106. 岛屿的周长
陷阱:虽然是岛屿问题,但是不需要用到任何 dfs 或 bfs
思路:遍历图,如果是陆地,看它上下左右格子是否越界或者为海洋。如果是,周长加 1。
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int[][] dir = {{1, 0}, {0, 1}, {-1, 0}, {0, -1}};
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] grid = new int[n][m];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
grid[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
int result = 0; // 周长
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; k++) {
int nextX = dir[k][0] + i;
int nextY = dir[k][1] + j;
// 如果越界或者为海洋,周长就加 1
if (nextX < 0 || nextX >= n || nextY < 0 || nextY >= m || grid[nextX][nextY] == 0) {
result++;
}
}
}
}
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
110. 字符串接龙
- 只由小写字母组成
- 不存在路径则输出 0
用 dfs 或 bfs 皆可。但适合用 bfs。因为 bfs 是一圈一圈的,当找到目标字符串时一定是最短路径长度。而 dfs 还要额外保存路径长度去求个最小。
思路:对字符串的每个字符,把它修改为 26 个字母中的每一个字符。判断修改后的字符串在不在字典中。中间一旦变成最终字符串,就返回长度。
需要一个 set 保存字典。
一个 map 保存已经遍历过的字符串。
易错点:
终点字符串不要求在字典中,所以求出 newStr 后要立马判断是不是等于终点字符串
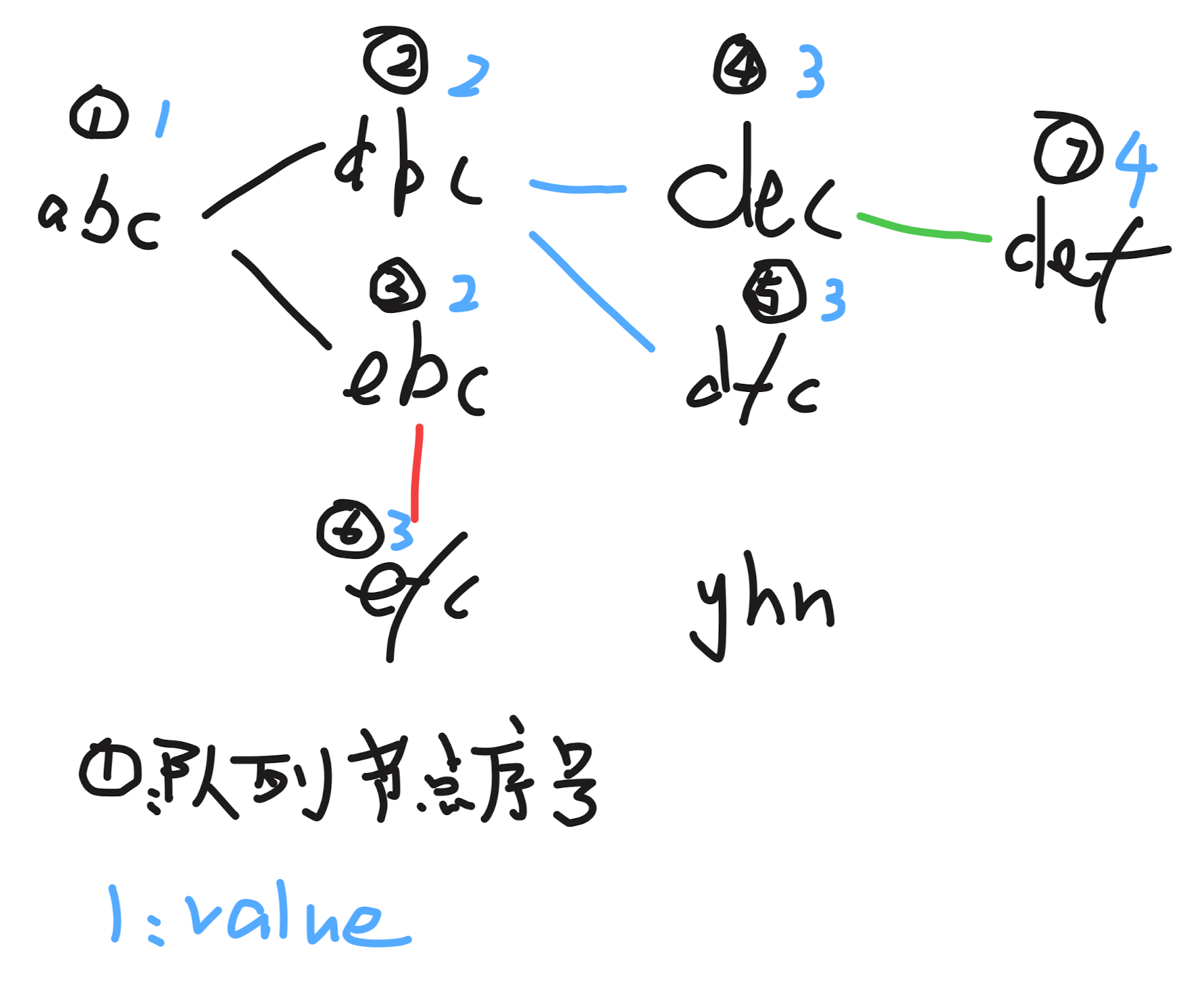
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
String beginStr = sc.next();
String endStr = sc.next();
HashSet<String> set = new HashSet<>(); // 保存字典
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
set.add(sc.next());
}
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // 保存已经遍历过的字符串,value 为当前的路径长度
Queue<String> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(beginStr); // 添加起点字符串
map.put(beginStr, 1); // 起点字符串路径长度为 1
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
String str = queue.poll();
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++) {
char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
chars[i] = (char) ('a' + j);
String newStr = new String(chars);
// 因为重点字符串不要求出现在字典中,所以需要立即判断是否等于终点字符串,如果是直接输出结果并返回
if (newStr.equals(endStr)) {
System.out.println(map.get(str) + 1);
return;
}
// 必须字典中包含新字符串,且没有遍历过该新字符串
if (!set.contains(newStr) || map.containsKey(newStr)) {
continue;
}
queue.offer(newStr); // 把新字符串添加到队列中
map.put(newStr, map.get(str) + 1); // 新字符串路径长度为旧字符串路径长度 + 1
}
}
}
System.out.println(0); // 遍历完都没找到,输出 0
}
}
105. 有向图的完全联通
读题:共 n 个节点。从节点 1 出发,要能到达每个节点。即判断是不是完全联通图。
dfs 或 bfs 皆可。
思路:
设置一个 visited[] 数组。从节点 1 出发,把它能直接到达的节点都标记为 true。再遍历这些能直接到达的节点。
最后看 visited[] 数组如果有 false,则不是完全联通。
方法一:dfs
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 节点数量
int k = sc.nextInt(); // 边数量
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { // i 必须从 0 开始,创建 n + 1 个空列表
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
while (k-- > 0) {
int s = sc.nextInt();
int t = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(s).add(t);
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n + 1];
dfs(graph, 1, visited);
// 判断 visited[] 中有没有 false
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) { // i 从 1 开始
if (!visited[i]) {
System.out.println(-1);
return;
}
}
System.out.println(1);
}
public static void dfs (List<List<Integer>> graph, int node, boolean[] visited) {
if (visited[node]) {
return;
}
visited[node] = true;
for (int nextNode : graph.get(node)) {
dfs(graph, nextNode, visited);
}
}
}
方法二:bfs
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 节点数量
int k = sc.nextInt(); // 边数量
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { // i 必须从 0 开始,创建 n + 1 个空列表
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
while (k-- > 0) {
int s = sc.nextInt();
int t = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(s).add(t);
}
boolean[] visited = new boolean[n + 1];
bfs(graph, visited);
// 判断 visited[] 中有没有 false
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) { // i 从 1 开始
if (!visited[i]) {
System.out.println(-1);
return;
}
}
System.out.println(1);
}
public static void bfs (List<List<Integer>> graph, boolean[] visited) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
queue.offer(1);
visited[1] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int node = queue.poll();
for (int nextNode : graph.get(node)) {
if (!visited[nextNode]) {
queue.offer(nextNode);
visited[nextNode] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
图总结
- 无权图求最短路径,不需要迪杰特斯拉算法,只需要 dfs 或 bfs 即可。
- 抽象图用 graph,二维图用 grid。
- 邻接矩阵用
graph[][],邻接表用List<List<Integer>> graph。
- 邻接矩阵用
邻接矩阵初始化(有向图,节点从 1 到 n):
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 节点数量
int k = sc.nextInt(); // 边数量
int[][] graph = new int[n + 1][n + 1];
while (k-- > 0) {
int s = sc.nextInt();
int t = sc.nextInt();
graph[s][t] = 1;
}
}
}
邻接表初始化(有向图,节点从 1 到 n):
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt(); // 节点数量
int k = sc.nextInt(); // 边数量
List<List<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++) { // i 必须从 0 开始,创建 n + 1 个空列表
graph.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
while (k-- > 0) {
int s = sc.nextInt();
int t = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(s).add(t);
}
}
}





















 1174
1174

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








