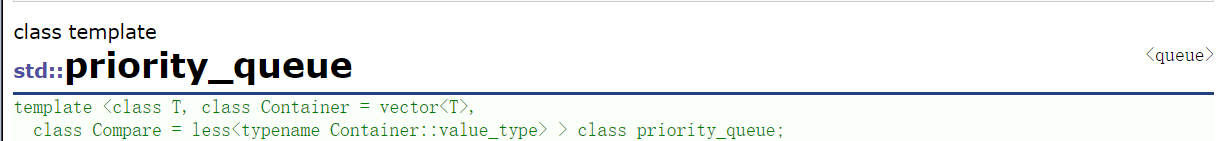
一个类模板,有3个模板参数。第1个模板参数就是优先级队列存储元素数据类型;第2个模板参数代表优先级队列底层容器,默认底层容器为vector;第3个模板参数与仿函数相关,一会再介绍。
那么优先级队列默认使用vector作为其底层存储数据的容器,在vector上又使用了堆算法将vector中元素构造成堆的结构,因此priority_queue就是堆,所有需要用到堆的位置,都可以考虑使用 priority_queue。注意:默认情况下priority_queue是大堆。
常用接口(C++98版本):
构造,其中:
- explicit priority_queue (const Compare& comp = Compare(), const Container& ctnr = Container())
构造一个空的优先级队列。
- template <class InputIterator>
priority_queue (InputIterator first, InputIterator last, const Compare& comp = Compare(), const Container& ctnr = Container())
用一段迭代器区间[first, last)构造优先级队列。
2.empty()
检测优先级队列是否为空,是返回true,否 则返回false。
3.top()
若大堆,返回优先级队列中最大元素,即堆顶元素。若小堆,返回优先级队列中最小元素,亦为堆顶元素。
4.push()
在优先级队列中插入元素x。
5.pop()
删除优先级队列中最大(最小)元素,即删除堆顶元素。
2.1.优先级队列(大堆)
写一份代码举栗吧:
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
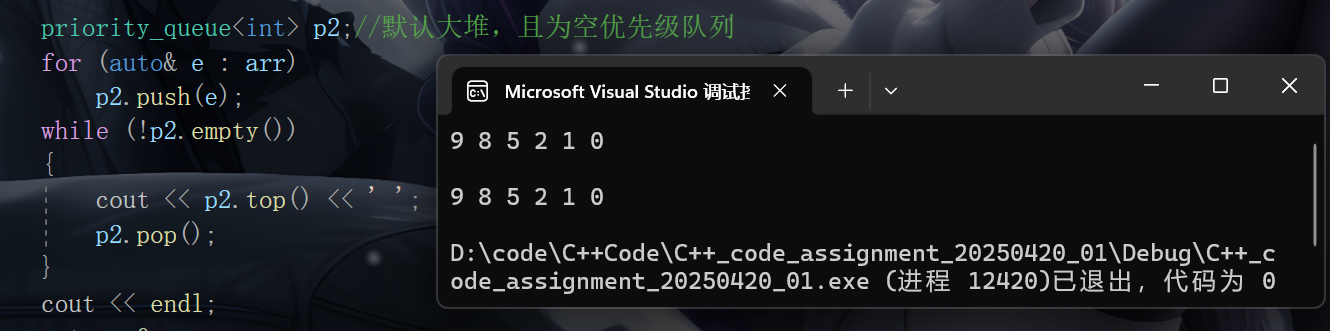
int arr[] = { 1, 5, 8, 2, 9, 0 };
priority_queue<int> p1(arr, arr + 6);//默认大堆
while (p1.size())
{
cout << p1.top() << ' ';
p1.pop();
}
cout << endl << endl;
priority_queue<int> p2;//默认大堆,且为空优先级队列
for (auto& e : arr)
p2.push(e);
while (!p2.empty())
{
cout << p2.top() << ' ';
p2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}运行结果,预料之中:
如何创建小堆呢?这就涉及仿函数的知识,所以先介绍仿函数!
2.2.仿函数
用冒泡排序,抛砖引玉:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void bubble_sort(int* a, size_t begin, size_t end)//冒泡排序(升序)
{
for (size_t R = end; R > begin; --R)
{
bool flag = true;
for (size_t L = begin + 1; L <= R; ++L)
{
if (a[L] < a[L - 1])
{
swap(a[L], a[L - 1]);
flag = false;
}
}
if (flag)
break;
}
}
int main()
{
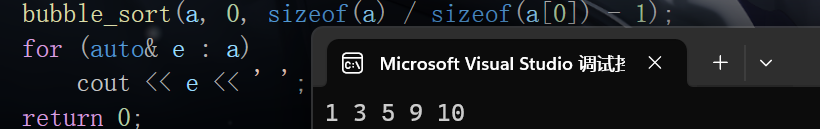
int a[] = { 1, 10, 5, 9, 3};
bubble_sort(a, 0, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]) - 1);
for (auto& e : a)
cout << e << ' ';
return 0;
}
如果想让这个冒泡排序排升序,有很多办法。其中使用仿函数,对冒泡排序进行改造是一个很不错的方案。
仿函数其实是一个类,需要重载操作符(),用这个类对象去调用()操作符重载。也用冒泡排序举例吧:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Greater//仿函数(类)
{
public:
bool operator()(int t1, int t2)//重载操作符()
{
return t1 > t2;
}
};
class Less//仿函数(类)
{
public:
bool operator()(int t1, int t2)
{
return t1 < t2;
}
};
template<class Compare = Less>
void bubble_sort(int* a, size_t begin, size_t end)
{
Compare com;
for (size_t R = end; R > begin; --R)
{
bool flag = true;
for (size_t L = begin + 1; L <= R; ++L)
{
if (com(a[L], a[L - 1]))//仿函数(类)对象调用operator()
{
swap(a[L], a[L - 1]);
flag = false;
}
/*if (a[L] < a[L - 1])
{
swap(a[L], a[L - 1]);
flag = false;
}*/
}
if (flag)
break;
}
}
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1, 10, 5, 9, 3};
bubble_sort(a, 0, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]) - 1);//升序
for (auto& e : a)
cout << e << ' ';
cout << endl;
bubble_sort<Greater>(a, 0, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]) - 1);//降序
for (auto& e : a)
cout << e << ' ';
return 0;
}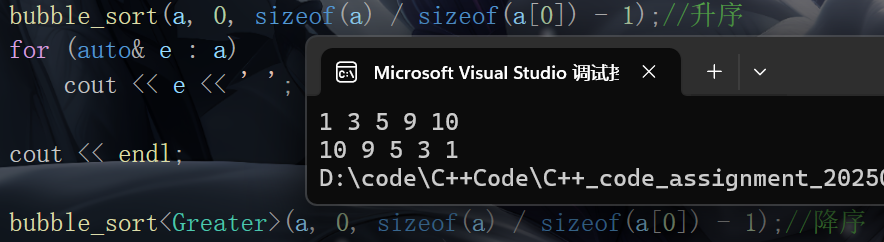
将冒泡排序实现成函数模板,根据模板参数的不同,可以实现升序或者降序排序 ,那降序来举例,画图理解:
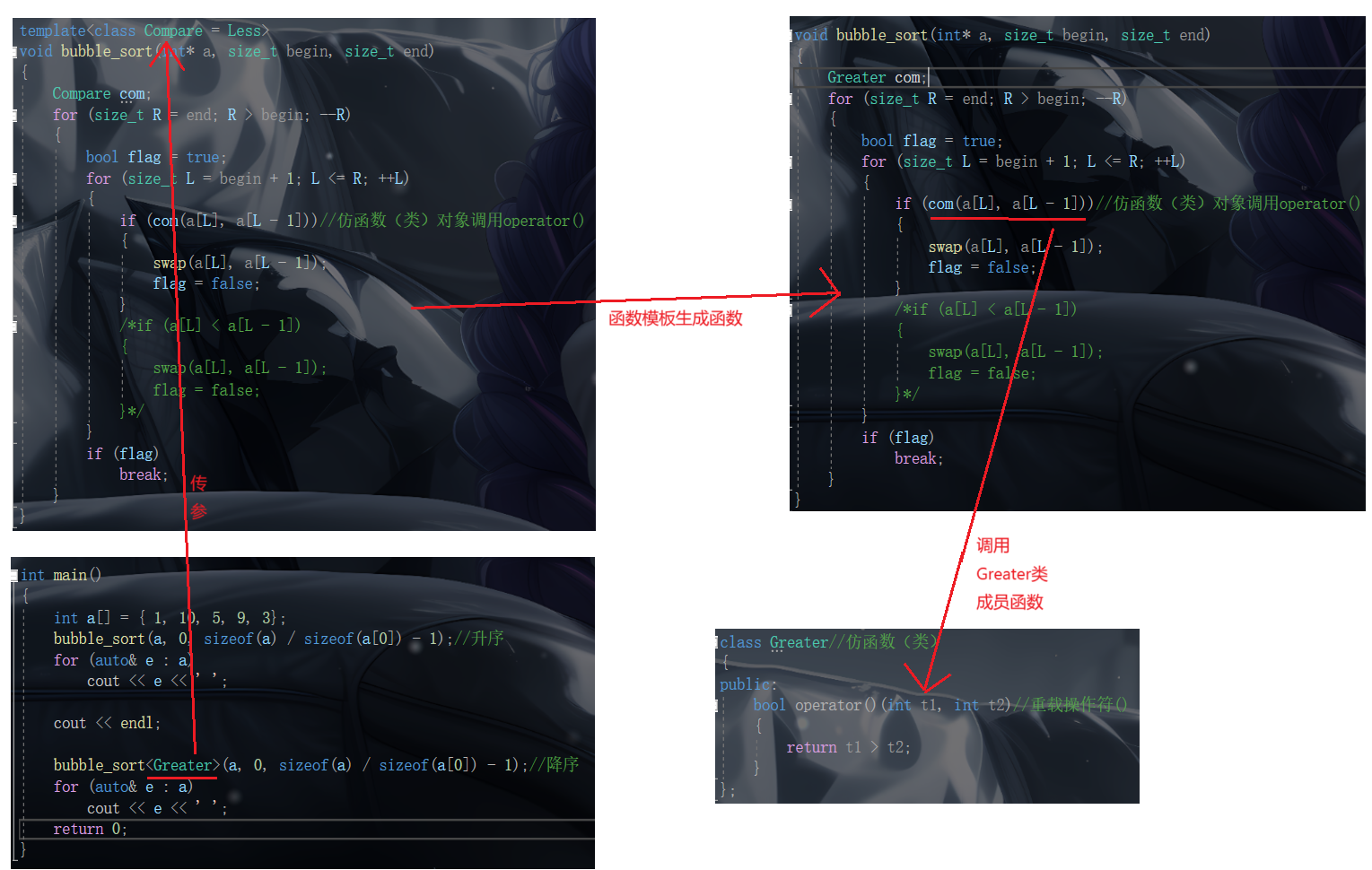
仿函数(类)对象调用operator()的时候像极了普通的函数调用,所以仿函数由此得名,但本质还是一个类。仿函数一般不需要自己实现,库里面是有现成的,并将仿函数实现成类模板,包含有头文件<functional>中。看到:
sort 当然也可以用仿函数实现升序或降序排序,例如:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = { 1, 2, 8, 10, 5, 4 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
less<int> com;
sort(a, a + sz, com);//升序
for (auto& e : a)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
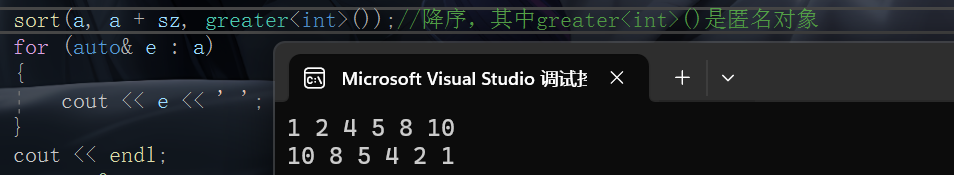
sort(a, a + sz, greater<int>());//降序,其中greater<int>()是匿名对象
for (auto& e : a)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
有了仿函数的知识,也就可以解释为什么优先级队列默认是大堆了,因为优先级队列这个类模板,第3个类模板参数缺省值是less<typename Container::value_type> 。
ps:
一般排序算法(包括sort_heap),如果排升序的逻辑是需要仿函数less<T>,因为升序排列整体看起来是'<'的;反之,排降序的逻辑是需要仿函数greater<T>,因为降序排列整体看起来是'>'的。
但是优先级队列是跟一般排序算法逻辑相反的。如果大堆,大堆元素排列整体看起来是'>'的,但是它就是需要仿函数less<T>;如果小堆,却需要仿函数greater<T>。具体为什么逻辑相反,其实就是C++标准库里面的优先级队列底层实现的比较逻辑相反于一般排序算法的比较逻辑。
2.3.优先级队列(小堆)
看代码举例:
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
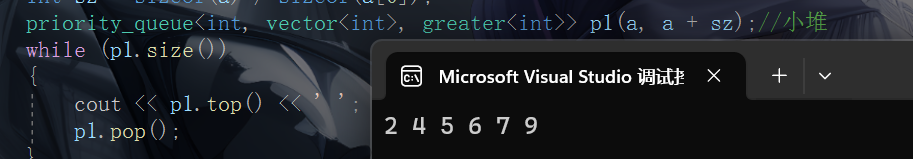
int a[] = { 5, 4, 7, 6, 2, 9 };
int sz = sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]);
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> p1(a, a + sz);//小堆
while (p1.size())
{
cout << p1.top() << ' ';
p1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
还需要注意的是:无论大堆还是小堆,如果在priority_queue中放自定义类型的数据,用户要么要在自定义类型中提供> 或者< 的重载;要么不使用库里面的仿函数,自己实现仿函数并使用。为什么呢?

原因简单啊,如果不提供>或者<的重载,那么库里面的仿函数对象调用operator()的时候,如何知道自定义类型数据该如何比较呢?
3.priority_queue模拟实现
为次,我建立了一个工程,该工程包含2个文件,分别是myPriorityQueue.h和test.cpp。
myPriorityQueue.h:
namespace HD
{
//仿函数(类模板)
template<typename T>
class Less
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& t1, const T& t2)
{
return t1 < t2;
}
};
//仿函数(类模板)
template<typename T>
class Greater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& t1, const T& t2)
{
return t1 > t2;
}
};
template<typename T, typename Container = vector<T>, typename Compare = Less<typename Container::value_type>>
class priority_queue
{
Container _con;
typedef T value_type;
typedef size_t size_type;
//向上调整算法
void up(size_type child)
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (0 <= parent && com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
}
//向下调整算法
void down(size_type parent)
{
Compare com;
size_type child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < size())
{
if (child + 1 < size() && com(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
child++;
if (com(_con[parent], _con[child]))
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
else
break;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
}
public:
size_type size()const
{
return _con.size();
}
void push(const value_type& val)
{
_con.push_back(val);
up(size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
down(0);
}
const value_type top()const
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty()const
{
return _con.empty();
}
};
}test.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <functional>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#include "myPriorityQueue.h"
namespace HD
{
void test()
{
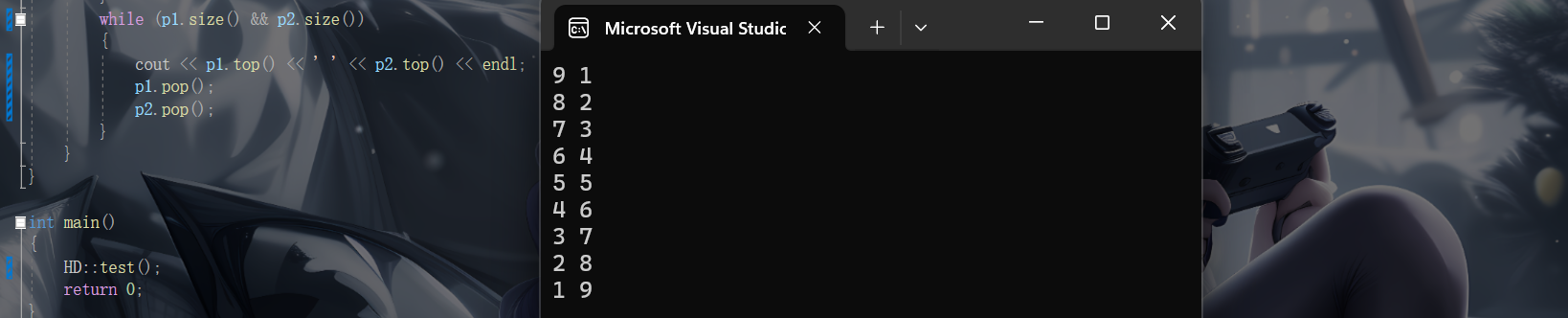
priority_queue<int> p1;//大堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, Greater<int>> p2;//小堆
for (int i = 1; i < 10; ++i)
{
p1.push(i);
p2.push(i);
}
while (p1.size() && p2.size())
{
cout << p1.top() << ' ' << p2.top() << endl;
p1.pop();
p2.pop();
}
}
}
int main()
{
HD::test();
return 0;
}看一下运行结果,意料之中:
当然了,priority_queue的模拟实现也可以用库里面现成的函数,这样子就不用自己手搓了。myPriorityQueue.h:
namespace HD
{
template<typename T, typename Container = vector<T>, typename Compare = less<typename Container::value_type>>
class priority_queue
{
Container _con;
typedef T value_type;
typedef size_t size_type;
public:
size_type size()const
{
return _con.size();
}
//void push(const value_type& val)
//{
// _con.push_back(val);
// push_heap(_con.begin(), _con.end(), Compare());//向上调整算法
//}
void push(const value_type& val)
{
_con.push_back(val);
make_heap(_con.begin(), _con.end(), Compare());
}
//void pop()
//{
// pop_heap(_con.begin(), _con.end(), Compare());//交换 + 向下调整算法
// _con.pop_back();
//}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
make_heap(_con.begin(), _con.end(), Compare());
}
const value_type top()const
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty()const
{
return _con.empty();
}
};
}4.小知识
介绍几个<algorithm>里面的函数模板,都是于堆有关系的。
库里实现的堆排序。默认排升序,需要注意的是待排序序列必须已经成大堆才能使用这个堆排序排升序;如果想要排降序,可以使用仿函数,需要注意的是带排序序列必须已经成小堆才能使用这个堆排序排降序。
判断是不是堆。默认判断是不是大堆,如果想要判断是不是小堆,其中一个办法就是第2个函数模板参数传greater的实例化。
默认建大堆。若想建小堆,其中一个办法就是第2个函数模板参数传greater的实例化。
作用类似于向上调整算法。
5.pop_heap
作用类似于交换+向下调整算法。具体请看文档。
感谢阅读,欢迎斧正!
























 1206
1206

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










