Java 中的数据类型分为 基本数据类型 和 引用数据类型。
基本数据类型共八种:
四种整数类型:byte(1字节)、short(2字节)、int(4字节)、long(8字节);
两种浮点数类型:float(4字节)、double(8字节);
一种字符类型:char(2字节);
一种布尔类型:boolean(1字节);
这八种基本类型都对应有引用类型。Java中将基本数据类型转换为引用数据类型的过程称为装箱,反之称为拆箱。
值传递和引用传递的知识点,可以参考:结合一道经典的京东面试题做的讲解
Integer和int的区别:
1、Integer是int的包装类,int则是Java的一种基本数据类型;
2、Integer变量必须实例化后才能使用,而int变量不需要;
3、Integer实际是对象的引用,当new一个Integer时,实际上是生成一个指针指向此对象;而int则是直接存储数据值;
4、Integer的默认值是null,int的默认值是0;
这篇文章的标题是我以前遇到的一个面试题。
自动装箱、拆箱的示例:
Interger i = 30; //Interger.valueOf(30)
Float f = 40.5f ;
int a = i ; //i.intValue();
float b = f ;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 127; //Interger.valueOf(127)
int i = a; //a.intValue();
}
javap -c Test.class
public static void main(java.lang.String[]);
Code:
0: bipush 127
2: invokestatic #2 // Method java/lang/Integer.valueOf:(I)Ljava/lang/Integer;
5: astore_1
6: aload_1
7: invokevirtual #3 // Method java/lang/Integer.intValue:()I
10: istore_2
手动装箱、拆箱的示例:
Interger i = new Interger(20) ;
Interger m = Interger.valueOf(20) ;
int num = i.intValue();
进入源码来分析:
private static class IntegerCache {
static final int low = -128;
static final int high;
static final Integer cache[];
static {
// high value may be configured by property
int h = 127;
String integerCacheHighPropValue =
sun.misc.VM.getSavedProperty("java.lang.Integer.IntegerCache.high");
if (integerCacheHighPropValue != null) {
try {
int i = parseInt(integerCacheHighPropValue);
i = Math.max(i, 127);
// Maximum array size is Integer.MAX_VALUE
h = Math.min(i, Integer.MAX_VALUE - (-low) -1);
} catch( NumberFormatException nfe) {
// If the property cannot be parsed into an int, ignore it.
}
}
high = h;
cache = new Integer[(high - low) + 1];
int j = low;
for(int k = 0; k < cache.length; k++)
cache[k] = new Integer(j++);
// range [-128, 127] must be interned (JLS7 5.1.7)
assert IntegerCache.high >= 127;
}
private IntegerCache() {}
}
Integer对于-128到127之间的数值进行了缓存,装箱时如果在缓存区间里直接取缓存,如果不在区间才会new Integer(i)。知道这一点有助于使用时避坑。
看源码可知,-128到127的区间,下限已写死,但上限可是可以修改的,通过运行时参数“-XX:AutoBoxCacheMax=256”,就可以修改上限为-128到256。
什么坑呢?
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 127;
Integer b = 127;
System.out.println(a == b); // true
Integer c = 128;
Integer d = 128;
System.out.println(c == d); // false
}
比较的值是127时还可以使用==比较,128时就不行了。
来看看Integer的缓存列表:
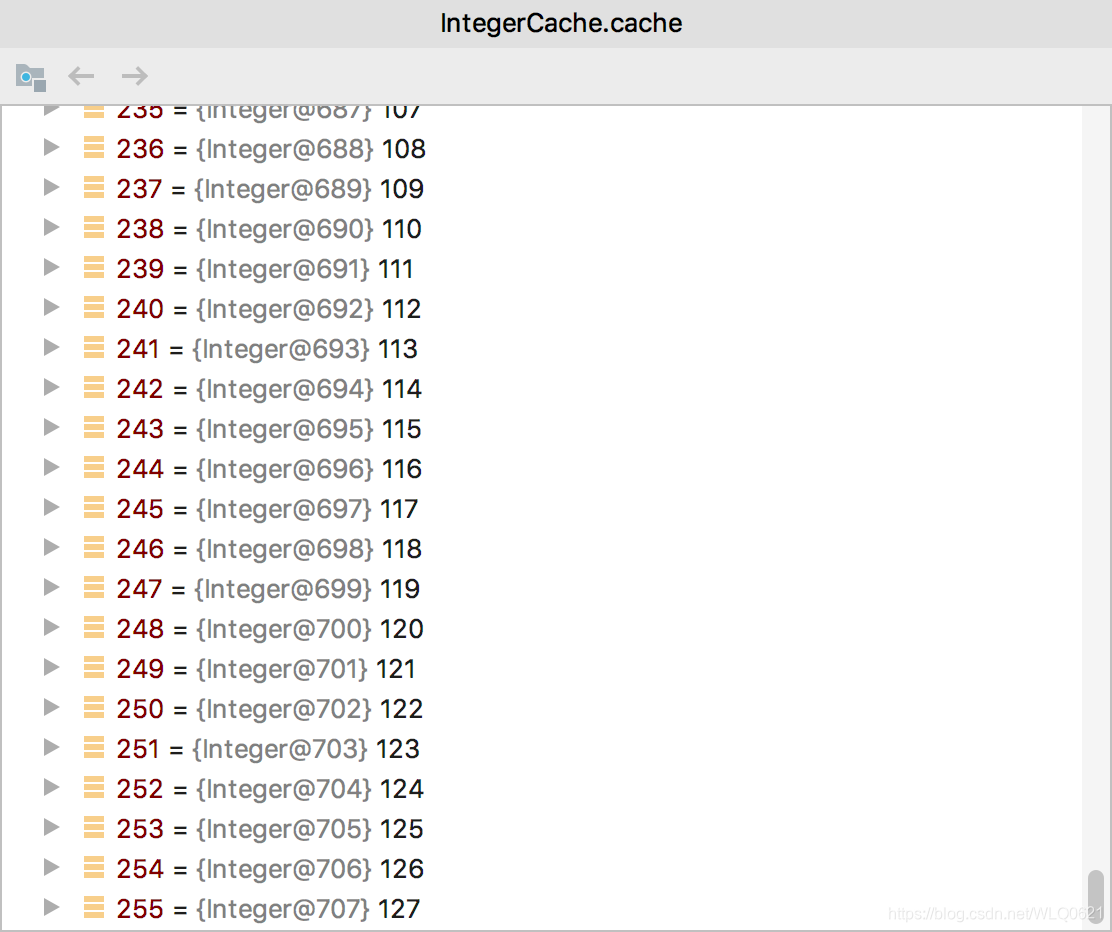
255是缓存下标的索引,等于127+128,当值是128时就只能new Integer(128)了。这个时候两个不同的对象,当然不能==比较啦,或者说比价当然是false啦。
public static Integer valueOf(int i) {
if (i >= IntegerCache.low && i <= IntegerCache.high)
return IntegerCache.cache[i + (-IntegerCache.low)];
return new Integer(i);
}
如果就是要比较c、d,有没有办法呢?
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 127;
Integer b = 127;
System.out.println(a == b); // true
Integer c = 128;
Integer d = 128;
System.out.println(c == d); // false
System.out.println(c.intValue() == d.intValue()); // true
System.out.println(c.equals(d)); // true
System.out.println(Objects.equals(c, d)); // true
}
可以比较它的值,也可以用equals(),因为Integer重写了此方法。
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj instanceof Integer) {
return value == ((Integer)obj).intValue();
}
return false;
}







 本文详细解析Java中的基本数据类型与引用数据类型,重点介绍Integer与int的区别,探讨自动装箱、拆箱过程及源码分析,揭示-128至127区间Integer缓存机制,避免潜在的比较陷阱。
本文详细解析Java中的基本数据类型与引用数据类型,重点介绍Integer与int的区别,探讨自动装箱、拆箱过程及源码分析,揭示-128至127区间Integer缓存机制,避免潜在的比较陷阱。
















 962
962

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








