const成员函数
const int a=10;
int b=a;
我知道const修饰的变量具有只读属性,a具有只读属性,不能修改直接通过a修改a,而b则可读可写。
int a=30;
const int*p=&a;
这里的const修饰的是指针变量*p,限定定义指针所指向位置的内容*p,不允许*p=50,可以改变的是指针所指向的位置p。允许p=&b
int a=30;
int*const p=&a;
此时,const修饰p,即就是指针变量p只读,指针指向位置被限定不允许p=&b,指针所指向的位置的内容可以改变允许*p=50
也就是p对比你会发现,仅仅是const和*的前后位置不同了而已。
上述复习了const修饰变量的用法,接下来我们看一下这段代码:
Time operator+(const Time &t) const
{
Time t1 = (*this);
Time t2 = t;
t1._minute += t2._minute;
t1._minute += t2._minute;
t1._second += t2._second;
while (!(t1._second < 60))
{
t1._second -= 60;
t1._minute += 1;
}
while (!(t1._minute < 60))
{
t1._minute -= 60;
t1._hour += 1;
}
while (!(t1._hour < 24))
t1._hour -= 24;
return t1;
}
void Show()const
{
cout << _hour << ':' << \
_minute << ':' << _second << ':' << endl;
}
在成员函数后面加const,const修饰this指针所修饰的对象,也就是保证这个const成员函数的对象在函数体内不会被改变。
重点思考:
const对象不可以调用非const成员函数,非const对象可以调用const成员函数。
const成员函数不可以调用其它非const成员函数,非const成员函数可以调用其它的const成员函数。
内联函数
以inline修饰的函数叫做内联函数,编译时C++编译器会在调用内联函数的地方展开内联函数。省去函数压栈的开销,以空间换时间的做法。
1、inline必须和函数定义放在一起才能成为内联函数, 仅将inline放在声明前不起作用。
2、inline对编译器来说只是建议,并非指令,编译器会自行优化。
3、定义在类内的成员函数,默认为内联函数。
4、代码很长或者有循环或者递归不适宜使用内联函数。
inline void Show()
{
cout << _hour << ':' << \
_minute << ':' << _second << ':' << endl;
}
友元
友元类
整个类是另一个类的友元。友元类的每一个成员函数都是另一个类的友元函数,都可以访问另一个类的保护或者私有数据成员。
class Time{
friend class Date;
private:
int _hour;
int _minute;
int _second;
};
class Date{
public:
void Display()
{
cout << _year << ":" <<\
_month << ":"\
<< _day << ":" \
<< _t._hour << ":" \
<< _t._minute << ":" \
<< _t._second << endl;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
Time _t;
};
友元类在一定程度上破坏了C++的封装性,应该尽量少用。
友元函数
友元函数允许类外访问该类的任何成员,就像成员函数一样,友元函数用关键字friend说明。
1、友元函数不是类的成员函数。
2、友元函数可以通过访问所有成员,私有和保护也一样。
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
class Time{
public:
friend void Show(const Time&d);
Time(const int hour = 23, const int minute = 59, const int second = 59)
:_hour(hour)
, _minute(minute)
, _second(second)
{
if (!Islegal(_hour, _minute, _second))
assert(0);
}
Time(const Time&t)
:_hour(t._hour)
, _minute(t._minute)
, _second(t._second)
{
}
~Time()
{}
private:
bool Islegal(int&hour, int&minute, int&second)
{
if (hour >= 0 && hour < 24 && minute >= 0 && minute < 60 && second >= 0 && second < 60)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int _hour;
int _minute;
int _second;
};
void Show(const Time&d)
{
cout << d._hour << ':' <<
d._minute << ':' <<
d._second << ':' << endl;
}
int main()
{
Time t1;
Show(t1);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
这里我们试着重载一下Time类的cin、cout
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Time{
int _hour;
int _minute;
int _second;
public:
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream&out, const Time&t)
{
out << t._hour<<":" << t._minute <<":"<< t._second << endl;
return out;
}
friend istream& operator>>(istream&in, Time&t)
{
cout << "请输入年月日:" << endl;
in >> t._hour;
in >> t._minute;
in >> t._second;
return in;
}
};
int main()
{
Time t1;
cin >> t1;
cout << t1;
system("pause");
return 0;
}

static成员
静态成员变量
1、类里边static修饰的成员,称为静态成员。
2、类的静态成员是该类的所有对象所共享。类内声明,类外定义。
静态成员函数
静态成员函数与普通成员函数的区别:
1、静态成员函数没有 this 指针,只能访问静态成员(包括静态成员变量和静态成员函数)。
2、普通成员函数有 this 指针,可以访问类中的任意成员。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Cpoint{
public:
static int value;
static int num;
Cpoint(int x,int y){
xp=x;yp=y;
value++;
cout << "调用构造:" << value << endl;
}
~Cpoint(){num++; cout << "调用析构:" << num << endl;}
private:
int xp,yp;
};
int Cpoint::value=0;
int Cpoint::num=0;
class CRect{
public:
CRect(int x1,int x2):mpt1(x1,x2),mpt2(x1,x2) {cout << "调用构造\n";}
~CRect(){cout << "调用析构\n";}
private:
Cpoint mpt1,mpt2;
};
int main()
{
CRect p(10,20);
cout << "Hello, world!" << endl;
return 0;
}
太聪明的编译器
案例一
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public :
Date()
{
cout<<"Date()" <<endl;
}
Date(const Date& d)
{
cout<<"Date(const Date& d)" <<endl;
}
Date& operator =(const Date& d )
{
cout<<"Date& operator=(const Date& d)"<< endl;
return *this ;
}
~Date()
{
cout<<"~Date()" <<endl;
}
};
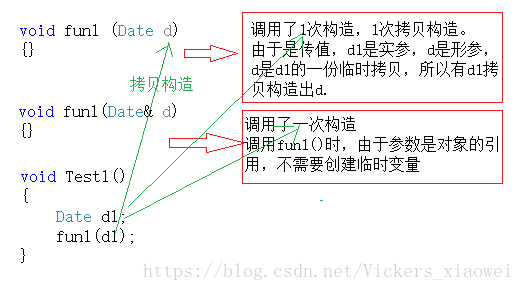
// 1.Date 对象做参数传值 & 传引用
void fun1 (Date d)
{}
//void fun1(Date& d)
//{}
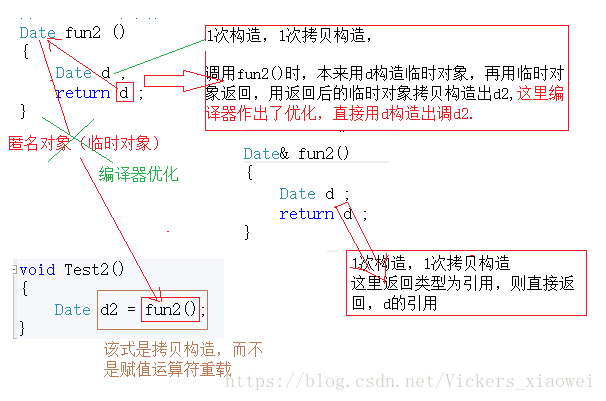
// 2.Date 对象做返回值传值 & 传引用
Date fun2 ()
{
Date d ;
return d ;
}
//Date& fun2()
//{
// Date d ;
// return d ;
//}
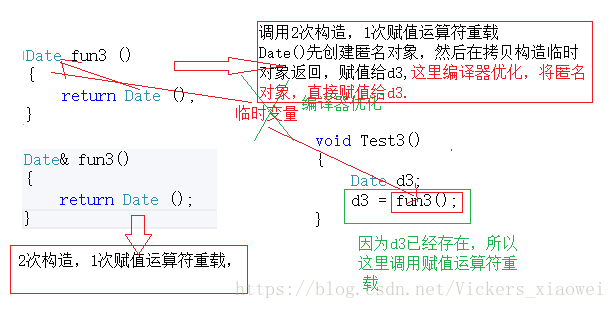
// 3.Date 对象做临时返回值传值 &传引用(编译器优化问题)
Date fun3 ()
{
return Date ();
}
//Date& fun3()
//{
// return Date ();
//}
void Test1()
{
Date d1;
fun1(d1);
}
void Test2()
{
Date d2 = fun2();
}
void Test3()
{
Date d3;
d3 = fun3();
}
Test1
Test2
Test3
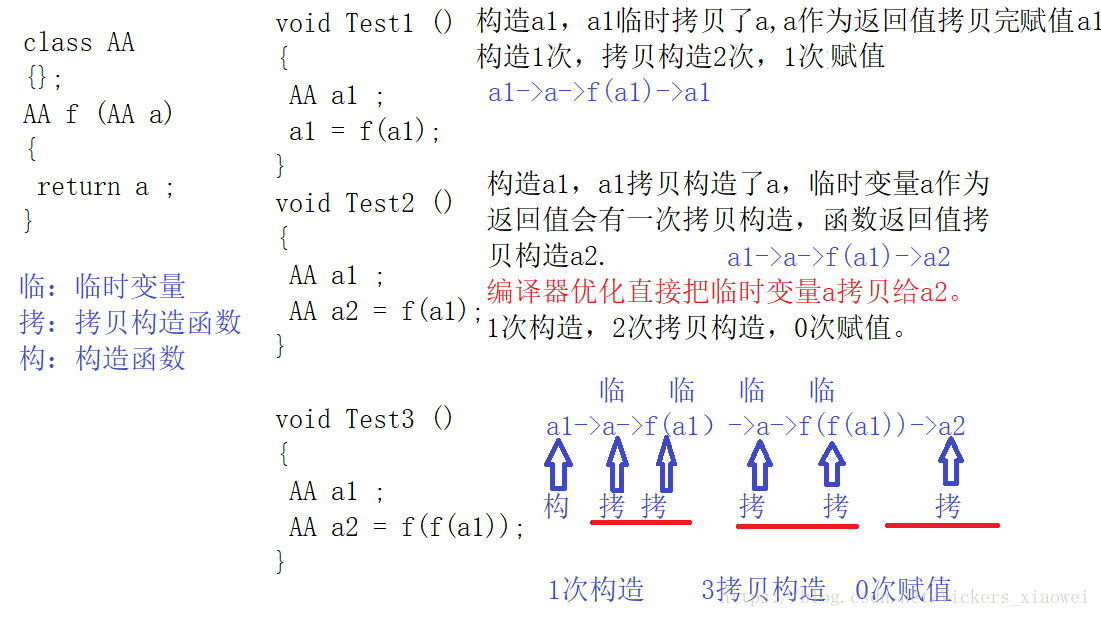
案例二
Test1中调用了___次AA的拷贝构造函数,___次AA的赋值运算符函数的重载。
Test2中调用了___次AA的拷贝构造函数,___次AA的赋值运算符函数的重载。
Test3中调用了___次AA的拷贝构造函数,___次AA的赋值运算符函数的重载。
class AA
{};
AA f (AA a)
{
return a ;
}
void Test1 ()
{
AA a1 ;
a1 = f(a1);
}
void Test2 ()
{
AA a1 ;
AA a2 = f(a1);
}
void Test3 ()
{
AA a1 ;
AA a2 = f(f(a1));
}




 本文深入探讨C++中的const成员函数、内联函数、友元、静态成员等特性,并通过实例解释这些特性的使用方法及注意事项。
本文深入探讨C++中的const成员函数、内联函数、友元、静态成员等特性,并通过实例解释这些特性的使用方法及注意事项。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








