1.算法课设题目
LOL 峡谷地图最优路径规划

以下问题的计算,按照该地图的基本规则来进行在该地图中分布着各种形状不规则的障碍区域环境。整个地图模型,可以根据需求进行自行简化。
问题一:在任意起点与终点之间,规划一条最短路径。
问题二:当你拥有一个闪现的情况下(只能用一次),规划出从起点到终点的一条最短 路径。
题目要求: 1. 生成障碍环境数据,提取障碍物区域。 2. 实现上述情况下,指定任意起始点到目标点下的最优路径规划算法。 3. 实现结果的可视化展示。
2.解决问题思路
2.1地图的简化和数据导入
此题的要求区分障碍物和非障碍物部分,可以将地图转化为由0和1(1表示障碍物部分)组成的像素图,精度要求因人而异,我这里是在piskel在线网站上创建了100×100的像素图(太大精度的绘图容易丢失文件,建议下载该应用离线使用),并用黑色像素格绘画障碍物部分,最后导出为png文件,如下图:

那么如何将此图转化成由0和1组成的二值图呢,我这里使用的是c++中stb_image.h头文件中的函数处理,代码如下
int width, height, channels;
unsigned char* image = stbi_load("C:\\Users\\M\\Downloads\\New Piskel2.png", &width, &height, &channels, STBI_grey);
vector<vector<char>> map(height,vector<char>(width));
int threshold = 128;//阈值
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
map[y][x] = (image[y * width + x] < threshold) ? 1 : 0;//黑色的像素点用数字1表示,白色的像素点用数字0表示
}
}2.2核心算法
A*算法解决最短路径问题步骤:
定义节点距离:为了使用 A* 算法找到最短路径,我们首先需要定义节点距离。节点距离是指从起点到节点的实际距离加上从节点到终点的估计距离。估计距离可以使用启发式函数来计算。
创建初始节点:从起点开始创建一个初始节点,并将其加入Open列表(待探索列表)中。同时将所有其他节点标记为未探索。
选择下一个节点:从Open列表中选择具有最小节点距离的节点作为下一个要探索的节点。将该节点从Open列表中移除,并标记为已探索。
更新相邻节点:对于所选节点的每个相邻节点,检查是否已经在Open或Close列表中。如果未被探索,则将其添加到Open列表中,同时计算节点距离和启发式函数的值。如果已经在Open或Close列表中,则更新该节点的距离值(如果经过当前节点到达它的路径更短)。
重复步骤3和4,直到找到终点或者Open列表为空。如果找到终点,输出最短路径;否则,无可行解决方案。
首先构建两个类,用于表示点的信息和调用A*算法处理函数,如下代码所示:
class point
{
public:
int x, y;//地图坐标
int f, g, h;//f=g+h
point* parent;
point(int _x, int _y) :x(_x), y(_y), f(0), g(0), h(0), parent(NULL) {}
};
class Astar
{
public:
void InitAstar(vector<vector<char>>& _map);//导入地图
list<point*>getpath(point& startpoint, point& endpoint);
private:
vector<vector<char>> map;//地图二维数组
int calf(point* p);//计算f值
int calg(point* startp, point* np);//计算g值
int calh(point* endp, point* np);//计算h值
list<point*> openList; //开启列表
list<point*> closeList; //关闭列表
point* getpoint();//得到开启列表中f值最小的点
point* isInList(list<point*>& l, point* p);//判断点是否在表中
bool isCanReach(point* p, point *target);//判断点能否到达
vector<point*>getSurroundPoints(point* p);//得到周围可到达的点
};关于解决问题二的一些设计:
//全局变量定义
bool onechance ;//是否可以闪现
int judge ;//判断数
//初始化
onechance = false;//是否可以闪现
judge = 0;//判断数
//进行一次闪现后禁掉之后闪现的可能
if (judge == 0 && map[Point->x][Point->y] == 1)
{
judge = 1;
}
if(judge==1&& map[Point->x][Point->y] == 0)
onechance = false;
以下是具体的函数功能的实现:
访问私有类型将地图数据导入
void Astar::InitAstar(vector<vector<char>>& _map)
{
map = _map;
}计算f
int Astar::calf(point* p)
{
return p->g + p->h;
}计算g
int Astar::calg(point* startp, point* np)
{
int parentg = np->parent == NULL ? 0 : np->parent->g;
int ng = (startp->x - np->x)* (startp->x - np->x) + (startp->y - np->y)* (startp->y - np->y);
return parentg + ng;
}计算h
int Astar::calh(point* endp, point* np)
{
return (endp->x - np->x) * (endp->x - np->x) + (endp->y - np->y) * (endp->y - np->y);
}得到open列表中f值最小的点
point* Astar::getpoint()
{
if (!openList.empty()) {
auto Point = openList.front();
for (auto& p : openList)//遍历open表
if (p->f < Point->f)
Point = p;
return Point;
}
return NULL;
}通过坐标点判断点是否在表中
point* Astar::isInList(list<point*>& l, point* P)
{
for (auto p : l)
if (p->x == P->x && p->y == P->y)//通过坐标点判断点是否在表中
return p;
return NULL;
}判断点是否可到达
bool Astar::isCanReach(point* p, point* target)
{
if (target->x<0 || target->x>map.size() - 1
|| target->y<0 || target->y>map[0].size() - 1
|| (map[target->x][target->y] == 1&& onechance == false)
|| target->x == p->x && target->y == p->y
|| isInList(closeList, target))//如果点与当前节点重合、超出地图、是障碍物、或者在关闭列表中,返回false
return false;
else if (map[target->x][target->y] == 1 &&onechance==true)//为障碍物但是有闪现的条件下可到达
{
return true;
}
else {
if (abs(p->x - target->x) + abs(p->y - target->y) == 1)//非斜角可以到达
return true;
else {
//斜对角要判断是否绊住
if (map[p->x][target->y] == 0 && map[target->x][p->y] == 0)
return true;
else
return false;
}
}
}
访问周围可到达的点
vector<point*> Astar::getSurroundPoints(point* p)
{
vector<point*> surroundpoints;
for (int x = p->x - 1; x <= p->x + 1; x++)
for (int y = p->y - 1; y <= p->y + 1; y++)
if (isCanReach(p, new point(x, y)))
surroundpoints.push_back(new point(x, y));
return surroundpoints;
}求最短路径
list<point*> Astar::getpath(point& startpoint, point& endpoint)
{
list<point*>path;
if (map[startpoint.x][startpoint.y] == 1|| map[endpoint.x][endpoint.y] == 1)//防止起点终点设置到障碍物中
return path;
openList.push_back(new point(startpoint.x, startpoint.y)); //置入起点
onechance = false;//是否可以闪现
judge = 0;//判断数
while (!openList.empty()) {
auto Point = getpoint(); //找到F值最小的点
openList.remove(Point);
closeList.push_back(Point);
//判断闪现有无结束
if (judge == 0 && map[Point->x][Point->y] == 1)
{
judge = 1;
}
if(judge==1&& map[Point->x][Point->y] == 0)
onechance = false;
// 1. 找到当前周围8个格中可以通过的格子
auto surroundPoints = getSurroundPoints(Point);
for (auto& target : surroundPoints) {
// 2. 对某一个格子,如果它不在开启列表中,加入到开启列表,设置当前格为其父节点,计算F G H
if (!isInList(openList, target)) {
target->parent = Point;
target->g = calg(Point, target);
target->h = calh( &endpoint, target);
target->f = calf(target);
openList.push_back(target);
}
// 3. 对某一格子,它在开启列表中,计算G值,如果比原来的大,就什么都不做,否则设置它的父节点为当前点,并更新G和F
else {
int tempg = calg(Point, target);
if (tempg < target->g) {
target->parent = Point;
target->g = tempg;
target->f = calf(target);
}
}
point* lastPoint = isInList(openList, &endpoint);
//终点在open表就将该路径存到一个列中
if (lastPoint)
{
point* ep = lastPoint;
while (ep) {
path.push_front(ep);
ep = ep->parent;
}
openList.clear();
closeList.clear();
return path;
}
}
}
return path;
}2.3可视化展示
使用c++语言下的QT项目进行实现
相关代码如下:
鼠标点击事件
void LOLDREWING::mousePressEvent(QMouseEvent* event)
{
// 获取鼠标坐标
QPoint pos = event->pos();
//更新状态
if (!start_pressed_)
{
start = pos;
start_pressed_ = true;
}
else {
end = pos;
update();
start_pressed_ =false;
}
}绘图事件
void LOLDREWING::paintEvent(QPaintEvent*event)
{
QWidget::paintEvent(event);
int width, height, channels;
unsigned char* image = stbi_load("C:\\Users\\M\\Downloads\\New Piskel2.png", &width, &height, &channels, STBI_grey);
// 转化为二维数组
vector<vector<char>> map(height, vector<char>(width));
int threshold = 128;//阈值
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
map[y][x] = (image[y * width + x] < threshold) ? 1 : 0; //黑色的像素点用数字1表示,白色的像素点用数字0表示
}
}
//地图可视化
QPainter painter(this);
painter.setPen(Qt::NoPen);
painter.setBrush(QBrush(Qt::black));
for (int i = 0; i < map.size(); ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < map[0].size(); ++j) {
if (map[i][j] == 1) {
painter.drawRect(j * 10, i * 10, 10, 10);//扩大十倍
}
}
}
Astar astar;
astar.InitAstar(map);
//设置起点和结束点
point O( start.y() / 10, start.x() / 10);
point P(end.y() / 10, end.x() / 10);
//A*算法找寻路径
list<point*> path = astar.getpath(O, P);
if (path.size())
for (const auto i : path)
{
painter.setBrush(QColor(255,0,0));
painter.drawRect(10 * i->y, 10 * i->x,10,10);
}
if (!start_pressed_)
{
painter.setPen(QColor(0, 255, 0));
painter.drawLine(start, end);
}
// 释放资源
stbi_image_free(image);
}3.代码实现展示
问题一:
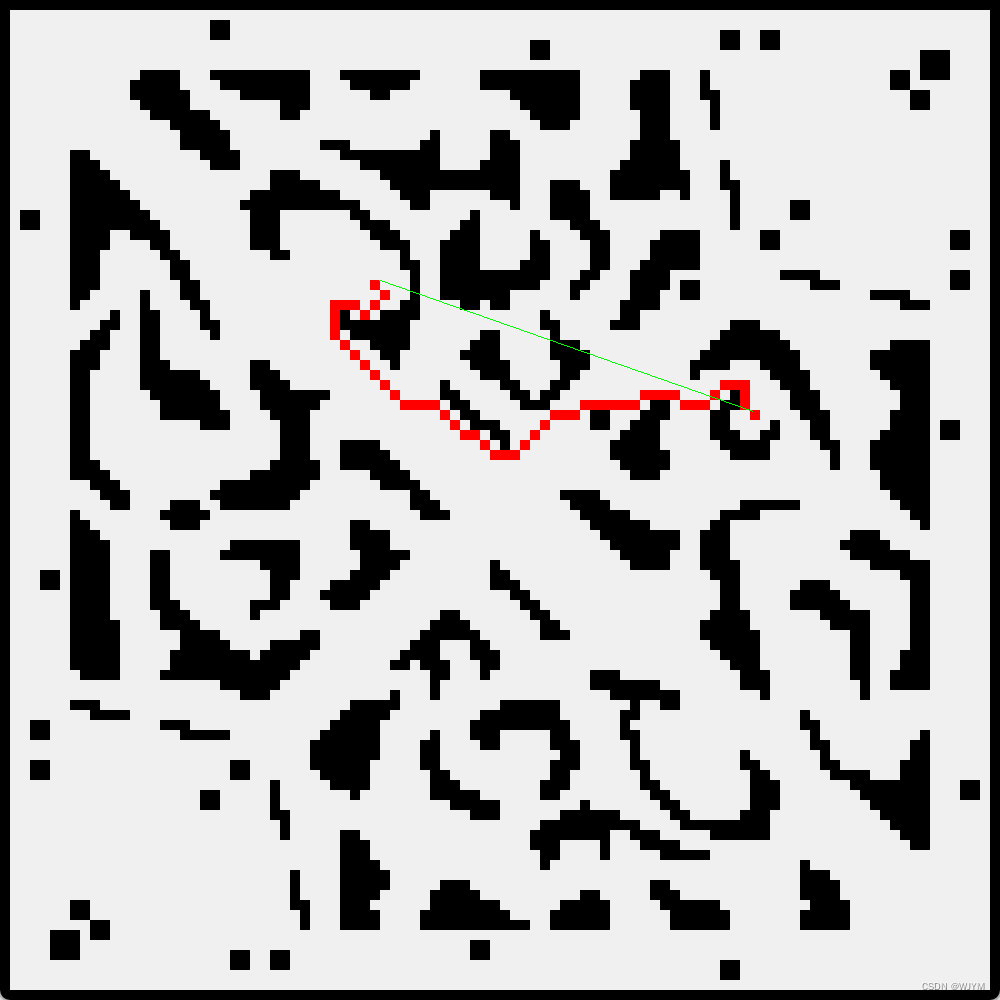
问题二:
只需将是否可以闪现的bool类型的值改为true即可
onechance = true;//是否可以闪现 闪现的使用节省了很多路程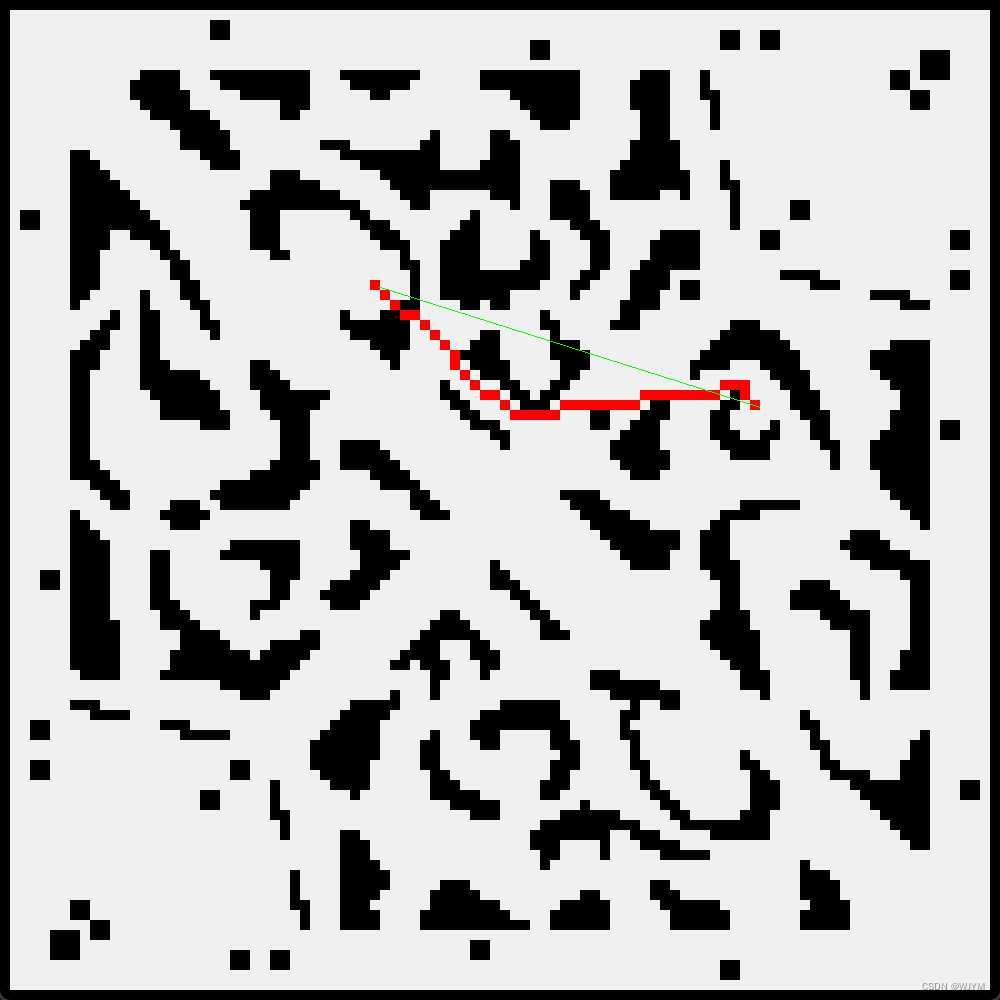
4.课设完成遇到的问题和心得体验
4.1课设解决途中遇到的问题
图像文件和QT绘图的x-y坐标系和二维数组的表示是相反的,硬是因为这个给我拖了一天进度,我就说怎么好多路径肆无忌惮地穿墙呢
4.2课设完成心得
对我来说使用c++解决具体问题还是第一次(本人也是c++语言初学者),从代码中可见我仅仅用到了c++和QT中一些最基础的用法,同时解决这个问题并没有花费我太多时间(大概五六天),一是由于上学期的人工智能课程已经介绍了A*算法的用途和具体原理,导致我能很快地上手解决,其次该问题已经很成熟,网上由许多的大佬讲解并进行借鉴
最后提供完全代码文件以供实验:阿里云盘分享




 文章描述了一个使用A*算法解决LOL峡谷地图中,考虑闪现情况下的最短路径规划问题。作者通过简化地图为二值图,利用C++的stb_image.h处理图像数据,并实现了地图的可视化展示。在A*算法的基础上,增加了闪现机制,当有一次闪现机会时,能规划出更短的路径。
文章描述了一个使用A*算法解决LOL峡谷地图中,考虑闪现情况下的最短路径规划问题。作者通过简化地图为二值图,利用C++的stb_image.h处理图像数据,并实现了地图的可视化展示。在A*算法的基础上,增加了闪现机制,当有一次闪现机会时,能规划出更短的路径。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








