IO流
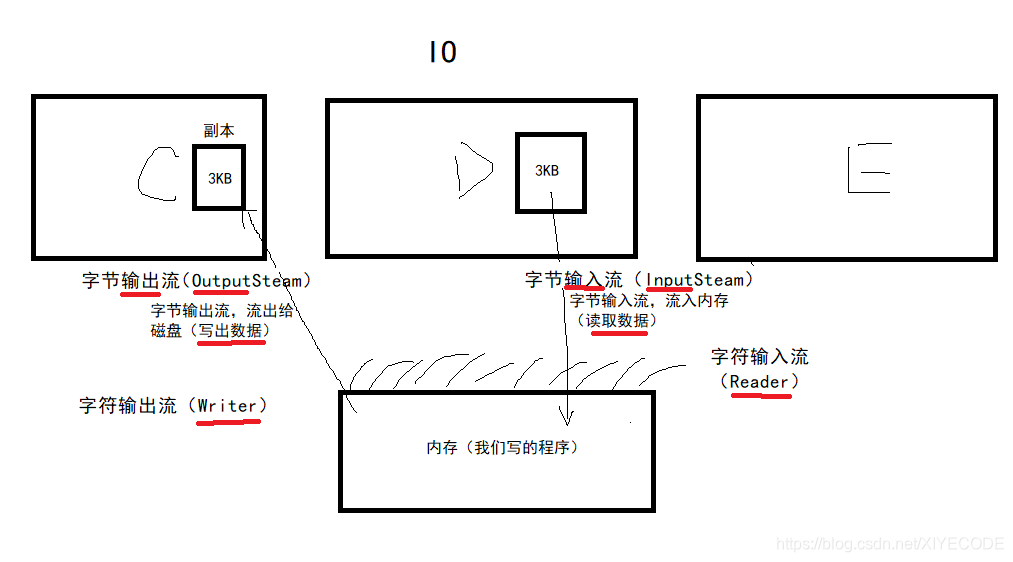
字节流
import java.io.*;
/**
* Create by xiye on 2019/12/4 11:54
*/
public class Demo1_IO流 {
/*IO流
* 内存获取硬盘文件是输入流,内存写回硬盘是输出流
* 输入流:字节输入流(InputStream)、字符输入流(Reader)
* 输出流:字节输出流(OutputStream)、字符输出流(Writer)
* 以上四个都是抽象类
*
* 文件的读写一般是字节流,如果需要读取中文,适合用字符流
*
* */
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//fileOutput();
method11();
method12();
}
/*
* 多字节读取
* */
private static void method12() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file_test/int.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
byte[] bytes = new byte[2];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(bytes, 0, len));
}
fis.close();
}
/*
* 单一字节读取
* */
private static void method11() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file_test/bytes.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(b);
}
fis.close();
}
private static void fileOutput() throws IOException {
method1();
method2();
mrthod3();
method4();
}
/*
* 追加写入
* */
private static void method4() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file_test/writeAppend.txt");
byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 101, 106, 113, 122};
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file, true);
fos.write(bytes);
fos.close();
}
/*
* 写入字节数组,指明起止位置和长度
* */
private static void mrthod3() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file_test/bytesWithOffAndLen.txt");
byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 101, 106, 113, 122};
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(bytes, 2, 3);
fos.close();
}
/*
* 写入字节数组
* */
private static void method2() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file_test/bytes.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write("写入字节数组".getBytes());
fos.close();
}
/*
* 写入Ascii码
* */
private static void method1() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file_test/int.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
fos.write(64);
fos.write(120);
fos.write(105);
fos.write(121);
fos.write(101);
fos.close();
}
}
示例
import java.io.*;
/**
* Create by xiye on 2019/12/4 15:41
*/
public class Demo2_IO示例 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(new File("D:/file_test/test.png")); // 源文件位置
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:/file_test/copy/test_copy.png")); // 目标文件位置
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
fos.write(b);
}
// 关闭遵循就近原则,即最新创建的资源最先关闭
fos.close();
fis.close();
}
}
扩展
字符流
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
* Create by xiye on 2019/12/4 16:22
*/
public class Demo3_字符流 {
/*
* 字符流中,写入的数据先保存在缓冲区,如果没有关闭(close)或刷新(flush),数据是无法保存到硬盘的
* 注:字节流中的刷新(flush)是无效的,根据源代码可得知,父类没有内容。子类又没有重写。
*
* */
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//fileReader();
method11();
}
private static void method11() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file_test/writer.txt");
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
fw.write("可以写入字符串");
fw.write('C');
fw.write(5000);
fw.flush();
fw.close();
}
private static void fileReader() throws IOException {
method1();
method2();
}
private static void method2() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file_test/bytes.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
char[] chars = new char[4];
int len;
while ((len = fr.read(chars)) != -1) {
System.out.println(new String(chars, 0, len));
}
fr.close();
}
private static void method1() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:/file_test/bytes.txt");
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
int b;
while ((b = fr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.println(b+ ":" + (char)b);
}
fr.close();
}
}
属性集
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* Create by xiye on 2019/12/4 17:12
*/
public class Demo4_属性集 {
/*属性集:Properties
* setProperty()设置一对键值,键值类型都是字符串
* getProperty()根据键获取值
* stringPropertyNames()获取所有键
* load()加载流
* */
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
// 加载文件
properties.load(new FileInputStream("Day18/resources/info.properties"));
// 添加一对键值
properties.setProperty("properties", "info");
// 获取所有键
Set<String> keys = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String k : keys) {
System.out.println(k + " --> " + properties.getProperty(k));
}
// 将属性集的内容写到指定文件,如下是写回原文件(会覆盖),并在文件开头加上注释信息“new info”
// properties.store(new FileOutputStream("Day18/resources/info.properties"), "new info");
}
}
示例info.properties
username=root
password=123456
url=localhost://mysql:3326...





 本文深入讲解Java中的IO流概念,包括字节流和字符流的使用,如FileInputStream、FileOutputStream、FileReader和FileWriter等。同时,通过实例演示了如何进行文件的读写操作,以及如何利用属性集(Properties)进行键值对的存储和读取。
本文深入讲解Java中的IO流概念,包括字节流和字符流的使用,如FileInputStream、FileOutputStream、FileReader和FileWriter等。同时,通过实例演示了如何进行文件的读写操作,以及如何利用属性集(Properties)进行键值对的存储和读取。

















 317
317

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








