Redis
Remote dictionary server
使用版本:6.2.4
高速缓存:放去热数据,计算很复杂的数据,下一次还要用的数据。
介绍
本身就可以理解为是一个大的HashMap
Redis 是一个开源的基于键值对NoSQL数据库,使用ANSI C语言编写,支持网络、基于内核但支持持久化。性能优秀,并提供多种语言的API。
Redis会将所有数据都放在内存中,所以它的读写性能非常惊人。不仅如此,Redis可以将内存的数据利用快照和日志的形式保存到硬盘上,这样在发生类似断电或者机器故障的时候,内存中的数据不会“丢失”。除了上述功能以外,Redis还提供了键过期、发布订阅、事务、流水线、Lua脚本等附加功能。
Redis不是一个可靠的数据库
从mysql读 2000次/s
从redis 可能10w次/s
Redis可以做的运用举例:缓存、排行榜系统、计数器运用、社交网络、消息队列
Redis特性
- 速度快
- 键值对的数据结构服务器
- 丰富的功能
- 简单稳定
- 持久化
- 主从复制
- 高可用和分布式转移
- 客户端语言多
- redis 的多线程多是在网络上,内存中读写是单线程的
Redis 操作
启动
不带参数启动
带参数启动
以配置文件的形式启动(Redis不提供)
关闭
Redis 全局命令
查看所有键
keys * set school enjoy set [key] [value]
键总数
dbsize [key]
检查键是否存在
exists [key]
删除键
del [key]
键过期
expire [key] [seconds]
expireat
键的数据结构
Java 操作 Redis
Jedis
maven 依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<!--
1. 1.x版本默认的连接池是Jedis, 2.0以上版本的连接池是Lettuce
2. 如果采用Jedis,需要排除Lettuce,然后引入Jedis依赖
-->
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettuce</groupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>
yml配置
此时这个yml配置还没有生效
spring:
redis:
host: 127.0.0.1
port: 6379
password:
# 选择哪个库 默认是0库
database: 0
# 连接超时
timeout: 10000
# 连接池配置
jedis:
pool:
# 最大链接数
max-active: 1024
# 最大阻塞连接等待时间,单位毫秒
max-wait: 10000
# 最大空闲连接
max-idle: 200
# 最小空闲连接
min-idle: 5
使用Jedis对象操作Redis
/**
* 通过jedis操作
*/
@Test
void initConn() {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("192.168.16.129", 6379);
System.out.println(jedis.ping());
jedis.set("name", "FengQian");
if (jedis != null) {
jedis.close();
}
}
使用JedisPool
/**
* 通过JedisPool操作
*/
@Test
void initConnByPool() {
JedisPool jedisPool = new JedisPool(new JedisPoolConfig(), "192.168.16.129", 6379);
Jedis jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
jedis.select(0);
System.out.println(jedis.ping());
jedis.set("score", "100");
jedis.close();
}
从配置文件加载Jedis配置
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.16.129
port: 6379
password: root
database: 0
timeout: 10000
jedis:
pool:
max-active: 1024
max-wait: 10000
max-idle: 200
min-idle: 5
配置类
@Configuration
public class JedisConfig {
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
public String host;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
public int port;
@Value("${spring.redis.password}")
public String password;
@Value("${spring.redis.database}")
public String database;
@Value("${spring.redis.timeout}")
public int timeout;
@Value("${spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active}")
public int maxActive;
@Value("${spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait}")
public String maxWaitMillis;
@Value("${spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle}")
public int maxIdle;
@Value("${spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle}")
public int minIdle;
@Bean
public JedisPool jedisPool() {
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal((maxActive));
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle((maxIdle));
jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle((minIdle));
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(Long.parseLong(maxWaitMillis));
return new JedisPool(jedisPoolConfig, host, port, timeout);
}
}
Test类
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
class RedisDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private JedisPool jedisPool;
Jedis jedis = null;
@BeforeEach
void init() {
System.out.println(jedisPool.toString());
if (jedis == null) {
jedis = jedisPool.getResource();
}
}
@AfterEach
void des() {
if (jedis != null) {
jedis.close();
}
}
@Test
void intiConnByConfig() {
System.out.println(jedis.ping());
}
}
操作String与hash
@Test
void intiConnByConfig() {
System.out.println(jedis.ping());
// string
jedis.set("lover", "weidehao");
jedis.mset("Lover", "Fengqian", "Love", "WeiDeHao");
List<String> mget = jedis.mget("Love", "Lover");
mget.forEach(System.out::println);
// hashMap
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name", "FengQian");
map.put("score", "100");
map.put("addr", "Chengdu");
jedis.hmset("user:FengQian", map);
List<String> hmget = jedis.hmget("user:FengQian", "name", "score", "addr");
hmget.forEach(System.out::println);
jedis.hdel("user:FengQian", "addr");
Map<String, String> stringMap = jedis.hgetAll("user:FengQian");
stringMap.entrySet().forEach(m -> {
System.out.println(m.getKey() +":" + m.getValue());
});
}
操作List 操作Set 操作OrderSet
@Test
void testJedisOpera() {
// list-string
jedis.lpush("students","WeiDehao", "FengQian", "Weijiali");
jedis.rpush("students","zouyuming", "weixianyao");
System.out.println(jedis.llen("students"));
String left = jedis.lpop("students");
String right = jedis.rpop("students");
System.out.println(left + " ; " + right);
System.out.println(jedis.llen("students"));
// set-string
jedis.sadd("lec", "aa", "bb", "cc");
Set<String> lec = jedis.smembers("lec");
lec.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println(jedis.scard("lec"));
jedis.srem("lec", "bb"); // remove
Set<String> lec1 = jedis.smembers("lec");
lec1.forEach(System.out::println);
// ordered-set-string
jedis.zadd("zlec", 3, "FengQian");
jedis.zadd("zlec", 1, "Weidehao");
jedis.zadd("zlec", 2, "Weijiali");
jedis.zadd("zlec", 4, "fw");
Set<String> zrange = jedis.zrange("zlec", 0, 4);
zrange.forEach(System.out::println);
jedis.zrem("zlec", "fw", "weijiali");
System.out.println(jedis.zcard("zlec"));
}
层级目录 和 失效时间
@Test
void testLayerAndExpired() {
// 层级目录
jedis.set("user:fengqian:addr", "Chengdu");
jedis.set("user:fengqian:score", "100");
// 失效时间 key 已经存在
jedis.set("code", "test");
jedis.expire("code", 20);
// 失效时间 key不存在
jedis.setex("state", 30, "test");
jedis.psetex("cur", 30000, "test");
System.out.println(jedis.pttl("code"));
}
@Test
void testExpire() {
// 失效时间
SetParams setParams = new SetParams();
setParams.xx(); // 不存在的时候才能成功
// setParams.nx(); // 存在的时候才能成功
setParams.ex(30);
jedis.set("code", "test", setParams);
}
获取Keys
@Test
void testKeys() {
Set<String> keys = jedis.keys("*");
keys.forEach(System.out::println);
}
事务
@Test
void testTransaction() {
// redis 事务比较弱
// 开启事务
Transaction transaction = jedis.multi();
jedis.setex("code", 10, "test");
// 提交事务
transaction.exec();
// 事务回滚
// transaction.discard();
}
byte数组
@Test
void testBytes() {
User user = new User(1, "FengQian", "123");
byte[] userKey = SerializableUtil.serialize("user:" + user.getId());
byte[] userVal = SerializableUtil.serialize(user);
jedis.set(userKey, userVal);
// 取出数据
byte[] bytes = jedis.get(userKey);
User unserialize = (User) SerializableUtil.unserialize(bytes);
System.out.println(unserialize);
}
持久化方案
bgsave
使用一次命令保存一次
rdb
每隔一段时间在磁盘上保存一次
aof
SpringDataRedis
项目搭建
pom配置文件
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--连接池依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
序列化 问题
配置类里 设置序列化方案
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
// 为String类型的key设置序列化
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 为string类型的value设置序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
// 为hash类型的key 和 value设置序列化
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
//
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(lettuceConnectionFactory);
return redisTemplate;
}
}
测试
pojo类
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serializeUUID = 27398172398L;
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", username='" + username + '\'' +
", password='" + password + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
测试类
@Autowired
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Test
void testConn() {
ValueOperations<String, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("name", "zhangsan");
}
@Test
void testSerialize() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setUsername("FengQian");
user.setPassword("123");
ValueOperations<String, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
ops.set("user:" + user.getId(), user);
User user0 = (User) ops.get("user:" + user.getId());
System.out.println(user0);
}
操作String类型数据
@Test
void testString() {
ValueOperations<String, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
// 一条数据
ops.set("name", "FengQian");
String val = (String) ops.get("name");
System.out.println(val);
// 多条数据
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("age", "22");
map.put("score", "100");
map.put("addr", "sichuan chengdu");
ops.multiSet(map);
// 获取多条数据
List<String> tag = new ArrayList<>();
tag.add("age");
tag.add("score");
tag.add("addr");
List<Object> ret = ops.multiGet(tag);
ret.forEach(System.out::println);
redisTemplate.delete("name");
}
操作hash类型数据
@Test
void testHash() {
// 一条数据
HashOperations<String, Object, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForHash();
// p1:redis_key, p2:hash_key,p3:val
ops.put("user", "name", "FengQian");
ops.put("user", "score", "100");
Object o = ops.get("user", "name");
System.out.println(o);
// 多条数据
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("addr", "chengdu");
map.put("work", "beauty");
ops.putAll("user", map);
System.out.println(ops.get("user", "addr"));
// 获取多条数据
List<Object> tag = new ArrayList<>();
tag.add("addr");
tag.add("work");
tag.add("name");
List<Object> os = ops.multiGet("user", tag);
os.forEach(System.out::println);
// 获取hash的所有数据
Map<Object, Object> entries = ops.entries("user");
entries.entrySet().forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getKey() + "," + e.getValue()));
}
操作list类型数据
@Test
void testList() {
ListOperations<String, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForList();
ops.leftPush("students", "zhangsan");
ops.leftPush("students", "lisi");
ops.rightPush("students", "wangwu");
ops.rightPush("students", "zhaoliu");
List<Object> students = ops.range("students", 0, 4);
students.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("size: " + ops.size("students"));
// 删除数据
ops.remove("students", 1, "lisi");
}
操作set类型数据
@Test
void testSet() {
SetOperations<String, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForSet();
String[] letters = new String[]{"aa", "bb", "cc"};
// ops.add("letters", "aa", "bb", "cc");
ops.add("letters", letters);
// 获取
Set<Object> members = ops.members("letters");
members.forEach(System.out::println);
ops.remove("letters", "aa");
}
操作order-set类型数据
@Test
void testOrderedSet() {
ZSetOperations<String, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
// 添加数据
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> dtt1 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("lisi", 6D);
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> dtt2 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("zhangsan", 3D);
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> dtt3 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("wangsu", 2D);
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> dtt4 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("zhaoliu", 5D);
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> dtt5 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("zhouqi", 9D);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(dtt1);
set.add(dtt2);
set.add(dtt3);
set.add(dtt4);
set.add(dtt5);
ops.add("people", set);
Set<Object> people = ops.range("people", 0, 4);
people.forEach(System.out::println);
ops.remove("people", "zhangsan", "lisi");
}
获取keys
@Test
void testKeys() {
Set<String> keys = redisTemplate.keys("*");
keys.forEach(System.out::println);
}
过期时间
@Test
void testExpired() {
ValueOperations<String, Object> ops = redisTemplate.opsForValue();
// 1. 给不存在的key设置失效时间
ops.set("code", "test", 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(redisTemplate.getExpire("code"));
// 2. 给已经存在的key设置失效时间
redisTemplate.expire("addr", 30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(redisTemplate.getExpire("addr"));
}
yml中配置
方案一:yml中配置
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.16.129
port: 6379
password: root
# 选择哪个库 默认是0库
database: 0
# 连接超时
timeout: 10000
# 连接池配置
lettuce:
pool:
# 最大链接数
max-active: 1024
# 最大阻塞连接等待时间,单位毫秒
max-wait: 10000
# 最大空闲连接
max-idle: 200
# 最小空闲连接
min-idle: 5
# 配置哨兵模式
sentinel:
master: mymaster
# 哨兵的节点
nodes: 192.168.10.100:26379 192.168.10.100:26380 192.168.10.100:26381
方案二:配置类配置
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(LettuceConnectionFactory lettuceConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate<>();
// 为String类型的key设置序列化
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
// 为string类型的value设置序列化
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
// 为hash类型的key 和 value设置序列化
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer());
//
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(lettuceConnectionFactory);
return redisTemplate;
}
@Bean
public RedisSentinelConfiguration redisSentinelConfiguration() {
RedisSentinelConfiguration redisSentinelConfiguration = new RedisSentinelConfiguration();
redisSentinelConfiguration.master("mymaster")
.sentinel("192.168.10.100", 26379)
.sentinel("192.168.10.100", 26380)
.sentinel("192.168.10.100", 26381);
return redisSentinelConfiguration;
}
}
如何应对缓存击穿 缓存穿透 缓存雪崩
key淘汰机制
Redis可以对存储在Redis中的缓存设置缓存时间,但是并非key过期时间一到就一定会被Redis给删除。
定期删除
Redis默认是每隔100ms就随机抽取一些过期了的Key,检查是否过期,如果过期就删除。选择随机抽取的原因是key太多全部检查一遍会降低性能。
惰性删除
定期删除不会删干净。所以在获取数据的时候,Redis会检查这个key是否过期,过期就会从缓存中删除这个key。
内存淘汰机制
仅仅使用前两周策略无法保证删干净,会有redis内存耗尽的风险。故需要Redis内存淘汰机制包含6中策略:
volatile-lru(推荐使用):从已设置过期时间的数据集中选择最少使用的数据淘汰volatile-ttl:从已经设置过期时间中挑选即将过期的数据淘汰volatile-random:从已经设置过期时间中任意淘汰数据allkeys-lru:当内存不足以容纳写入数据时移除最少使用的keyallkeys-random:从数据集中任意选择数据淘汰no-enviction(默认使用):当内存不足,写入数据报错
缓存击穿
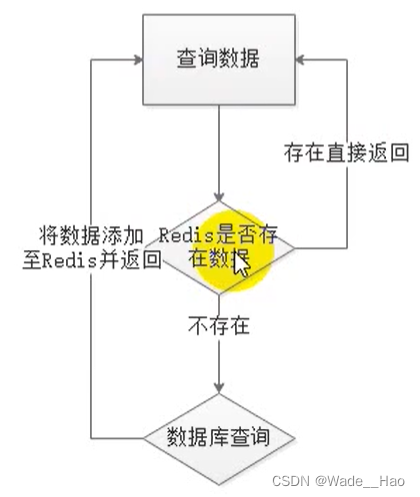

缓存穿透

缓存雪崩























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








