BP-反向传播
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as sio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy.optimize import minimize
data = sio.loadmat('ex4data1.mat')
raw_X = data['X']
raw_y = data['y']
X = np.insert(raw_X,0,values=1,axis=1) #输入层加偏值
1.对y进行独热编码处理:one-hot编码
def one_hot_encoder(raw_y):
result = []
for i in raw_y:
y_temp = np.zeros(10)
y_temp[i-1] = 1
result.append(y_temp)
return np.array(result)
theta = sio.loadmat('ex4weights.mat')
theta1,theta2 = theta['Theta1'],theta['Theta2']
theta1.shape,theta2.shape
2. 序列化权重参数
def serialize(a,b):
return np.append(a.flatten(),b.flatten())
theta_serialize = serialize(theta1,theta2)
theta_serialize.shape
#(10285,)
3.解序列化权重参数
def deserialize(theta_serialize):
theta1 = theta_serialize[:25*401].reshape(25,401)
theta2 = theta_serialize[25*401:].reshape(10,26)
return theta1,theta2
theta1,theta2 = deserialize(theta_serialize)
theta1.shape,theta2.shape
#((25, 401), (10, 26))
4.前向传播
def sigmoid(z):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
def feed_forward(theta_serialize,X):
theta1,theta2 = deserialize(theta_serialize)
a1 = X
z2 = a1 @ theta1.T
a2 = sigmoid(z2)
a2 = np.insert(a2,0,values=1,axis=1)
z3 = a2 @ theta2.T
h = sigmoid(z3)
return a1,z2,a2,z3,h
5.损失函数
5-1 不带正则化的损失函数
def cost(theta_serialize,X,y):
a1,z2,a2,z3,h = feed_forward(theta_serialize,X)
J = -np.sum(y * np.log(h)+(1-y) * np.log(1-h))/len(X)
return J
cost(theta_serialize,X,y)
# 0.2876291651613189
5-2带正则化的损失函数
def reg_cost(theta_serialize,X,y,lamda):
sum1 = np.sum(np.power(theta1[:,1:],2))
sum2 = np.sum(np.power(theta2[:,1:],2))
reg = (sum1+sum2)*lamda/(2 * len(X))
return reg + cost(theta_serialize,X,y)
lamda = 1
reg_cost(theta_serialize,X,y,lamda)
# 0.38376985909092365
6.反向传播
6-1 无正则化的梯度
# g(z)求导
def sigmoid_gradient(z):
return sigmoid(z)*(1-sigmoid(z))
def gradient(theta_serialize,X,y):
theta1,theta2 = deserialize(theta_serialize)
a1,z2,a2,z3,h = feed_forward(theta_serialize,X)
d3 = h-y
d2 = d3 @ theta2[:,1:] * sigmoid_gradient(z2)
D2 = (d3.T @ a2)/len(X)
D1 = (d2.T @ a1)/len(X)
return serialize(D1,D2)
6-2 带正则化的梯度
def reg_gradient(theta_serialize,X,y):
D = gradient(theta_serialize,X,y)
D1,D2 = deserialize(D)
theta1,theta2 = deserialize(theta_serialize)
D1[:,1:]=D1[:,1:]+theta1[:,1:]*lamda/len(X)
D2[:,1:]=D2[:,1:]+theta2[:,1:]*lamda/len(X)
return serialize(D1,D2)
7.神经网络优化
def nn_training(X,y):
init_theta = np.random.uniform(-0.5,0.5,10285)
res = minimize(fun=cost,
x0=init_theta,
args=(X,y),
method='TNC',
jac=gradient
#options={'maxiter':300}
)
return res
res = nn_training(X,y)
raw_y = data['y'].reshape(5000,)
_,_,_,_,h = feed_forward(res.x,X)
y_pred = np.argmax(h,axis=1)+1
acc = np.mean(y_pred == raw_y)
acc
#0.9994
8.可视化隐藏层
def plot_hidden_layer(theta):
theta1,_=deserialize(theta)
hidden_layer = theta1[:,1:]
fig,ax = plt.subplots(ncols=5,nrows=5,figsize=(8,8),sharex=True,sharey=True)
for r in range(5):
for c in range(5):
ax[r,c].imshow(hidden_layer[5*r+c].reshape(20,20),cmap='gray_r')
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.show
plot_hidden_layer(res.x)
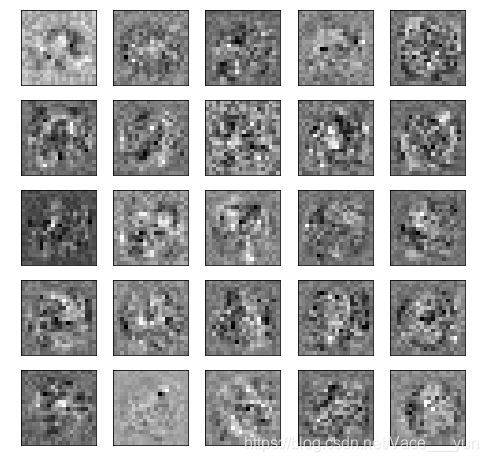





 本文介绍了使用Python实现的BP(反向传播)算法,包括前向传播、成本函数(带/不带正则化)、梯度计算、神经网络训练过程,并展示了如何对权重参数进行序列化和解序列化。关键步骤包括独热编码、激活函数sigmoid、损失函数计算及可视化隐藏层。
本文介绍了使用Python实现的BP(反向传播)算法,包括前向传播、成本函数(带/不带正则化)、梯度计算、神经网络训练过程,并展示了如何对权重参数进行序列化和解序列化。关键步骤包括独热编码、激活函数sigmoid、损失函数计算及可视化隐藏层。
















 284
284

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








